(Press-News.org) About The Study: This study found that major U.S. cities with higher populations of Black individuals are more likely to be affected by mass shooting events, suggesting that structural racism may have a role in their incidence. Public health initiatives aiming to prevent mass shooting events should target factors associated with structural racism to address gun violence.
Authors: Michael Ghio, M.D., of Tulane University in New Orleans, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2023.2846)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamasurgery/fullarticle/10.1001/jamasurg.2023.2846?guestAccessKey=e9f8c3ff-0949-48b6-9e6e-3ae5e5d756b5&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=071923
END
Association between markers of structural racism and mass shooting events in major US cities
JAMA Surgery
2023-07-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Trends, seasonality of emergency department visits, hospitalizations for suicidality among children and adolescents
2023-07-19
About The Study: The findings of this study of 73,000 emergency department visits and hospitalizations for suicidality indicated the presence of seasonal patterns and an observed unexpected decrease in suicidality among children and adolescents after COVID-19–related school closures in March 2020, which suggest a potential association between suicidality and the school calendar.
Authors: Scott D. Lane, Ph.D., of the University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit ...
Two-faced star exposed
2023-07-19
In a first for white dwarfs, the burnt-out cores of dead stars, astronomers have discovered that at least one member of this cosmic family is two faced. One side of the white dwarf is composed of hydrogen, while the other is made up of helium.
“The surface of the white dwarf completely changes from one side to the other,” says Ilaria Caiazzo, a postdoctoral scholar at Caltech who leads a new study on the findings in the journal Nature. “When I show the observations to people, they are blown away.”
White dwarfs are the scalding remains of stars that were once like our sun. As the ...
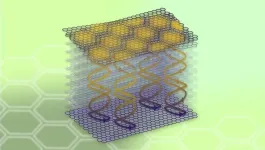
Researchers put a new twist on graphite
2023-07-19
FROM: James Urton
University of Washington
206-543-2580
jurton@uw.edu
(Note: researcher contact information at the end)
Embargoed by Nature
For public release at 11 a.m. Eastern Time (8 a.m. Pacific Time; 4 p.m. British Summer Time) on Wednesday, July 19, 2023
Researchers put a new twist on graphite
For decades, scientists have been probing the potential of two-dimensional materials to transform our world. 2D materials are only a single layer of atoms thick. Within them, subatomic particles like electrons can only move in two dimensions. This simple restriction can trigger unusual electron behavior, ...
Understanding the many different ways animals are evolving in response to fire could help conservation efforts
2023-07-19
In our modern era of larger, more destructive, and longer-lasting fires—called the Pyrocene—plants and animals are evolving quickly to survive. By synthesizing the wide body of research about rapid animal evolution in response to fire in a review publishing in Trends in Ecology & Evolution on July 19, a multidisciplinary team of ecology experts hopes to leverage what we already know to help foster evolution-informed conservation plans. In this way, they suggest, we can try to harness the ways in which fire impacts animals to protect vulnerable species—working with evolution instead of against it.
In response to climate change and changes in land use, ...
Astronomers find new type of stellar object
2023-07-19
An international team led by astronomers from the Curtin University node of the International Centre for Radio Astronomy Research (ICRAR) has discovered a new type of stellar object that challenges our understanding of the physics of neutron stars.
The object could be an ultra-long period magnetar, a rare type of star with extremely strong magnetic fields that can produce powerful bursts of energy.
Until recently, all known magnetars released energy at intervals ranging from a few seconds to a few minutes. The newly discovered object emits radio waves every 22 minutes, making it the longest period magnetar ever detected.
The research was published ...
PNU researcher investigates left-tail momentum in the Korean stock market
2023-07-19
Left-tail risk (LT) stocks are those whose returns fall into the extreme end on the left side of the return distribution. In the hopes of mean-reverting to the normal price, investors usually hold on to these stocks. However, contrary to mean-reverting expectations, these stocks that have experienced extreme losses and high tail risks in the past tend to continue declining in the future, resulting in financial losses. This phenomenon, referred to as left-tail momentum (LTM), appears to challenge the traditional notion of a positive relationship between risk and return.
To investigate this market anomaly, a team of researchers, led by Prof. Eom from the School of Business at Pusan National ...
The puzzle of the galaxy with no dark matter
2023-07-19
A team of scientists, led by the researcher at the IAC and the University of La Laguna (ULL) Sebastién Comerón, has found that the galaxy NGC 1277 does not contain dark matter.This is the first time that a massive galaxy (it has a mass several times that of the Milky Way) does not show evidence for this invisible component of the universe. “This result does not fit in with the currently accepted cosmological models, which include dark matter” explains Comerón.
In the current standard model cosmology massive galaxies contain substantial quantities of dark matter, a type of matter which does not interact in the same ...
New catalysts for solar hydrogen production
2023-07-19
Finding sustainable and clean fuels is crucial in today’s global energy and climate crisis. One promising candidate that is increasingly gaining relevance is hydrogen. However, today’s industrial hydrogen production still has a considerable CO2 footprint, especially considering processes like steam reforming or non-sustainable electrolysis.
A team led by Prof. Dominik Eder from the Institute of Materials Chemistry (TU Wien) is therefore focusing on the development of environmentally friendly processes for obtaining hydrogen, for example by photocatalysis. This process enables the conversion of ...
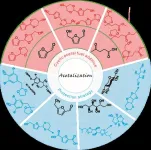
Acetalization: A feasible and sustainable strategy for biomass valorization
2023-07-19
Biomass, mainly composed of lignocellulose and vegetable oil, has been acclaimed as one of the most promising sustainable sources of raw carbon material for the synthesis of transport fuels and value-added chemicals. The catalytic conversion of lignocellulose/vegetable oil and their related derivatives has attracted great attention in biomass valorization. Many elegant methods including hydrolysis, dehydration, hydrogenation, hydrogenolysis, oxidation, etherification, esterification, amination, aldol condensation, ...
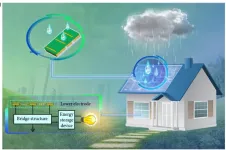
Collecting energy from raindrops using solar panel technology
2023-07-19
When raindrops fall from the sky, they can produce a small amount of energy that can be harvested and turned into electricity. It is a small-scale version of hydropower, which uses the kinetic energy of moving water to produce electricity. Researchers have proposed that the energy collected from raindrops could be a potential source of clean, renewable power. However, this technology has been difficult to develop on a large scale, which has limited its practical application.
To collect raindrop energy, a device called a triboelectric ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Association between markers of structural racism and mass shooting events in major US citiesJAMA Surgery