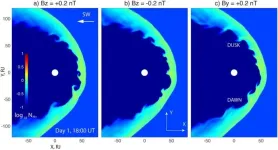
(Press-News.org) SAN ANTONIO — July 17, 2023 —A team led by Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) and The University of Texas at San Antonio (UTSA) has found that NASA’s Juno spacecraft orbiting Jupiter frequently encounters giant swirling waves at the boundary between the solar wind and Jupiter’s magnetosphere. The waves are an important process for transferring energy and mass from the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emitted by the Sun, to planetary space environments.
Jake Montgomery, a doctoral student in the joint space physics program between UTSA and SwRI, noted that these phenomena occur when a large difference in velocity forms across the boundary between two regions in space. This can create a swirling wave, or vortex, at the interface that separates a planet’s magnetic field and the solar wind, known as the magnetopause. These Kelvin-Helmholtz waves are not visible to the naked eye but can be detected through instrument observations of plasma and magnetic fields in space. Plasma — a fundamental state of matter made up of charged particles, ions and electrons — is ubiquitous across the universe.
“Kelvin-Helmholtz instabilities are a fundamental physical process that occurs when solar and stellar winds interact with planetary magnetic fields across our solar system and throughout the universe,” Montgomery said. “Juno observed these waves during many of its orbits, providing conclusive evidence that Kelvin-Helmholtz instabilities play an active role in the interaction between the solar wind and Jupiter.”
Montgomery is the lead author of a study published in Geophysical Research Letters that uses data from multiple Juno instruments, including its magnetometer and the SwRI-built Jovian Auroral Distributions Experiment (JADE).
“Juno’s extensive time near Jupiter’s magnetopause has enabled detailed observations of phenomena such as Kelvin-Helmholtz instabilities in this region,” said Dr. Robert Ebert, a staff scientist at SwRI who also serves as an adjoint professor at UTSA. “This solar wind interaction is important as it can transport plasma and energy across the magnetopause, into Jupiter’s magnetosphere, driving activity within that system.”
The paper “Investigating the Occurrence of Kelvin-Helmholtz Instabilities at Jupiter’s Dawn Magnetopause” appears in Geophysical Research Letters and can be accessed at https://doi.org/10.1029/2023GL102921.
For more information, visit https://www.swri.org/planetary-science.
END
SwRI team identifies giant swirling waves at the edge of Jupiter’s magnetosphere
Waves produced by Kelvin-Helmholtz instabilities transfer energy in the solar system
2023-07-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Immune cells in single file
2023-07-17
The cells of the immune system circulate mainly in the blood and migrate into the body's tissues after an inflammation. Some types of immune cells, however, are permanently located in the tissues, where they come together to form three-dimensional networks.
How do these networks form and how are they maintained? For the long-lived macrophages (phagocytes), the answer is already known: They settle in so-called niches. These are environments of connective tissue cells that supply the macrophages with nutrients and keep them ...
New research shows babies’ immunological weak spot and strength
2023-07-17
NEW YORK, NY--A pair of new studies led by researchers at Columbia University explains why babies get so many common respiratory infections and identifies a specialized cluster of immune cells found only in babies that help them better cope with new pathogens.
“We know little about how the immune system develops throughout life, and most of what we know about immune system development in children comes from animal studies,” says Donna Farber, PhD, an expert in immune system development at Columbia University ...
National Poll: Less than half of parents utilize patient portal benefits for their children
2023-07-17
ANN ARBOR, Mich. – For many busy families, online access to a child’s health provider for medical advice, health records or prescription refills is likely a convenient option.
Yet, only 43% of parents have set their child up for a patient portal – an online tool allowing communication between patients and medical providers – and others may not be optimizing portal use, suggests the University of Michigan Health C.S. Mott Children’s Hospital National Poll on Children’s Health.
“Patient portals offer a wide range of benefits, including decreasing unnecessary hassles for providers and patients and improving access to both the medical ...
The missing Americans: Unprecedented US mortality far exceeds other wealthy nations
2023-07-17
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Monday, July 17, 2023
Contact:
Jillian McKoy, jpmckoy@bu.edu
Michael Saunders, msaunder@bu.edu
##
The Missing Americans: Unprecedented US Mortality Far Exceeds Other Wealthy Nations
A new study found that more than one million US deaths a year—including many young and working-age adults—could be avoided if the US had mortality rates similar to its peer nations.
In 2021, 1.1 million deaths would have been averted ...
Addressing the future challenges of global surface water quality
2023-07-17
As the world's population continues to grow, ensuring access to clean and safe water has become an increasingly important concern, yet little is known about how surface water quality will change in the future. Recent scientific research has shed light on the potential challenges that surface water quality may face in the coming years, particularly in Sub-Saharan Africa. “While surface water quality is projected to improve in most developed countries, there is an important caveat: the outlook for the poorest nations is bleak”.
A recent study, published in Nature Water, has projected an increase in surface water pollution in Sub-Saharan Africa. These findings ...
Study finds how to reduce risk of kids playing with a found gun
2023-07-17
COLUMBUS, Ohio – In a lab at The Ohio State University masquerading as a playroom, pairs of kids ages 8 to 12 participating in a study found a variety of toys and games to play with – as well as a mysterious file cabinet.
Inside one of the drawers of the unlocked cabinet were two disabled 9-mm handguns.
As they played in the room, nearly all the children eventually found the guns. But some kids in the study were much more likely to tell an adult they found a gun, less likely to touch the gun, and were less reckless if they did touch it – and they were the kids who had watched a one-minute gun safety video a week earlier.
The study may be the ...
Trading sickness for health: Swapping brain cells points to new Huntington's therapies
2023-07-17
NNew research appearing in the journal Nature Biotechnology answers important questions about the viability of treatments that seek to replace diseased and aged cells in the central nervous system with healthy ones. Its findings have implications for a number of neurological and psychiatric disorders—including Huntington’s disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), and schizophrenia—that have been linked to glia, a population of cells that support brain health and function.
“A broad variety of disorders we associate with neuronal loss now appear to be caused ...
Researchers craft ‘origami DNA’ to control virus assembly
2023-07-17
Griffith University researchers have played a key role in using DNA ‘origami’ templates to control the way viruses are assembled.
The global team behind the research, published in Nature Nanotechnology, developed a way to direct the assembly of virus capsids – the protein shell of viruses - at physiological conditions in a precise and programmable manner.
Dr Frank Sainsbury and Dr Donna McNeale from the Griffith Institute for Drug Discovery were part of the research team and said forcing viruses to assemble onto DNA folded into different shapes “like origami” was a question that this project answered.
“We achieved control over the virus protein ...
Cap top 20% of energy users to reduce carbon emissions
2023-07-17
Consumers in the richer, developed nations will have to accept restrictions on their energy use if international climate change targets are to be met, warn researchers.
The big challenge is to identify the fairest and most equitable way that governments can curtail energy use, a process known as energy demand reduction.
Writing in the journal Nature Energy, the research team - led by Milena Büchs, Professor of Sustainable Welfare at the University of Leeds - analysed several scenarios to identify a potential ...
Excess mortality with Alzheimer disease and related dementias as an underlying or contributing cause during pandemic
2023-07-17
About The Study: This study found that large increases in mortality with Alzheimer disease and related dementias as an underlying or contributing cause of death occurred in COVID-19 pandemic year 1 but were largely mitigated in pandemic year 2. The most pronounced declines were observed for deaths in nursing home/long-term care settings. Conversely, excess deaths at home and in medical facilities remained high in year 2.
Authors: M. Maria Glymour, Sc.D., of the Boston University School of Public Health ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
Plants pause, play and fast forward growth depending on types of climate stress
University of Minnesota scientists reveal how deadly Marburg virus enters human cells, identify therapeutic vulnerability
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
The gut can drive age-associated memory loss
Enhancing gut-brain communication reversed cognitive decline, improved memory formation in aging mice
Mothers exposure to microbes protect their newborn babies against infection
How one flu virus can hamper the immune response to another
Researchers uncover distinct tumor “neighborhoods”, with each cell subtype playing a specific role, in aggressive childhood brain cancer
[Press-News.org] SwRI team identifies giant swirling waves at the edge of Jupiter’s magnetosphereWaves produced by Kelvin-Helmholtz instabilities transfer energy in the solar system