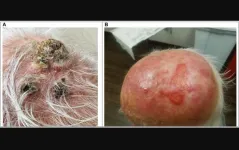
Cetuximab's effectiveness and toxicity in advanced cutaneous squamous cell skin cancer
2023-07-12
(Press-News.org)
“Our data demonstrate that cetuximab plus radiotherapy represents an active treatment option for laCSCC, with manageable toxicity.”
BUFFALO, NY- July 12, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on July 7, 2023, entitled, “Effectiveness and toxicity of cetuximab with concurrent RT in locally advanced cutaneous squamous cell skin cancer: a case series.”
Treatment for locally advanced cutaneous squamous cell cancers (laCSCC) remains poorly defined. Most laCSCC tumors express high levels of epidermal growth factor receptors (EGFR). Cetuximab has activity in other EGFR expressing cancers and enhances the effectiveness of radiotherapy.
In this new study, researchers Mark Chang, Wolfram Samlowski and Raul Meoz from University Medical Center of Southern Nevada, Comprehensive Cancer Centers of Nevada, University of Nevada Las Vegas, and University of Nevada Reno conducted a retrospective review of institutional data and identified 18 patients with laCSCC treated with cetuximab induction and concurrent radiotherapy.
“We performed a retrospectively review of treatment outcome and toxicity in our patients who received concurrent cetuximab and radiotherapy to show an additional potentially effective treatment option for patients with laCSCC. The goal is also to provide data to inform the design of potential prospective clinical trials.”
The loading dose of cetuximab was 400 mg/m² IV. Subsequent weekly doses of 250 mg/m² IV were infused throughout the period of radiation. The treatment doses ranged from 4500–7000 cGy, with a dose fraction of 200-250 cGy. The objective response rate was 83.2% with 55.5% complete responses and 27.7% partial responses.
Median progression-free survival was 21.6 months. Progression-free survival was 61% at 1 year and 40% at 2 years. With longer follow-up, some patients developed a local recurrence (16.7%), distant metastases (11.1%) or a second primary cancer (16.3%). Cetuximab was well tolerated, with 68.4% patients experienced only mild acneiform skin rash or fatigue (Grade 1 or 2). Radiotherapy produced expected side effects (skin erythema, moist desquamation, mucositis).
“Cetuximab plus radiotherapy represents an active and tolerable treatment option for laCSCC, including patients with contraindications for checkpoint inhibitor therapy.”
Read the full paper: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.28470
Correspondence to: Wolfram Samlowski
Email: wsamlowski1@gmail.com
Keywords: keratinocyte carcinoma, squamous cell skin cancer, cetuximab, epidermal growth factor receptor, radiation therapy
About Oncotarget: Oncotarget (a primarily oncology-focused, peer-reviewed, open access journal) aims to maximize research impact through insightful peer-review; eliminate borders between specialties by linking different fields of oncology, cancer research and biomedical sciences; and foster application of basic and clinical science.
To learn more about Oncotarget, visit Oncotarget.com and connect with us on social media:
Twitter
Facebook
YouTube
Instagram
LinkedIn
Pinterest
LabTube
Soundcloud
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article: https://oncotarget.altmetric.com/details/email_updates?id=10.18632%2Foncotarget.28470
Click here to subscribe to Oncotarget publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact: media@impactjournals.com.
Oncotarget Journal Office
6666 East Quaker Str., Suite 1A
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957 (option 2)
###
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-07-12
The University of Texas at Arlington received an Award of Excellence for Innovation from the International Parking & Mobility Institute (IPMI).
The award was for the RAPID (Rideshare, Automation and Payment Integration Demonstration) program, a self-driving shuttle system for students and the general public that started in 2021. It was originally funded through the city of Arlington and a Federal Transit Administration grant, with additional support from the North Central Texas Council of Governments. Via Transportation Inc. and May Mobility also are partners in the program.
RAPID, the first program in the United States to integrate on-demand, ...
2023-07-12
The incidence of primary involuntary childlessness, the rate of women seeking treatment for infertility, as well as the success rate of assisted reproductive technology all increased in birth cohorts studied from 1916 to 1975, according to a new study published this week in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Finn Egil Skjeldestad of the Arctic University of Norway.
There have been tremendous advances in assisted reproductive technologies (ARTs) over the past 50 years. In the new study, Dr. Skjeldestad analyzed data on 11,064 women born between 1916 and 1975 ...
2023-07-12
Ice Age saber-tooth cats and dire wolves experienced a high incidence of bone disease in their joints, according to a study published July 12, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Hugo Schmökel of Evidensia Academy, Sweden and colleagues.
Osteochondrosis is a developmental bone disease known to affect the joints of vertebrates, including humans and various domesticated species. However, the disease is not documented thoroughly in wild species, and published cases are quite rare. In this study, Schmökel and colleagues identify signs of this disease in fossil limb bones of Ice Age saber-tooth cats (Smilodon fatalis) ...
2023-07-12
A new mathematical model of UK cat populations suggests that neutering of cats that belong to people not only affects the population dynamics of owned cats, but also affects feral, stray, and shelter subpopulations. Jenni McDonald of Cats Protection and co-authors present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on July 12.
More than ten million cats live as owned pets in UK homes, and hundreds of thousands of additional cats live in shelters or as free-roaming feral or stray cats. Cats may transition from any of these subpopulations to another. However, while many prior studies have investigated cat population ...
2023-07-12
Slow population declines might be going undetected, while later rates of extinction could increase exponentially
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0285945
Article Title: The rate of species extinction in declining or fragmented ecological communities
Author Countries: Greece, USA
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
2023-07-12
Simulation study of how body shapes and sizes affected energetic efficiency helps explain relative success of early Polynesian voyaging
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0287290
Article Title: Estimated energetic demands of thermoregulation during ancient canoe passages from Tahiti to Hawaii and New Zealand, a simulation analysis
Author Countries: USA, Australia, New Zealand
Funding: AM received financial support from the Maritime Encounters (M21-0018) project funded by Sweden's Riksbankens Jubileumsfond. ...
2023-07-12
Prosthetic limbs are the most common solution to replace a lost extremity. However, they are hard to control and often unreliable with only a couple of movements available. Remnant muscles in the residual limb are the preferred source of control for bionic hands. This is because patients can contract muscles at will, and the electrical activity generated by the contractions can be used to tell the prosthetic hand what to do, for instance, open or close. A major problem at higher amputation levels, such as above the elbow, is that not many muscles remain to command the many robotic joints needed to truly restore the function of an arm and hand.
A multidisciplinary team of surgeons and engineers ...
2023-07-12
On the Moon, there are raw materials that humanity could one day mine and use. Various space agencies, such as the European Space Agency (ESA), are already planning missions to better explore Earth’s satellite and find minerals. This calls for appropriate exploration vehicles. Swiss researchers led by ETH Zurich are now pursuing the idea of sending not just one solitary rover on an exploration tour, but rather an entire team of vehicles and flying devices that complement each other.
The researchers equipped three ANYmal – a type of legged robot developed ...
2023-07-12
COLUMBUS, Ohio – For the first time, researchers have developed a model to estimate how much energy the original colonizers of New Zealand expended to maintain their body temperatures on the cold, harrowing ocean journey from Southeast Asia.
Results showed that people making the first voyages from Tahiti to New Zealand in sailing canoes would expend 3.3 to 4.8 times more energy on thermoregulation – the technical term for maintaining body temperature - than those making a trip of similar length to Hawaii.
The ocean route to New Zealand required much more energy for thermoregulation ...
2023-07-12
AUKLAND, NZ and DURHAM, N.C. – Companion robots enhanced with artificial intelligence may one day help alleviate the loneliness epidemic, suggests a new report from researchers at Auckland, Duke, and Cornell Universities.
Their report, appearing in the July 12 issue of Science Robotics, maps some of the ethical considerations for governments, policy makers, technologists, and clinicians, and urges stakeholders to come together to rapidly develop guidelines for trust, agency, engagement, and real-world efficacy.
It also proposes a new way to measure whether a companion robot is helping someone.
“Right now, all the evidence ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Cetuximab's effectiveness and toxicity in advanced cutaneous squamous cell skin cancer