Single-end hybrid Rayleigh Brillouin and Raman distributed fibre-optic sensing system
2023-07-14
(Press-News.org)
The real-time monitoring of facilities, particularly large facilities (such as rail transit systems, large bridges, and buildings), can provide information regarding their surrounding environment and allow their health conditions to be assessed, which is essential for establishing the current concept of smart cities based on the Internet of Things. As a precise real-time monitoring technique, distributed fiber-optic sensing (DFOS) systems, which require long-distance simultaneous measurements along a sensing fiber, are in high demand for various industrial applications. However, most DFOS systems can only measure a single kind of parameter, which limits the use in applications. Additionally, a simple combining of different DFOS systems is complex and costly.
In a new paper published in Light: Advanced Manufacturing, a team of scientists, led by Professor Xinyu Fan from Shanghai Jiao Tong University, China, proposed a simplified hybrid DFOS system for simultaneously measuring multi-parameters along the sensing fiber. They used a normal single-mode fiber as a sensor to obtain the temperature, strain and vibration information of the optical fiber with the length of several kilometers. They integrated three schemes using different backscattered lightwave and simplified the hybrid systems. The proposed hybrid system requires only one light source, two receiving ends and a single access of the fiber for launching lightwave, which highly reduces the complexity of application. As such, the simplified hybrid system can be used in real-time monitoring of large structure, automated control and perimeter security. The technique can be a powerful tool promoting the construction of smart cities.
Among different DFOS systems, a technique using Rayleigh backscattering known as phase-sensitive optical time-domain reflectometry (φ-OTDR), which is used to measure dynamic parameters such as vibration. Brillouin optical time domain analysis (BOTDA) based on stimulated Brillouin scattering is used to measure temperature and static strains with high signal-to-noise ratio. Raman scattering can be used in Raman optical time-domain reflectometry (ROTDR) to measure the distributed temperature without being disturbed by strain as it is only temperature sensitive.
The hybrid DFOS system integrates the three different scattering schemes. Rayleigh scattering is used for vibration sensing and also acts as the probe of Brillouin scattering process to realize temperature and strain measurement. Raman scattering is used to overcome the temperature-strain cross sensitivity. Pulse code modulation is employed to separate Raman scattering of two pulses with very close optical frequencies. In this way, a single-end simplified hybrid DFOS system works successfully for simultaneous multi-parameters measurement.
The hybrid system shows its ability of measuring temperature, strain and vibration along a 9-kilometer long single mode fiber, with a favorable measurement accuracy.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-07-14
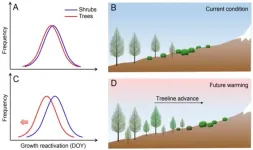
The findings from this study, led by Professor Eryuan Liang (Institute of Tibetan Plateau Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences), were published as a research article in the journal National Science Review. The study also involved researchers from, CREAF, CSIC, Global Ecology Unit CREAF-CSIC-UAB, Instituto Pirenaico de Ecología (IPE-CSIC), Spain and Université du Québec à Chicoutimi, Canada.
Climatic warming is altering the structure and function of alpine ecosystems, including shifts of vegetation boundaries. The upward shift of alpine treelines, the uppermost limit of tree growth forming the boundary between montane forest and alpine communities, ...
2023-07-14
A new 145-million-year-old pterosaur (extinct flying reptiles that lived alongside the dinosaurs) was named today by a team of British, American and German researchers. The animal was nicknamed ‘Elvis’ when the fossil was first unearthed in Bavaria, Germany because of the giant pompadour-like bony crest on its skull.
Now the animal has been given a formal scientific name of Petrodactyle wellnhoferi. The name translates as ‘Wellnhofer’s stone-finger’ honouring legendary German palaeontologist ...
2023-07-14
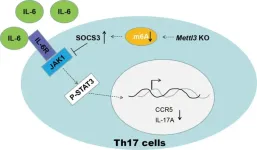
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is the most extensive studied RNA modification across various species, and the important effect of m6A modification in immune system has been revealed in distinct contexts, including mRNA metabolism, cell differentiation, proliferation and response to stimulation. Previous studies from Hua-Bing Li group demonstrated that m6A methyltransferase METTL3 control T cells homeostasis and sustain the suppressive function of regulatory T cells (Tregs). However, the role of m6A methyltransferase in other subtype of T cells remains unknown.
T helper cells 17 ...
2023-07-14
Patients who engage in light exercise while undergoing dialysis are physically fitter and are admitted to hospital less frequently than those who do not. These are the findings of a large-scale study conducted by a consortium led by the Technical University of Munich (TUM). The researchers believe that exercise programs should be offered to dialysis patients as standard.
Around 558,000 people in the United States have such severely impaired kidney function that they require dialysis several times per week. In Germany, about 80,000 people regularly undergo ...
2023-07-14
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a ubiquitous virus, and most people are infected at some point in their lives. HPV can infect epithelial cells of the skin and mucosa at various sites. There are more than 100 known HPV subtypes, most of which cause only benign lesions such as warts and condyloma. Thanks to a well-functioning immune response, most people who are infected don’t develop serious symptoms. However, some HPV subtypes are not so harmless. These subtypes, and especially subtype HPV16, can transform infected cells to become neoplastic, and these malignant transformed cells then develop into precancerous ...
2023-07-14
A team led by researchers at the Mechanisms of Inherited Kidney Disorders (MIKADO) group at the University of Zurich (Zurich, Switzerland) has used Insilico Medicine’s generative artificial intelligence (AI) target discovery engine, PandaOmics, to identify actionable drug targets for the lysosomal storage disease cystinosis and to validate them in preclinical models of the disease. These results, which open new therapeutic possibilities for this devastating disease, were published June 14 in the journal Nature Communications. Collaborators include scientists from Microsoft Research-University of Trento Centre for Computational ...
2023-07-14
University of Virginia School of Medicine researchers have discovered a way to identify pregnant women at risk of preeclampsia, a serious disorder characterized by high blood pressure and kidney dysfunction which can result in premature delivery, seizures and even death. Complications from the condition are the second-leading cause of maternal death around the world.
The UVA scientists, led by Charles E. Chalfant, PhD, found that they could predict the risk of preeclampsia by examining lipids (fats) ...
2023-07-14
New observations using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) have distinguished the sites of star formation and a possible site of star death from the surrounding nebula in a galaxy 13.2 billion light-years away. This is the farthest that such structures have been observed.
A team led by Yoichi Tamura, an astronomer at Nagoya University, attempted high-resolution observations of MACS0416_Y1, located 13.2 billion light-years away in the constellation Eridanus. Previous observations of this galaxy by the same team had detected radio waves emitted by both oxygen and dust, two components of interstellar nebulae. Detailed observations of the ...
2023-07-14
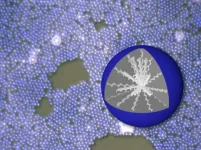
A research group led by Dr. Jialei He of Nagoya University's Graduate School of Engineering has developed a method for processing cholesteric liquid crystals (CLCs) into micrometer-sized spherical particles. CLCs are a type of liquid crystal that possess a helical structure, giving them unique optical properties and the ability to selectively reflect light. By combining spherical CLC particles with commercially available pigments, the researchers developed a unique anti-counterfeiting QR code that can only be displayed under a specific circular polarizer. The results were published in the journal Advanced Optical Materials.
CLCs are an example of how nature can be ...
2023-07-14
Ishikawa, Japan -- Although grasping objects is a relatively straightforward task for us humans, there is a lot of mechanics involved in this simple task. Picking up an object requires fine control of the fingers, of their positioning, and of the pressure each finger applies, which in turn necessitates intricate sensing capabilities. It’s no wonder that robotic grasping and manipulation is a very active research area within the field of robotics.
Today, industrial robotic hands have replaced humans in various complex and hazardous ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Single-end hybrid Rayleigh Brillouin and Raman distributed fibre-optic sensing system