(Press-News.org) New York, NY—July 13, 2023—New research published in Science Advances, led by Yuan Yang, associate professor of materials science at Columbia Engineering, and collaborators at Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory, demonstrates a novel technique for isolating isotopes.
High Stakes
Oxygen is a critical component in the positron emission tomography (PET) scans oncologists use to search for tumors. But not just any oxygen will work. While most oxygen atoms have eight neutrons, about 1 in 500 atoms has ten. Those extra neutrons are necessary for the PET imaging scans to work.
The Challenge
It’s extremely expensive to isolate the slightly heavier oxygen atoms. A cubic meter of regular water (H2O) costs less than $2 from your tap. When the lighter oxygen atoms (and hydrogen) are removed, the heavier oxygen atoms that remain are worth closer to $30,000.
The Breakthrough
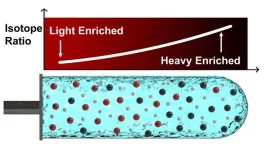
Researchers at Columbia figured out how to isolate heavier or lighter atoms — called isotopes — by dissolving the target element and salts in water before spinning that solution in a centrifuge. It’s more effective, cheaper, and easier to scale than the current state-of-the-art techniques, which also use toxic chemicals that aren’t necessary for the new method.
Broader Applications
Pure isotopes are extremely useful — and extremely valuable. Every year, tens of millions of people across the world receive medical tests that require a hard-to-extract isotope called 100-Molybdenum. Calcium isotope Ca-48 is so rare and sought-after that a single gram currently costs $500,000. And if nuclear fusion becomes a viable source of energy, it will take thousands of tons of a lithium isotope to satisfy the world’s energy demands.
Looking Ahead
Since collaborating with Columbia Technology Ventures to patent the new technology, the researchers have been in touch with several companies about building prototypes and developing a plant to begin isolating isotopes. They’ve used computational modeling to discover several innovative methods that further increase the method’s efficiency.
Dive Deeper
This research is described in a paper published July 12 in Science Advances.
The Yang lab addresses a range of problems in the fields of sustainable technologies and clean materials. While a large emphasis is on developing next-generation lithium-based batteries using modern electrochemical engineering and nanoscience, other recent directions have included developing methods to separate important isotopes which have broad applications in the fields of nuclear fusion and radiomedicine.
###
ABOUT THE STUDY
JOURNAL: Science Advances
TITLE: "Liquid solution centrifugation for safe, scalable, and efficient isotope separation"
AUTHORS: Joseph F. Wild, Heng Chen, Keyue Liang, Jiayu Liu, Stephen E. Cox, Alex N. Halliday, Yuan Yang
FUNDING: This work was supported by the U.S. Department of Energy, grant number DE-SC0022256, and the seed funding support from Columbia University’s Research Initiatives in Science and Engineering (RISE) competition, started in 2004 to trigger high-risk, high-reward, and innovative collaborations in the basic sciences, engineering, and medicine.
A provisional patent (U.S. 63/425,181) has been filed related to this work. The authors declare that they have no other competing interests.
END
A scalable, safer, and potentially cheaper way to isolate valuable isotopes
A team of researchers, led by Yuan Yang, have developed a new method for purifying materials that are crucial for energy, medicine, and scientific research
2023-07-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Alien invasion: Study reveals alarming economic costs of biological invasions to the European Union
2023-07-13
Biological invasions are a major threat to ecosystems, biodiversity, and human well-being, resulting in ecosystem degradation and causing economic costs in the multi-trillions of euros globally. A study led by McGill University sheds light on the stark economic cost resulting from biological invasions in the European Union (EU).
The European Union continues to be exposed to thousands of invasive alien species — harmful species introduced by humans from outside of their natural habitat. The EU is ...
Under representation of women in policing: Study reveals persistent barriers and gender differences in career advancement
2023-07-13
A new study published this week examines the under-representation of women in policing. It reveals that cultural and structural barriers persist and are impacting female career advancement when compared to that of male colleagues.
The research, carried out by the University of Portsmouth as part of Dr Jackie Alexander’s doctoral research, is based on unique survey and interview data with female and male senior police leaders in England and Wales. It highlights the challenges faced by women en route to a senior rank and the impact of gender differences ...
High-quality sleep promotes resilience to depression and anxiety
2023-07-13
Research has shown quality sleep can help bolster resilience to depression and anxiety.
The study, led by researchers at the University of York, highlights that chronic stress is a major risk factor for a number of mental health disorders, including depression and pathological anxiety, but high-quality sleep and coping strategies - such as the ability to reframe a situation to see the positive side - can help to prevent poor mental health when faced with negative or stressful experiences.
The research studied data from over 600 participants during the COVID-19 pandemic ...
Multicultural Psychology Consultation Team promotes culturally responsive care in hospital system
2023-07-13
July 13, 2023 — The synergistic epidemics of COVID-19, racial injustice, and health inequities have prompted patients and communities to press harder for culturally responsive health care. In Harvard Review of Psychiatry (HRP), published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer, members of the originating Multicultural Psychology Consultation Team (MPCT) describe how they're delivering culturally responsive mental health treatment while promoting inclusive health care workplace environments.
The ...
The MemTrax Continuous Recognition Test for advanced cognitive impairment screening
2023-07-13
“[...] MemTrax quickly demonstrates and quantifies the pertinent memory dysfunction of Alzheimer’s disease.”
BUFFALO, NY- July 13, 2023 – A new editorial paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 12, entitled, “Advancing screening for cognitive impairment: the memtrax continuous recognition test.”
Extensive efforts to find a treatment for Alzheimer’s disease (AD) span over 40 years, with the often-repeated request ...
People with more empathy more likely to support international sharing of coronavirus vaccines, study shows
2023-07-13
People with more empathy and cosmopolitan beliefs are more likely to support the international sharing of coronavirus vaccines, a new study shows.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, many residents of high-income countries were eligible for COVID-19 vaccine boosters, while many residents of lower-income countries had not yet received a first dose.
Researchers analysed the levels and predictors of international vaccine solidarity through a survey of around 2,000 German adults in the autumn of 2021. They measured their ...
Central component of infection revealed in people living with HIV
2023-07-13
Québec, July 13, 2023 – Professor Simona Stäger’s team has made a breakthrough in the study of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). The researchers have identified the mechanism by which memory CD4+ T lymphocytes—cells that play a major role in our immune response—are predisposed to cell death in people living with HIV. The team’s findings have just been published in JCI Insight.
In this new study, Professor Stäger and her research team built on work done on mice infected with the Leishmania donovani parasite (published in Cell Reports in 2018), which described how a chronic inflammatory environment predisposes ...
Controlled cruelty: New study from VCU finds aggression can arise from successful self-control
2023-07-13
RICHMOND, Va. (July 13, 2023) — A new study by a Virginia Commonwealth University researcher has found that aggression is not always the product of poor self-control but, instead, often can be the product of successful self-control in order to inflict greater retribution.
The new paper, “Aggression As Successful Self-Control,” by corresponding author David Chester, Ph.D., an associate professor of social psychology in the Department of Psychology at VCU’s College of Humanities and Sciences, was published by the journal Social and Personality Psychology Compass and uses meta-analysis to summarize evidence from dozens of existing ...
Successful cooperation depends on good mindreading abilities - study
2023-07-13
A person’s ‘mindreading ability’ can predict how well they are able to cooperate, even with people they have never met before.
Researchers at the University of Birmingham found that people with strong mind reading abilities – the ability to understand and take the perspective of another person’s feelings and intentions– are more successful in cooperating to complete tasks than people with weaker mind reading abilities.
These qualities, also called ‘theory of mind’, are not necessarily related to intelligence and could be improved through training programmes to foster improved cooperation, for example in ...
Low-dose atropine eyedrops no better than placebo for slowing myopia progression
2023-07-13
Use of low-dose atropine eyedrops (concentration 0.01%) was no better than placebo at slowing myopia (nearsightedness) progression and elongation of the eye among children treated for two years, according to a randomized controlled trial conducted by the Pediatric Eye Disease Investigator Group (PEDIG) and funded by the National Eye Institute (NEI). The trial aimed to identify an effective way to manage this leading and increasingly common cause of refractive error, which can cause serious uncorrectable vision loss later in life. Results from the trial were published in JAMA Ophthalmology.
Importantly, the findings contradict results from recent trials, primarily in East Asia, which ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Scientists sharpen genetic maps to help pinpoint DNA changes that influence human health traits and disease risk
AI, monkey brains, and the virtue of small thinking
Firearm mortality and equitable access to trauma care in Chicago
Worldwide radiation dose in coronary artery disease diagnostic imaging
Heat and pregnancy
Superagers’ brains have a ‘resilience signature,’ and it’s all about neuron growth
New research sheds light on why eczema so often begins in childhood
Small models, big insights into vision
Finding new ways to kill bacteria
An endangered natural pharmacy hidden in coral reefs
The Frontiers of Knowledge Award goes to Charles Manski for incorporating uncertainty into economic research and its application to public policy analysis
Walter Koroshetz joins Dana Foundation as senior advisor
Next-generation CAR-T designs that could transform cancer treatment
As health care goes digital, patients are being left behind
A clinicopathologic analysis of 740 endometrial polyps: risk of premalignant changes and malignancy
Gibson Oncology, NIH to begin Phase 2 trials of LMP744 for treatment of first-time recurrent glioblastoma
Researchers develop a high-efficiency photocatalyst using iron instead of rare metals
Study finds no evidence of persistent tick-borne infection in people who link chronic illness to ticks
New system tracks blockchain money laundering faster and more accurately
In vitro antibacterial activity of crude extracts from Tithonia diversifolia (asteraceae) and Solanum torvum (solanaceae) against selected shigella species
Qiliang (Andy) Ding, PhD, named recipient of the 2026 ACMG Foundation Rising Scholar Trainee Award
Heat-free gas sensing: LED-driven electronic nose technology enhances multi-gas detection
Women more likely to choose wine from female winemakers
E-waste chemicals are appearing in dolphins and porpoises
Researchers warn: opioids aren’t effective for many acute pain conditions
Largest image of its kind shows hidden chemistry at the heart of the Milky Way
JBNU researchers review advances in pyrochlore oxide-based dielectric energy storage technology
Novel cellular phenomenon reveals how immune cells extract nuclear DNA from dying cells
Printable enzyme ink powers next-generation wearable biosensors
6 in 10 US women projected to have at least one type of cardiovascular disease by 2050
[Press-News.org] A scalable, safer, and potentially cheaper way to isolate valuable isotopesA team of researchers, led by Yuan Yang, have developed a new method for purifying materials that are crucial for energy, medicine, and scientific research