(Press-News.org) Ischemic stroke, which occurs when a blood vessel in the brain gets blocked by a clot, is among the leading causes of death worldwide. Fortunately, surgeons now have access to advanced imaging techniques that allow them to visualize the interior of a patient’s brain during a stroke. This helps them pinpoint the location of the clot and analyze the extent of damage to the brain tissue.
Computed tomography-perfusion (CT-P) is one of the most useful imaging modalities in the early stages of an acute stroke. However, it is challenging to accurately identify segmentation—the outline of stroke lesions—in a CT-P scan, and the final diagnosis depends greatly on the surgeon’s expertise and ability. To address this issue, scientists have come up with various machine learning models that perform automatic segmentation of CT-P scans. Unfortunately, none of them has reached a level of performance suitable for clinical applications.
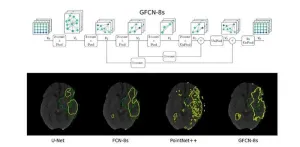
Against this backdrop, a team of researchers from Germany recently developed a new segmentation algorithm for stroke lesions. As reported in their study published in the Journal of Medical Imaging, the team built a geometric deep learning model called “Graph Fully-Convolutional Network” (GFCN). The internal operations performed by their geometric algorithm differ fundamentally from those of the more widely used Euclidean models. In their study, the researchers explored the benefits and limitations of this alternative approach.
A key advantage of the proposed model is that it can better learn and preserve important features inherent to brain topology. By using a graph-based neural network, the algorithm can detect complex inter-pixel relationships from different angles. This, in turn, enables it to detect stroke lesions more accurately.
In addition, the team adopted “pooling” and “unpooling” blocks in their network structure. Put simply, the pooling operations, also called “downsampling,” reduce the overall size of the feature maps extracted by the network from input images. This reduces the computational complexity of the algorithm, enabling the model to extract the most salient features of the CT-P scans. In contrast, the unpooling operations (or “upsampling”) revert the pooling operations to help properly localize the detected features in the original image based on contextual cues. By combining these two operations, the network structure can extract richer geometric information.
The team conducted a series of analyses to determine the effect of each component of GFCN on its segmentation performance. They then compared the performance of the proposed algorithm against the state-of-the-art models, all trained using the same public dataset. Interestingly, although their model used basic unpooling techniques and a simple input configuration, it performed better than the conventional models under most conditions.
Notably, GFCN-8s, with three pooling layers and eight-fold upsampling, achieved a Dice coefficient score—a metric indicating the overlap between the predicted and actual lesion areas—of 0.4553, which is significantly higher than other models. Moreover, the proposed model could adapt to irregular segmentation boundaries better than the state-of-the-art models.
Overall, the findings of this study showcase the potential of geometric deep learning for segmentation problems in medical imaging. Further research on similar strategies could pave the way for highly accurate models for automatic stroke diagnosis that could improve patient outcomes and save lives.
Read the Gold Open Access article by A. Iporre-Rivas et al., “Stroke-GFCN: ischemic stroke lesion prediction with a fully convolutional graph network,” J. Med. Imag. 10(4) 044502 (2023), doi 10.1117/1.JMI.10.4.044502.
END
New geometric deep learning model for detecting stroke lesions
The proposed approach outperforms other neural network architectures by leveraging rich geometric information to segment brain stroke lesion images
2023-07-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Luther studying forest fragmentation & climate change
2023-07-18
David Luther, Assistant Professor, Biology, received funding from the National Science Foundation for: "Collaborative Research: LTREB: Forest fragmentation and climate change result in understory warming that adversely affects tropical avian biodiversity at the BDFFP."
Luther and his collaborators posit that remnant bird communities in Amazonian forest fragments are a precursor of future bird assemblages in continuous forest due to understory forest drying from edge effects in fragments and climate change in continuous ...
Can we use plastic waste to build roads, buildings, and more?
2023-07-18
Stanford engineers Michael Lepech and Zhiye Li have a unique vision of the future: buildings and roads made from plastic waste.
In a new white paper commissioned by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM), Lepech and Li study the current status, challenges, and needs of recycling plastics in a circular economy, and examine the long-term durability and environmental costs of doing so for use in infrastructure.
Using a mix of computer modeling, scientific research, experimental and field data, as well as interviews with recycling industry stakeholders, Lepech and Li analyze case studies using plastic ...
Sylvester, Dana-Farber researchers to receive funding to study how diet, exercise impact mental and physical functioning in older cancer survivors
2023-07-18
MIAMI, FLORIDA (JULY 18, 2023) – Researchers from Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine and Dana Farber Cancer Institute in Boston have been awarded $7 million in total funding to study how diet and exercise impact mental and physical functioning in older cancer survivors and their caregivers.
The funding is being provided by the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI), a nonprofit, Washington, D.C.-based organization that supports research designed to help patients, caregivers and clinicians make better informed healthcare decisions.
Tracy ...
The cost of being a non-native English speaker in science
2023-07-18
English serves as a convenient, common language for science. However, this practice poses insurmountable barriers to those whose first language is not English — the majority of people around the world. According to research published on July 18th in the open access journal PLOS Biology, led by Dr. Tatsuya Amano at the University of Queensland, Australia, the disadvantages of being a non-native English speaker in science range from difficulties in reading and writing papers to reduced participation in international conferences.
Few studies to date have ...
Science language barrier could cost countless careers
2023-07-18
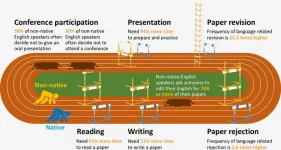
A “clear and significant” language barrier cost faced by non-native English-speaking scientists has been quantified by a University of Queensland-led international survey.
The study, led by UQ’s Dr Tatsuya Amano, surveyed 908 environmental science researchers on scientific activities across five categories – paper reading, writing, publication, dissemination, and conference participation – finding a substantial disadvantage for non-native English speakers in all five.
“Compared to native English speakers, non-native English speakers need up to twice as ...
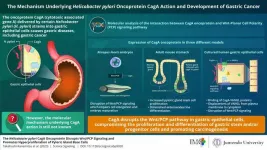
New study throws light on mechanisms underlying helicobacter pylori-induced gastric cancer
2023-07-18
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infections are commonly associated with abdominal pain, bloating, and acidity. Clinical evidence suggests that infection with H. pylori cagA+ strains dramatically increases the risk of developing gastric cancer. A specialized protein delivered by H. pylori to the host, oncoprotein “CagA,” has been shown to interact with multiple host proteins and promote gastric carcinogenesis (transformation of normal cells to cancer cells). However, the underlying mechanisms associated with its biochemical activity have not been fully determined yet.
A new study published in Science Signaling on 18 July 2023 shares insights ...
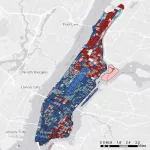
Natural hazard vulnerability shows disproportionate risk
2023-07-18
TUSCALOOSA, Ala. – A fifth of neighborhood blocks in the continental United States most vulnerable to natural disaster account for a quarter of the lower 48 states’ risk, according to a detailed assessment of vulnerability.
Leaders in data-driven risk modeling, researchers at The University of Alabama used advanced data analysis and machine learning of more than 100 factors that influence vulnerability to natural hazards for about 11 million United States Census Bureau blocks, finding significant differences can exist between neighboring blocks.
The result published in the journal Nature Communications is the first mapping ...
IU-developed statewide initiative shows primary care clinicians can diagnose autism in young children with high accuracy
2023-07-18
INDIANAPOLIS—A new study led by Indiana University School of Medicine researchers shows primary care clinicians who receive specialized training can make accurate autism diagnoses for over 80 percent of young children referred with developmental delays, providing compelling evidence that community-based models of autism evaluation are a potential solution for improving access to this needed service. They recently published their findings in Pediatrics.
One in 36 children are now diagnosed with autism, according to the latest 2023 report from the Centers for Disease Control. In many regions of the county, waitlists ...
VUMC receives $7 million award from PCORI to compare breathing tube sedation
2023-07-18
Vanderbilt University Medical Center has received a $7 million, five-year funding award from PCORI (Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute) to compare two sedatives used to place breathing tubes in the emergency department (ED) or intensive care unit (ICU).
To provide support with a breathing machine, doctors must place a breathing tube into a patient’s mouth and throat, and they are given a medication to make them sleep during this procedure. The two medications doctors most often give ...
Lewy body disease can be detected before symptoms
2023-07-18
Lewy body disease is the second most common neurodegenerative disease after Alzheimer's disease. A research group from Lund University has now shown that the disease can be detected before symptoms appear, using a spinal fluid test. The studies are published in Nature Medicine, where the researchers also demonstrate that reduced sense of smell is strongly linked to Lewy body disease even before other clear symptoms have developed. The findings are also reported simultaneously at the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference.
Lewy ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
Researchers find that landowner trust, experience influence feral hog management
Breaking down the battery problem
ACMG Foundation to present adaptive bikes to Baltimore-area children with genetic conditions at heartwarming “Day of Caring” event on March 13
Racial disparities in food insecurity for high- and low-income households
Incidence of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest on a postholiday weekday
Prior authorization bans for buprenorphine alone may not improve treatment retention
When light boosts protein evolution
New model may predict preeclampsia in late pregnancy
[Press-News.org] New geometric deep learning model for detecting stroke lesionsThe proposed approach outperforms other neural network architectures by leveraging rich geometric information to segment brain stroke lesion images