(Press-News.org) Today at the International Alzheimer's Congress (AAIC) in Amsterdam, new guidelines for diagnosing Alzheimer's disease developed by clinicians and researchers from around the world were presented. In these criteria, the disease is diagnosed in the clinic through the use of blood biomarkers, just as with other major diseases such as diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
A blood test has been developed for this purpose in recent years that gives very good results, according to recent research. Charlotte Teunissen, professor of neurochemistry at Amsterdam UMC, was involved in drafting the new guidelines and says, “A new generation of biomarkers is now available to detect Alzheimer's disease more and more effectively. We have already gained a lot of experience with this in our Alzheimer's centre, but in the long term the test can also be successfully implemented after a GP's referral.”
Desire for Diagnosis
New research by Amsterdam UMC with Alzheimer Nederland shows that many people with cognitive symptoms want to know whether they are in the early stages of Alzheimer's. A diagnosis enables patients to take more control over the next phase of their lives. The desire to know whether or not you have Alzheimer's disease makes the use of blood biomarkers so relevant, it is also the gateway to treatment.
A blood test is also a relatively inexpensive method and can be used in many places. Previously, only specialised clinics could do a proper analysis, and thus offer a diagnosis, via a blood test. Swedish research, presented at the ADPD conference in March, has shown that biomarkers can be more reliable than the analysis of a primary care physician. In addition, the blood test is much less stressful for the patient than the current method. Currently, Alzheimer's is diagnosed through the analysis of cerebrospinal fluid, acquired through an invasive lumbar puncture, or via an expensive PET scan. It is believed that both of these methods will soon also be less necessary in the diagnose of Alzheimer's.
Guidelines
The new guidelines were developed by an international committee of practitioners and researchers on behalf of the International Alzheimer's Association and the American National Institute on Aging. Previously, Alzheimer's was defined by identifying brain pathology and cognitive decline with which the disease manifested itself. In the new guideline, the disease is diagnosed using biomarkers. More biomarkers with excellent diagnostic performance have been developed and clinically validated in recent years. And more are coming.
The new approach to Alzheimer's is also relevant and gaining momentum because some targeted therapies, such as lecanemab, against Alzheimer's have already been approved in the US. Currently these drugs are subject to the EMA review in the EU.
END
New guidelines for diagnosing Alzheimer's
Together with international colleagues, Amsterdam UMC reveals the results of a committee constructed on behalf of the International Alzheimer's Association and the American National Institute on Aging.
2023-07-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Discovery could lead to more treatments to prevent cancer and infectious diseases
2023-07-16
Researchers have cracked how a particular type of immune cell develops in the body and protects against infection and disease. And the discovery could help in the development of more preventive treatments, according to a new study.
The research, led by Murdoch Children’s Research Institute and Federation University Australia, has uncovered how these specialised white blood cells operate and can produce an immune response.
Associate Professor Dan Pellicci said by understanding the function of these cells, they could be harnessed to help prevent cancer and highly infectious diseases such as ...
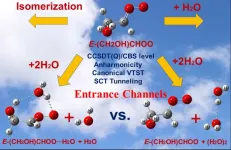
Unimolecular reactions of anti-glycolaldehyde oxide and its reactions with one and two water molecules
2023-07-15
Criegee intermediates are produced in the ozonolysis of unsaturated compounds in the atmosphere. These intermediates are especially importanct because they contribute to the formation of OH radical during the night and to formation of secondary organic aerosols. The OH radicals increase the oxidative capacity of the atmosphere, and the aerosols may reflect or absorb sunlight and contribute to cloud formation. Criegee intermediates also lay key roles in conversion of sulfur dioxide into sulfur trioxide, finally resulting in the formation ...
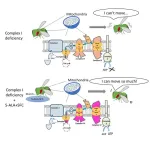
5-aminolevulinic acid might help fight mitochondrial disorders
2023-07-15
Tokyo, Japan – Scientists from Tokyo Metropolitan University have shown that 5-aminolevulinic acid (5-ALA) helps bypass deficiencies in Complex I (CI), the first in a series of protein complexes that transport electrons and help power the mitochondria. They showed that fruit flies missing the analogous protein showed improved health when given a cocktail of drugs including 5-ALA. CI deficiency is responsible for the majority of mitochondrial disorders; the team’s findings might lead to new therapies.
Mitochondrial diseases arise from problems in the mitochondria, a small organelle in cells which produces adenosine triphosphate (ATP), ...
Mobile app enables students with special needs to self-monitor behavior, focus more in class
2023-07-14
COLUMBIA, Mo. -- When Sara Estrapala started her career as a high school paraeducator supporting students with disabilities such as autism, down syndrome, learning disorders and challenging behaviors, she quickly recognized a challenge — her teenage students desire to make their own decisions and their teachers’ struggle to keep them engaged and following directions.
Now an assistant research professor in the University of Missouri College of Education and Human Development, Estrapala is leading a four-year, $519,939 early career development and mentoring ...
Remote plant worlds
2023-07-14
Oceanic islands provide useful models for ecology, biogeography and evolutionary research. Many ground-breaking findings – including Darwin's theory of evolution – have emerged from the study of species on islands and their interplay with their living and non-living environment. Now, an international research team led by the University of Göttingen has investigated the flora of the Canary Island of Tenerife. The results were surprising: the island's plant-life exhibits a remarkable diversity ...
Renewal for university network Enlight
2023-07-14
The European university network Enlight has been renewed: the EU has funded the Enlight Network consisting of the University of Göttingen with nine other research-oriented universities for four more years with a total of around 14.4 million euros. The Network plans to use a large part of the funds for academic initiatives, underlining its commitment to supporting researchers and students. In addition to the University of Göttingen, the Network includes the Universities of Ghent, Groningen, Uppsala and Tartu, the University of the Basque Country, the Universities of Bordeaux and Galway as well as Comenius University Bratislava; and Enlight's tenth and ...
UVA engineer innovates a liquid safety cushioning technology
2023-07-14
The discovery that football players were unknowingly acquiring permanent brain damage as they racked up head hits throughout their professional careers created a rush to design better head protection. One of these inventions is nanofoam, the material on the inside of football helmets.
Thanks to mechanical and aerospace engineering associate professor Baoxing Xu at the University of Virginia and his research team, nanofoam just received a big upgrade and protective sports equipment could, too. This newly invented design integrates nanofoam with “non-wetting ionized liquid," a ...
Your neighborhood may increase risk of hospitalization from respiratory diseases like COVID-19.
2023-07-14
The range of COVID-19 symptoms varies—some feel a mild cold, others are hospitalized, while others perish. Many studies have linked the severity of COVID-19 symptoms with an individual’s biological factors, but less is known about the impact of non-biological factors, such as the environment in which people live.
A new study that published on June 14, 2023, in the journal PLoS ONE, is the first to show that the neighborhood-built environment might pose an independent risk determining the individuals hospitalized due to COVID-19 illness.
The authors found that in a cohort of more than 18,000 individuals with SARS-CoV-2 infections, living in ...
Multiple uses of tropical mosaic landscapes
2023-07-14
Many landscapes in the tropics consist of a mosaic of different types of land use. How people make use of these different ecosystems, with their particular plant communities, was unclear until now. Researchers, many of them from Madagascar, have now investigated this in an interdisciplinary Malagasy research project at the University of Göttingen. When considering biodiversity, forests often get the most attention. But this research shows that rural households use a wide range of plant species ...
Parkinson's disease, intense exercise helps to keep the disease at bay
2023-07-14
Neuroscientists from the Faculty of Medicine of the Catholic University, Rome Campus, and the A. Gemelli IRCCS Polyclinic Foundation found that intensive exercise could slow the course of Parkinson's disease and described the biological mechanisms. The finding could pave the way for new non-drug approaches.
The study "Intensive exercise ameliorates motor and cognitive symptoms in experimental Parkinson's disease by restoring striatal synaptic plasticity" is published in the journal Science Advances. The research was led by Catholic University, Rome Campus ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
[Press-News.org] New guidelines for diagnosing Alzheimer'sTogether with international colleagues, Amsterdam UMC reveals the results of a committee constructed on behalf of the International Alzheimer's Association and the American National Institute on Aging.