(Press-News.org) About The Study: This nationwide cross-sectional study demonstrated that residing in a highly segregated neighborhood was associated with a statistically significantly lower life expectancy by four years, which was partially mediated by neighborhood-level socioeconomic factors. These findings help to quantify the contribution of residential segregation as a key structural driver of racial inequities.
Authors: Sadiya S. Khan, M.D., M.Sc., of the Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine in Chicago, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2023.1805)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama-health-forum/fullarticle/10.1001/jamahealthforum.2023.1805?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=071423
About JAMA Health Forum: JAMA Health Forum is an international, peer-reviewed, online, open access journal that addresses health policy and strategies affecting medicine, health and health care. The journal publishes original research, evidence-based reports and opinion about national and global health policy; innovative approaches to health care delivery; and health care economics, access, quality, safety, equity and reform. Its distribution will be solely digital and all content will be freely available for anyone to read.
END
Associations between neighborhood-level racial residential segregation, socioeconomic factors, and life expectancy
JAMA Health Forum
2023-07-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Lifestyle enrichment in later life and its association with dementia risk
2023-07-14
About The Study: In this study of 10,000 older individuals in Australia, more frequent participation in adult literacy activities (taking education classes, using a computer, and writing letters or journals) and in active mental activities (playing games, cards, or chess and doing crosswords or puzzles) was associated with reduced dementia risk over 10 years. However, social outings and interactions were not associated with dementia risk.
Authors: Joanne Ryan, Ph.D., of Monash University in Melbourne, Australia, is ...
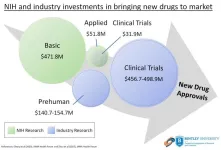
NIH spent $8.1B for phased clinical trials of drugs approved 2010-19, ~10% of reported industry spending
2023-07-14
BENTLEY UNIVERSITY
The U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH) contributed $8.1 billion in project funding for phased clinical trials involving drugs approved by the FDA from 2010-2019, according to a new study from Bentley University’s Center for Integration of Science and Industry. The study, published in JAMA Health Forum, shows that NIH funding for clinical trials represents <3.5% of total NIH spending for basic or applied research related to these products and was significantly less than reported industry spending on clinical development. ...
Coordination could spare billions in grid upgrade costs and accelerate electrification
2023-07-14
The electric grids of the future will need to handle much bigger loads due to electrification of transportation and other sectors. This could mean expensive infrastructure upgrades to ensure their reliable operation, but a new study from Stanford University says most of those upgrades may be unnecessary.
Better grid reliability could be achieved instead by installing software in homes and businesses that coordinates various consumer demands and resources. Such coordination not only improves reliability of the electric grid, but also ...
Conditional cash transfer programs have prevented 739,919 child deaths in Latin America
2023-07-14
Over the past two decades, conditional cash transfer programmes have led to a 24% reduction in child mortality in Brazil, Mexico and Ecuador, equivalent to more than 700,000 child deaths averted, according to an impact evaluation study led by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), an institution supported by “la Caixa” Foundation. The results, published in JAMA Network Open, also show that expanding these programmes could save more than 150,ooo lives by mitigating the effects of the ...
Neighborhood racial segregation linked to shorter life spans by four years
2023-07-14
New nationwide study is first to examine implications of racial segregation on life expectancy by neighborhood
Findings quantify how neighborhood segregation contributes to racial inequities in life expectancy
Black residents living in heavily segregated areas experienced higher rates of poverty and unemployment and less education
CHICAGO --- Black residents living in highly segregated neighborhoods have significantly shortened life expectancies, reports a new Northwestern Medicine study.
Compared to residents living in less segregated predominantly ...
Fintetuning for antibodies
2023-07-14
Antibodies are crucial, not only for treating tumors and infections. Sometimes, however, the immune reaction they trigger can be too strong and end up causing more damage, for example in the case of people infected with Covid-19. Problems such as these can often be avoided by finetuning antibodies, as Prof. Dr. Falk Nimmerjahn from Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg (FAU) and two of his colleagues in the Netherlands and in the UK have now reported in the journal Nature Immunology.
In his laboratories, the FAU researcher is carrying out research into immunoglobulin ...
Single-end hybrid Rayleigh Brillouin and Raman distributed fibre-optic sensing system
2023-07-14
The real-time monitoring of facilities, particularly large facilities (such as rail transit systems, large bridges, and buildings), can provide information regarding their surrounding environment and allow their health conditions to be assessed, which is essential for establishing the current concept of smart cities based on the Internet of Things. As a precise real-time monitoring technique, distributed fiber-optic sensing (DFOS) systems, which require long-distance simultaneous measurements along a sensing fiber, are in high demand for various industrial applications. However, ...
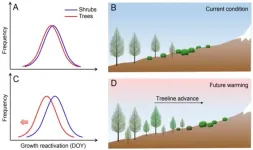
Why trees outcompete shrubs to shift upward?
2023-07-14
The findings from this study, led by Professor Eryuan Liang (Institute of Tibetan Plateau Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences), were published as a research article in the journal National Science Review. The study also involved researchers from, CREAF, CSIC, Global Ecology Unit CREAF-CSIC-UAB, Instituto Pirenaico de Ecología (IPE-CSIC), Spain and Université du Québec à Chicoutimi, Canada.
Climatic warming is altering the structure and function of alpine ecosystems, including shifts of vegetation boundaries. The upward shift of alpine treelines, the uppermost limit of tree growth forming the boundary between montane forest and alpine communities, ...
New fossil flying reptile ‘Elvis’ takes flight
2023-07-14
A new 145-million-year-old pterosaur (extinct flying reptiles that lived alongside the dinosaurs) was named today by a team of British, American and German researchers. The animal was nicknamed ‘Elvis’ when the fossil was first unearthed in Bavaria, Germany because of the giant pompadour-like bony crest on its skull.
Now the animal has been given a formal scientific name of Petrodactyle wellnhoferi. The name translates as ‘Wellnhofer’s stone-finger’ honouring legendary German palaeontologist ...
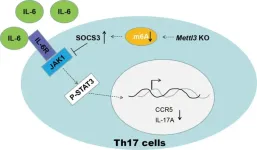
m6A mRNA modification potentiates Th17 functions to inflame autoimmunity
2023-07-14
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is the most extensive studied RNA modification across various species, and the important effect of m6A modification in immune system has been revealed in distinct contexts, including mRNA metabolism, cell differentiation, proliferation and response to stimulation. Previous studies from Hua-Bing Li group demonstrated that m6A methyltransferase METTL3 control T cells homeostasis and sustain the suppressive function of regulatory T cells (Tregs). However, the role of m6A methyltransferase in other subtype of T cells remains unknown.
T helper cells 17 ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
6 in 10 US women projected to have at least one type of cardiovascular disease by 2050
People’s gut bacteria worse in areas with higher social deprivation
Unique analysis shows air-con heat relief significantly worsens climate change
Keto diet may restore exercise benefits in people with high blood sugar
Manchester researchers challenge misleading language around plastic waste solutions
Vessel traffic alters behavior, stress and population trends of marine megafauna
Your car’s tire sensors could be used to track you
Research confirms that ocean warming causes an annual decline in fish biomass of up to 19.8%
Local water supply crucial to success of hydrogen initiative in Europe
New blood test score detects hidden alcohol-related liver disease
High risk of readmission and death among heart failure patients
Code for Earth launches 2026 climate and weather data challenges
Three women named Britain’s Brightest Young Scientists, each winning ‘unrestricted’ £100,000 Blavatnik Awards prize
Have abortion-related laws affected broader access to maternal health care?
Do muscles remember being weak?
Do certain circulating small non-coding RNAs affect longevity?
How well are international guidelines followed for certain medications for high-risk pregnancies?
New blood test signals who is most likely to live longer, study finds
Global gaps in use of two life-saving antenatal treatments for premature babies, reveals worldwide analysis
Bug beats: caterpillars use complex rhythms to communicate with ants
High-risk patients account for 80% of post-surgery deaths
Celebrity dolphin of Venice doesn’t need special protection – except from humans
Tulane study reveals key differences in long-term brain effects of COVID-19 and flu
The long standing commercialization challenge of lithium batteries, often called the dream battery, has been solved.
New method to remove toxic PFAS chemicals from water
The nanozymes hypothesis of the origin of life (on Earth) proposed
Microalgae-derived biochar enables fast, low-cost detection of hydrogen peroxide
Researchers highlight promise of biochar composites for sustainable 3D printing
Machine learning helps design low-cost biochar to fight phosphorus pollution in lakes
Urine tests confirm alcohol consumption in wild African chimpanzees
[Press-News.org] Associations between neighborhood-level racial residential segregation, socioeconomic factors, and life expectancyJAMA Health Forum