(Press-News.org)
Food insecurity rate hits 17% for the second time in 18 months
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. – Reported food insecurity has reached 17%, matching the rate last reached in March 2022, according to the June Consumer Food Insights Report. The new report also includes consumer changes in food spending as a result of a hypothetical recession and sentiments on artificial intelligence.
The survey-based report out of Purdue University’s Center for Food Demand Analysis and Sustainabilityassesses food spending, consumer satisfaction and values, support of agricultural and food policies, and trust in information sources. Purdue experts conduct and evaluate the survey, which includes 1,200 consumers across the U.S.
“Overall, there continues to be a similar narrative of extended upward pressure on food prices as we try to discern whether this stress has led to a tipping point where consumers are struggling to buy the foods that they want,” said Jayson Lusk, the head and Distinguished Professor of Agricultural Economics at Purdue, who leads the center.
“The 17% food insecurity rate is up from 14% just two months ago, which is not necessarily far outside of the normal variation we have measured. However, this increase could be concerning given the sum of external pressures being exerted on more vulnerable consumers,” Lusk said.
He noted that pandemic-related boosts to the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) ended in March. The insecurity rise could be a lag from households adjusting to this policy change.
In the event of a recession, consumers report that they would cut back most on steak, pork and dining out. These results align with what Lusk would expect to occur if incomes fell.
“Discretionary spending on eating out will go first if consumers have to face a recession. Then people will cut back on more expensive items that they can easily substitute in their diets. Steak and bacon, for example,” Lusk said. “It is interesting to see that the items with a large share of ‘does not apply’ are also largely items that will be cut back the most as many people are already choosing to forgo them.”
Additional key results include:
Reported food spending has risen by 2.1% from last June, which is much less than the 6.7% government estimate of food inflation.
Households making less than $50,000 annually are buying groceries online at a higher rate than other households.
The report noted that the pandemic opened the online option to SNAP recipients, which evidently remains a key tool for a range of shoppers.
Households making more than $100,000 annually are slightly greater risk-takers, which is reflected by a higher willingness to eat unwashed fruits and undercooked meat.
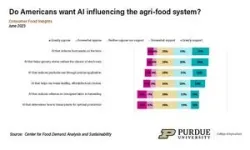
Consumers largely have positive or neutral feelings about applying artificial intelligence (AI) in the food and agriculture sectors.
“The artificial intelligence questions are much more speculative since there are not yet widely known examples of AI being used across the food system,” said Sam Polzin, a food and agriculture survey scientist for the center and co-author of the report. “People really do not have enough information about AI to have thoughtful positions, as seen in the large share of indifference.”
Surprisingly to Polzin, 50% of consumers said they would be OK with AI helping them make food choices, which is generally considered a personal decision. “This proportion might be indicative of how eager people are to make the ‘best’ choices,” Polzin said.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, annual inflation for food-at-home fell below inflation for food-away-from-home (FAFH) this spring, he noted. This poses the question: Will consumers continue to spend at faster rates on dining out?
“The highest earners are driving a larger share of the increase in FAFH spending and have no clear reason to slow down. We will keep track of whether two different patterns emerge in which higher-income households continue to thrive while lower-income households might be forced to pull back,” Polzin said.
The report’s results about food behaviors align with other research showing that high-wage consumers take higher risks than those earning less. “The fact that higher earners report eating unwashed fruits, undercooked meat and raw dough slightly more often could reflect this risk-taking,” Polzin said.
Other reported food behaviors are fairly expected. High-income households, for example, will choose premium local and organic products more often than lower-income households. They also often have more resources to track and understand food labeling or follow recycling and composting practices.
Lusk further discusses the report in his blog.
The Center for Food Demand Analysis and Sustainability is part of Purdue’s Next Moves in agriculture and food systems and uses innovative data analysis shared through user-friendly platforms to improve the food system. In addition to the Consumer Food Insights Report, the center offers a portfolio of online dashboards.
Writer: Steve Koppes
END
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, JULY 12, 2023
MINNEAPOLIS – Older people who have little social contact with others may be more likely to have loss of overall brain volume, and in areas of the brain affected by dementia, than people with more frequent social contact, according to a study published in the July 12, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
The study does not prove that social isolation causes brain shrinkage; it only shows an association.
“Social isolation is a growing problem for older ...
“Our data demonstrate that cetuximab plus radiotherapy represents an active treatment option for laCSCC, with manageable toxicity.”
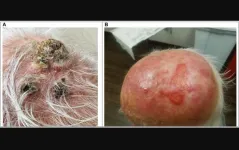
BUFFALO, NY- July 12, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on July 7, 2023, entitled, “Effectiveness and toxicity of cetuximab with concurrent RT in locally advanced cutaneous squamous cell skin cancer: a case series.”
Treatment for locally advanced cutaneous squamous cell cancers (laCSCC) remains poorly defined. Most laCSCC tumors express high levels of epidermal growth factor receptors (EGFR). Cetuximab has activity in other EGFR expressing cancers and enhances the effectiveness ...
The University of Texas at Arlington received an Award of Excellence for Innovation from the International Parking & Mobility Institute (IPMI).
The award was for the RAPID (Rideshare, Automation and Payment Integration Demonstration) program, a self-driving shuttle system for students and the general public that started in 2021. It was originally funded through the city of Arlington and a Federal Transit Administration grant, with additional support from the North Central Texas Council of Governments. Via Transportation Inc. and May Mobility also are partners in the program.
RAPID, the first program in the United States to integrate on-demand, ...
The incidence of primary involuntary childlessness, the rate of women seeking treatment for infertility, as well as the success rate of assisted reproductive technology all increased in birth cohorts studied from 1916 to 1975, according to a new study published this week in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Finn Egil Skjeldestad of the Arctic University of Norway.
There have been tremendous advances in assisted reproductive technologies (ARTs) over the past 50 years. In the new study, Dr. Skjeldestad analyzed data on 11,064 women born between 1916 and 1975 ...
Ice Age saber-tooth cats and dire wolves experienced a high incidence of bone disease in their joints, according to a study published July 12, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Hugo Schmökel of Evidensia Academy, Sweden and colleagues.
Osteochondrosis is a developmental bone disease known to affect the joints of vertebrates, including humans and various domesticated species. However, the disease is not documented thoroughly in wild species, and published cases are quite rare. In this study, Schmökel and colleagues identify signs of this disease in fossil limb bones of Ice Age saber-tooth cats (Smilodon fatalis) ...
A new mathematical model of UK cat populations suggests that neutering of cats that belong to people not only affects the population dynamics of owned cats, but also affects feral, stray, and shelter subpopulations. Jenni McDonald of Cats Protection and co-authors present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on July 12.
More than ten million cats live as owned pets in UK homes, and hundreds of thousands of additional cats live in shelters or as free-roaming feral or stray cats. Cats may transition from any of these subpopulations to another. However, while many prior studies have investigated cat population ...
Slow population declines might be going undetected, while later rates of extinction could increase exponentially
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0285945
Article Title: The rate of species extinction in declining or fragmented ecological communities
Author Countries: Greece, USA
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
Simulation study of how body shapes and sizes affected energetic efficiency helps explain relative success of early Polynesian voyaging
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0287290
Article Title: Estimated energetic demands of thermoregulation during ancient canoe passages from Tahiti to Hawaii and New Zealand, a simulation analysis
Author Countries: USA, Australia, New Zealand
Funding: AM received financial support from the Maritime Encounters (M21-0018) project funded by Sweden's Riksbankens Jubileumsfond. ...
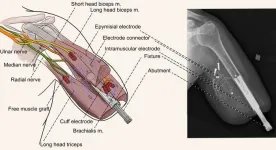
Prosthetic limbs are the most common solution to replace a lost extremity. However, they are hard to control and often unreliable with only a couple of movements available. Remnant muscles in the residual limb are the preferred source of control for bionic hands. This is because patients can contract muscles at will, and the electrical activity generated by the contractions can be used to tell the prosthetic hand what to do, for instance, open or close. A major problem at higher amputation levels, such as above the elbow, is that not many muscles remain to command the many robotic joints needed to truly restore the function of an arm and hand.
A multidisciplinary team of surgeons and engineers ...
On the Moon, there are raw materials that humanity could one day mine and use. Various space agencies, such as the European Space Agency (ESA), are already planning missions to better explore Earth’s satellite and find minerals. This calls for appropriate exploration vehicles. Swiss researchers led by ETH Zurich are now pursuing the idea of sending not just one solitary rover on an exploration tour, but rather an entire team of vehicles and flying devices that complement each other.
The researchers equipped three ANYmal – a type of legged robot developed ...