(Press-News.org) About The Study: This study found that large increases in mortality with Alzheimer disease and related dementias as an underlying or contributing cause of death occurred in COVID-19 pandemic year 1 but were largely mitigated in pandemic year 2. The most pronounced declines were observed for deaths in nursing home/long-term care settings. Conversely, excess deaths at home and in medical facilities remained high in year 2.
Authors: M. Maria Glymour, Sc.D., of the Boston University School of Public Health in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2023.2226)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaneurology/fullarticle/10.1001/jamaneurol.2023.2226?guestAccessKey=92347e2b-9efc-44bb-a012-04f5b6b00195&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=071723
END
Excess mortality with Alzheimer disease and related dementias as an underlying or contributing cause during pandemic
JAMA Neurology
2023-07-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Comparison of history of present illness summaries generated by a chatbot and senior internal medicine residents
2023-07-17
About The Study: History of present illnesses generated by a chatbot or written by senior internal medicine residents were graded similarly by internal medicine attending physicians. These findings underscore the potential of chatbots to aid clinicians with medical documentation.
Authors: Ashwin Nayak, M.D., M.S., of Stanford University in Stanford, California, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2023.2561)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, ...
Addressing adaptation inequalities in climate research
2023-07-17
A new study proposes ways to better incorporate adaptation in climate change research, addressing the uneven distribution of adaptation capacities and needs worldwide.
Research on adaptation to the risks posed by climate change has witnessed significant growth in the past decade, with increasing recognition of its urgency in policy agendas at the international, national, and local levels. Adaptation needs and capacities are not evenly distributed worldwide, with countries in the Global South generally experiencing the highest challenges. ...
Heading frequency and risk of cognitive impairment in retired male professional soccer players
2023-07-17
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that repetitive heading during a professional soccer career is associated with an increased risk of cognitive impairment in later life. Further study is needed to establish the upper threshold for heading frequency to mitigate this risk.
Authors: Weiya Zhang, Ph.D., of the University of Nottingham in Nottingham, United Kingdom, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.23822)
Editor’s Note: Please ...
COVID-19 vaccines saved dementia patients' lives in nursing homes
2023-07-17
Deaths among older adults with dementia fell starkly in nursing homes and long-term care centers after COVID-19 vaccinations became available, yet remained high for those living at home, according to a new study led by UC San Francisco.
The nationwide study published July 17, 2023 in JAMA Neurology, is the first to use data from 2019 to 2022 to quantify “excess” deaths – or those above what would have been anticipated had there been no pandemic – taking into account age, sex, racial and ethnic groups, as well as the settings where people died.
In the first year, there were 509,179 dementia-related ...
Reprogramming the shape of virus capsids could advance biomedicine
2023-07-17
Bioengineers have found a way to program the size and shape of virus particles by combining viral protein building blocks and templates made from DNA. The resulting nanostructures could have applications in vaccine development and transporting drugs inside the body.
Virus capsid proteins—the proteins that shield the genome of a virus—can be used to build precisely structured protein assemblies. Their shapes and geometry, however, depend largely on the virus strain. Reprogramming these assemblies, no matter the original ...
World-first clinical trial to help millions with penicillin allergies
2023-07-17
Penicillin allergy affects more than 25 million people in the United States (up to 1 in 10 Americans) and has been shown to lead to particularly poor health outcomes in pregnant women and surgical patients. It is also a public health threat, leading to antibiotic resistance and infections in hospitalized patients that can be life threatening.
Seventy-five% or more penicillin allergy labels come on by age 3 due to, for example, confusion with a viral rash. The majority of these rashes were never allergic, but the labels ‘stick’ into adulthood and carry many adverse consequences.”
Many low-risk patients with a penicillin allergy were able to have their ...
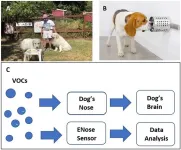
Scent dogs can detect COVID-19 more rapidly and accurately than current tests
2023-07-17
Scent dogs may represent a cheaper, faster and more effective way to detect COVID-19, and could be a key tool in future pandemics, a new review of recent research suggests. The review, published in De Gruyter’s Journal of Osteopathic Medicine, found that scent dogs are as effective, or even more effective, than conventional COVID-19 tests such as RT-PCR.
Dogs possess up to 300 million olfactory cells, compared to just 5 or 6 million in humans, and use one-third of their brains to process scent information, ...
Robotics: New skin-like sensors fit almost everywhere
2023-07-17
“Detecting and sensing our environment is essential for understanding how to interact with it effectively,” says Sonja Groß. An important factor for interactions with objects is their shape. “This determines how we can perform certain tasks,” says the researcher from the Munich Institute of Robotics and Machine Intelligence (MIRMI) at TUM. In addition, physical properties of objects, such as their hardness and flexibility, influence how we can grasp and manipulate them, for example.
Artificial hand: interaction with the robotic system
The ...
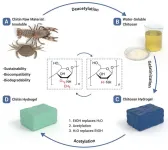
Team fabricates chitin hydrogel via chemical transformation of chitosan
2023-07-17
Chitin hydrogel is recognized as a promising material for a variety of biomedical applications. Its biocompatibility and biodegradability make it useful in tissue repair, artificial organs, and wound healing. Yet scientists continue to face challenges in fabricating chitin hydrogel. A team of researchers has developed a green, efficient and scalable preparation method for chitin hydrogels.
The team’s work provides a rational strategy to fabricate chitin hydrogels and paves the way for its practical applications as a superior biomedical material.
Their ...
Report highlights public health impact of serious harms from diagnostic error in US
2023-07-17
Improving diagnosis in health care is a moral, professional and public health imperative, according to the U.S. National Academy of Medicine. However, little is known about the full scope of harms related to medical misdiagnosis — current estimates range widely. Using novel methods, a team from the Johns Hopkins Armstrong Institute Center for Diagnostic Excellence and partners from the Risk Management Foundation of the Harvard Medical Institutions sought to derive what is believed to be the first rigorous national estimate of permanent disability and death from diagnostic error.
The original research article ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
Rapid evolution can ‘rescue’ species from climate change
Molecular garbage on tumors makes easy target for antibody drugs
New strategy intercepts pancreatic cancer by eliminating microscopic lesions before they become cancer
Embryogenesis in 4D: a developmental atlas for genes and cells
CNIO research links fertility with immune cells in the brain
Why do lithium-ion batteries fail? Scientists find clues in microscopic metal 'thorns'
Surface treatment of wood may keep harmful bacteria at bay
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
[Press-News.org] Excess mortality with Alzheimer disease and related dementias as an underlying or contributing cause during pandemicJAMA Neurology