Case Report: Intrathoracic synovial sarcoma with BRAF V600E mutation
2023-07-18
(Press-News.org)
“The prognosis of recurrent/metastatic SS remains poor, highlighting the need for a novel therapeutic strategy.”
BUFFALO, NY- July 18, 2023 – A new case report was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on July 7, 2023, entitled, “Intrathoracic synovial sarcoma with BRAF V600E mutation.”
Synovial sarcoma (SS) is a highly malignant mesenchymal tumor that occurs mainly in adolescents and young adults. The treatment of SS is multimodal, involving surgery, radiotherapy and chemotherapy. The overall prognosis is generally quite satisfactory in children and adolescents with localized SS at diagnosis. However, the outcome remains poor for patients who relapse, with a reported 5-year post-relapse survival of around 30%.
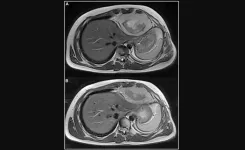
In this new paper, researchers Ida Russo, Sabina Barresi, Pier Luigi Di Paolo, Valentina Di Ruscio, Giada Del Baldo, Annalisa Serra, Silvia Vallese, Evelina Miele, Angela Mastronuzzi, Rita Alaggio, Andrea Ferrari, and Giuseppe Maria Milano from Italy’s Istituto di Ricovero e Cura a Carattere Scientifico (IRCCS) report the case of a 15-year-old boy with intrathoracic synovial sarcoma who relapsed after standard chemotherapy, surgery and radiotherapy. The molecular analysis of the tumor identified a BRAF V600E mutation at time of progression of relapsed disease under third-line systemic treatment.
This mutation is commonly seen in melanomas and papillary thyroid cancers, but less prevalent (typically <5%) across a variety of other cancer types. The patient underwent selective BRAF inhibitor Vemurafenib treatment achieving partial response (PR) with a progression-free survival (PFS) ratio of 1.6 months and an overall survival of 19 months, alive in continuous PR. This case highlights the role of routine next-generation sequencing (NGS) used to drive treatment choice and to investigate SS tumors for BRAF mutations.
“Our data highlight the importance of implementing molecular tests in SS patients to evaluate BRAF mutational actual incidence in these neoplasms.”
Read the full report: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.28475
Correspondence to: Giuseppe Maria Milano
Email: giuseppemaria.milano@opbg.net
Keywords: synovial sarcoma, next-generation sequencing, BRAF V600E mutation, targeted therapy
About Oncotarget: Oncotarget (a primarily oncology-focused, peer-reviewed, open access journal) aims to maximize research impact through insightful peer-review; eliminate borders between specialties by linking different fields of oncology, cancer research and biomedical sciences; and foster application of basic and clinical science.
To learn more about Oncotarget, visit Oncotarget.com and connect with us on social media:
Twitter
Facebook
YouTube
Instagram
LinkedIn
Pinterest
LabTube
Soundcloud
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article: https://oncotarget.altmetric.com/details/email_updates?id=10.18632%2Foncotarget.28475
Click here to subscribe to Oncotarget publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact: media@impactjournals.com.
Oncotarget Journal Office
6666 East Quaker Str., Suite 1A
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957 (option 2)
###
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-07-18
ROCKVILLE, MD—JULY 13, 2023 – The American Association for Anatomy (AAA) announced the deserving recipients of the AAA Predoctoral Fellowship, the DEI Dissertation Completion Award, and the EUReka EDI Undergraduate Research Award. In 2023, AAA expanded its portfolio of awards, grants, and scholarships by an additional $100,000, now topping out at over $650,000. These opportunities provide much-needed financial support to undergraduate and graduate students, enabling them to conduct groundbreaking research and make valuable contributions to the field.
AAA has continuously demonstrated ...
2023-07-18
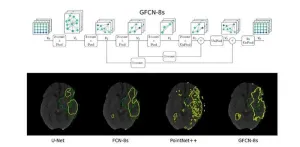
Ischemic stroke, which occurs when a blood vessel in the brain gets blocked by a clot, is among the leading causes of death worldwide. Fortunately, surgeons now have access to advanced imaging techniques that allow them to visualize the interior of a patient’s brain during a stroke. This helps them pinpoint the location of the clot and analyze the extent of damage to the brain tissue.
Computed tomography-perfusion (CT-P) is one of the most useful imaging modalities in the early stages of an acute stroke. However, it is challenging to accurately identify ...
2023-07-18
David Luther, Assistant Professor, Biology, received funding from the National Science Foundation for: "Collaborative Research: LTREB: Forest fragmentation and climate change result in understory warming that adversely affects tropical avian biodiversity at the BDFFP."
Luther and his collaborators posit that remnant bird communities in Amazonian forest fragments are a precursor of future bird assemblages in continuous forest due to understory forest drying from edge effects in fragments and climate change in continuous ...
2023-07-18
Stanford engineers Michael Lepech and Zhiye Li have a unique vision of the future: buildings and roads made from plastic waste.
In a new white paper commissioned by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM), Lepech and Li study the current status, challenges, and needs of recycling plastics in a circular economy, and examine the long-term durability and environmental costs of doing so for use in infrastructure.
Using a mix of computer modeling, scientific research, experimental and field data, as well as interviews with recycling industry stakeholders, Lepech and Li analyze case studies using plastic ...
2023-07-18
MIAMI, FLORIDA (JULY 18, 2023) – Researchers from Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine and Dana Farber Cancer Institute in Boston have been awarded $7 million in total funding to study how diet and exercise impact mental and physical functioning in older cancer survivors and their caregivers.
The funding is being provided by the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI), a nonprofit, Washington, D.C.-based organization that supports research designed to help patients, caregivers and clinicians make better informed healthcare decisions.
Tracy ...
2023-07-18
English serves as a convenient, common language for science. However, this practice poses insurmountable barriers to those whose first language is not English — the majority of people around the world. According to research published on July 18th in the open access journal PLOS Biology, led by Dr. Tatsuya Amano at the University of Queensland, Australia, the disadvantages of being a non-native English speaker in science range from difficulties in reading and writing papers to reduced participation in international conferences.
Few studies to date have ...
2023-07-18
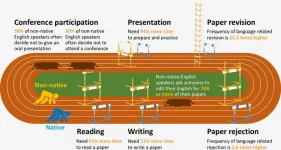
A “clear and significant” language barrier cost faced by non-native English-speaking scientists has been quantified by a University of Queensland-led international survey.
The study, led by UQ’s Dr Tatsuya Amano, surveyed 908 environmental science researchers on scientific activities across five categories – paper reading, writing, publication, dissemination, and conference participation – finding a substantial disadvantage for non-native English speakers in all five.
“Compared to native English speakers, non-native English speakers need up to twice as ...
2023-07-18
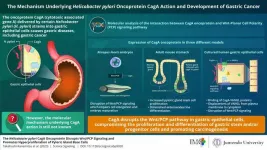
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infections are commonly associated with abdominal pain, bloating, and acidity. Clinical evidence suggests that infection with H. pylori cagA+ strains dramatically increases the risk of developing gastric cancer. A specialized protein delivered by H. pylori to the host, oncoprotein “CagA,” has been shown to interact with multiple host proteins and promote gastric carcinogenesis (transformation of normal cells to cancer cells). However, the underlying mechanisms associated with its biochemical activity have not been fully determined yet.
A new study published in Science Signaling on 18 July 2023 shares insights ...
2023-07-18
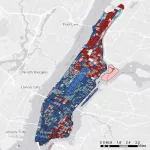
TUSCALOOSA, Ala. – A fifth of neighborhood blocks in the continental United States most vulnerable to natural disaster account for a quarter of the lower 48 states’ risk, according to a detailed assessment of vulnerability.
Leaders in data-driven risk modeling, researchers at The University of Alabama used advanced data analysis and machine learning of more than 100 factors that influence vulnerability to natural hazards for about 11 million United States Census Bureau blocks, finding significant differences can exist between neighboring blocks.
The result published in the journal Nature Communications is the first mapping ...
2023-07-18
INDIANAPOLIS—A new study led by Indiana University School of Medicine researchers shows primary care clinicians who receive specialized training can make accurate autism diagnoses for over 80 percent of young children referred with developmental delays, providing compelling evidence that community-based models of autism evaluation are a potential solution for improving access to this needed service. They recently published their findings in Pediatrics.
One in 36 children are now diagnosed with autism, according to the latest 2023 report from the Centers for Disease Control. In many regions of the county, waitlists ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Case Report: Intrathoracic synovial sarcoma with BRAF V600E mutation