(Press-News.org)
The transition to chaos is ubiquitous in nonlinear systems. Continuous-wave-driven photonic-chip-based Kerr microresonators exhibit spatiotemporal chaos, also known as chaotic modulation instability.
For more than fifteen years such modulation instability states have been considered impractical for applications compared to their coherent-light-state counterparts, such as soliton states. The latter have been the centerpiece for numerous high-profile application demonstrations, from long-range optical communication to photonic computing.
Now, researchers from the group of Tobias Kippenberg at EPFL have found a new way to harness the unique features of chaotic frequency combs to implement unambiguous and interference-immune massively parallel laser ranging by utilizing the intrinsic random amplitude and phase modulation of the chaotic comb lines.
The research introduces a new paradigm for massively parallel laser ranging using incoherent and chaotic states of light in optical microresonators. This innovative approach offers significant advantages over conventional methods and opens up new possibilities for applications in various fields.
The concept behind this novel laser ranging technique is based on the principle of random modulation continuous-wave (RMCW), where random amplitude and phase modulation of a carrier is used to interrogate a target using amplitude and frequency cross-correlation at the detector.
Unlike conventional continuous-wave (CW) systems, which rely on external modulation, the approach developed at EPFL utilises the inherent random amplitude and phase modulation of the chaotic comb lines in an optical microresonator. The system can support hundreds of multicolor independent optical carriers, enabling massively parallel laser ranging and velocimetry.
RMCW technology is becoming more attractive, and several LiDAR companies employ this approach in their commercial products. "In the foreseen epoch of unmanned vehicles, the immunity to mutual interference with other LiDARs and ambient light sources makes this advantage of RMCW significant,” says Anton Lukashchuk, a PhD student in Kippenberg’s lab and the study’s First Author. “Furthermore, our approach does not require stringent conditions on frequency noise and tuning agility and linearity of the lasers and does not necessitate waveform initiation routines.”
Johann Riemensberger, a postdoc at Kippenberg’s lab and a co-author of the paper, adds: “Surprisingly, the operation in the chaotic modulation instability regime is accompanied by a wideband signal modulation of the comb lines, often surpassing the resonance bandwidth and resulting in centimeter-scale range resolution. Moreover, chaotic microcombs are power-efficient, thermally stable, simple to operate, and provide a flat-top optical spectrum.”
The team's breakthrough opens up new possibilities for optical ranging, spread spectrum communication, optical cryptography, and random number generation. The results of this research not only advance our understanding of chaotic dynamics in optical systems but also provide practical solutions for high-precision laser ranging in various domains.
The chip samples were fabricated in the EPFL Center of MicroNanoTechnology (CMi).
Reference
Anton Lukashchuk, Johann Riemensberger, Aleksandr Tusnin, Junqiu Liu, Tobias J. Kippenberg. Chaotic microcomb-based parallel ranging. Nature Photonics 20 July 2023. DOI: 10.1038/s41566-023-01246-5
END
For years, unrecycled plastic bottles have been dumped in landfills. Now, thanks to new research from UBC Okanagan, those bottles may have a second life in that landfill—stabilizing its earth walls.
Used plastic bottles and textiles pose an increasing problem for landfills worldwide. Researchers say nearly a hundred million metric tons of polyethylene terephthalate (PET), also known as microplastics, are produced globally each year—with a fraction of that number being recycled—making it one of the largest sources of plastic waste.
“One ...
Bat activity falls as farms make the transition to organic agriculture, new research shows.
Organic farming is better for biodiversity than conventional farming, which relies heavily on substances such as pesticides, herbicides and fertilisers.
However, little is known about how wildlife is affected by the transition period when a farm goes organic.
The new study, led by the universities of Bristol, Göttingen and Exeter, assessed the effects of organic farming by monitoring insect-eating bats at citrus ...
Post-menopause female killer whales protect their sons – but not their daughters – from fights with other whales, new research shows.
Scientists studied “tooth rake marks” – the scarring left when one whale scrapes their teeth across the skin of another – and found males had fewer marks if their mother was present and had stopped breeding.
Only six species – humans and five species of toothed whales – are known to experience menopause, and scientists have long been puzzled about why this occurs.
The new study – by the universities ...
Seagrasses evolved from freshwater plants and use sunlight and carbon dioxide (CO2) for photosynthesis and are able to thrive in depths down to 50 metres. In contrast to algae, they possess roots and rhizomes that grow in sandy to muddy sediments. The grass-like, leaf-shoots produce flowers and complete their life cycle entirely underwater. Seeds are negatively buoyant but seed-bearing shoots can raft, thus greatly enhancing dispersal distances at oceanic scale.
As a foundational species, eelgrass provides critical shallow-water habitats for diverse biotas and also provides numerous ecosystem services including carbon uptake. Seagrasses have recently been recognised as one of the important ...
WASHINGTON, DC – The Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) today announced the approval of $9 million for the first seven studies through its groundbreaking Science of Engagement initiative. An unprecedented research program dedicated to funding studies to demonstrate how best to engage patients, caregivers and other health care community members in comparative clinical effectiveness research (CER) and other health research, the initiative aims to grow a more robust evidence base to advance patient-centered, community-driven approaches to conducting research.
Since ...
Individual palladium atoms attached to the surface of a catalyst can remove 90% of unburned methane from natural-gas engine exhaust at low temperatures, scientists reported today in the journal Nature Catalysis.
While more research needs to be done, they said, the advance in single atom catalysis has the potential to lower exhaust emissions of methane, one of the worst greenhouse gases, which traps heat at about 25 times the rate of carbon dioxide.
Researchers from the Department of Energy’s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory and Washington State University ...
Patients and members of the public will be able to more easily take part in impactful research thanks to a new tool developed by the University of Birmingham’s work on Long COVID.
These resources are detailed in a paper published today in Nature Medicine from researchers working within the University of Birmingham’s Institute of Applied Health Research, the NIHR Birmingham Biomedical Research Centre (BRC) and NIHR Applied Research Collaboration West Midlands, reporting the evaluation ...
Like us, cells communicate. Well, in their own special way. Using waves as their common language, cells tell one another where and when to move. They talk, they share information, and they work together – much like the interdisciplinary team of researchers from the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA) and the National University of Singapore (NUS). They conducted research on how cells communicate – and how that matters to future projects, e.g. application to wound healing.
What comes to your mind when you think of biology? Animals, plants, theoretical computer models? The last one, you might not associate with it right away, although ...
Key Takeaways:
Volunteering later in life may protect the brain against cognitive decline and dementia.
New study of older adults found better memory and executive function among those who volunteered.
Watch the video.
(Sacramento) Volunteering in late life is associated with better cognitive function — specifically, better executive function and episodic memory. Those are the findings of a new study from UC Davis Health presented today (July 20) at the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference 2023 in Amsterdam.
“We ...
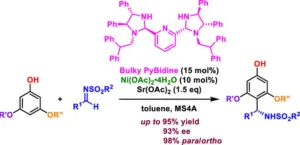
From life-saving drugs and synthetic polymers to diverse advanced materials, the products containing organic compounds seem endless, thanks in part to regioselectivity, a feature in chemical reactions where a substituent is selectively added to a specific position of an organic compound. This favors the formation of desired products with specific functionalities. One notable regioselective reaction used for the precise design of organic compounds is the Friedel−Crafts reaction, which enables the addition of substituents to specific positions on aromatic compounds ...