(Press-News.org) Individual palladium atoms attached to the surface of a catalyst can remove 90% of unburned methane from natural-gas engine exhaust at low temperatures, scientists reported today in the journal Nature Catalysis.
While more research needs to be done, they said, the advance in single atom catalysis has the potential to lower exhaust emissions of methane, one of the worst greenhouse gases, which traps heat at about 25 times the rate of carbon dioxide.
Researchers from the Department of Energy’s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory and Washington State University showed that the catalyst removed methane from engine exhaust at both the lower temperatures where engines start up and the higher temperatures where they operate most efficiently, but where catalysts often break down.
“It’s almost a self-modulating process which miraculously overcomes the challenges that people have been fighting – low temperature inactivity and high temperature instability,” said Yong Wang, Regents Professor in WSU’s Gene and Linda Voiland School of Chemical Engineering and Bioengineering and one of four lead authors on the paper.
A growing source of methane pollution
Engines that run on natural gas power 30 million to 40 million vehicles worldwide and are popular in Europe and Asia. The natural gas industry also uses them to run compressors that pump gas to people’s homes. They are generally considered cleaner than gasoline or diesel engines, creating less carbon and particulate pollution.
However, when natural-gas engines start up, they emit unburnt, heat-trapping methane because their catalytic converters don’t work well at low temperatures. Today's catalysts for methane removal are either inefficient at lower exhaust temperatures or they severely degrade at higher temperatures.
“There’s a big drive towards using natural gas, but when you use it for combustion engines, there will always be unburnt natural gas from the exhaust, and you have to find a way to remove that. If not, you cause more severe global warming,” said co-author Frank Abild-Pedersen, a SLAC staff scientist and co-director of the lab’s SUNCAT Center for Interface Science and Catalysis, which is run jointly with Stanford University. “If you can remove 90% of the methane from the exhaust and keep the reaction stable, that’s tremendous.”
A catalyst with single atoms of the chemically active metal dispersed on a support also uses every atom of the expensive and precious metal, Wang added.
“If you can make them more reactive,” he said, “that’s the icing on the cake.”
Unexpected help from a fellow pollutant
In their work, the researchers showed that their catalyst made from single palladium atoms on a cerium oxide support efficiently removed methane from engine exhaust, even when the engine was just starting.
They also found that trace amounts of carbon monoxide that are always present in engine exhaust played a key role in dynamically forming active sites for the reaction at room temperature. The carbon monoxide helped the single atoms of palladium migrate to form two- or three-atom clusters that efficiently break apart the methane molecules at low temperatures.
Then, as the exhaust temperatures rose, the clusters broke up into single atoms and redispersed, so that the catalyst was thermally stable. This reversible process enabled the catalyst to work effectively and used every palladium atom the entire time the engine was running – including when it started cold.
“We were really able to find a way to keep the supported palladium catalyst stable and highly active and, because of the diverse expertise across the team, to understand why this was occurring,” said SLAC staff scientist Christopher Tassone.
The researchers are working to further advance the catalyst technology. They would like to better understand why palladium behaves in one way while other precious metals such as platinum act differently.
The research has a way to go before it will be put inside a car, but the researchers are collaborating with industry partners as well as with DOE’s Pacific Northwest National Laboratory to move the work closer to commercialization.
Along with Wang, Abild-Pedersen, and Tassone, Dong Jiang, senior research associate in WSU’s Voiland School, also led the work. The work was funded by the DOE Office of Science, and included research carried out at SLAC’s Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource (SSRL), Argonne National Laboratory’s Advanced Light Source (ALS) and the National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center (NERSC), which are all DOE Office of Science user facilities.
This article has been adapted from a press release written by Washington State University.
Citation: Dong Jiang et al., Nature Catalysis, 20 July 2023 (10.1038/s41929-023-00983-8)
SLAC is a vibrant multiprogram laboratory that explores how the universe works at the biggest, smallest and fastest scales and invents powerful tools used by scientists around the globe. With research spanning particle physics, astrophysics and cosmology, materials, chemistry, bio- and energy sciences and scientific computing, we help solve real-world problems and advance the interests of the nation.
SLAC is operated by Stanford University for the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science. The Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time.
END
New catalyst could dramatically cut methane pollution from millions of engines
Researchers demonstrate a way to remove the potent greenhouse gas from the exhaust of engines that burn natural gas.
2023-07-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New resources to improve patient and public involvement in health research
2023-07-20
Patients and members of the public will be able to more easily take part in impactful research thanks to a new tool developed by the University of Birmingham’s work on Long COVID.
These resources are detailed in a paper published today in Nature Medicine from researchers working within the University of Birmingham’s Institute of Applied Health Research, the NIHR Birmingham Biomedical Research Centre (BRC) and NIHR Applied Research Collaboration West Midlands, reporting the evaluation ...
(How) cells talk to each other
2023-07-20
Like us, cells communicate. Well, in their own special way. Using waves as their common language, cells tell one another where and when to move. They talk, they share information, and they work together – much like the interdisciplinary team of researchers from the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA) and the National University of Singapore (NUS). They conducted research on how cells communicate – and how that matters to future projects, e.g. application to wound healing.
What comes to your mind when you think of biology? Animals, plants, theoretical computer models? The last one, you might not associate with it right away, although ...
Volunteering in late life may protect the brain against cognitive decline and dementia
2023-07-20
Key Takeaways:
Volunteering later in life may protect the brain against cognitive decline and dementia.
New study of older adults found better memory and executive function among those who volunteered.
Watch the video.
(Sacramento) Volunteering in late life is associated with better cognitive function — specifically, better executive function and episodic memory. Those are the findings of a new study from UC Davis Health presented today (July 20) at the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference 2023 in Amsterdam.
“We ...
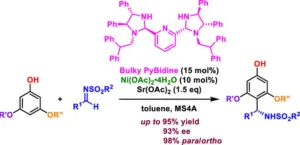
New study expands the scope of aza-friedel−crafts reactions
2023-07-20
From life-saving drugs and synthetic polymers to diverse advanced materials, the products containing organic compounds seem endless, thanks in part to regioselectivity, a feature in chemical reactions where a substituent is selectively added to a specific position of an organic compound. This favors the formation of desired products with specific functionalities. One notable regioselective reaction used for the precise design of organic compounds is the Friedel−Crafts reaction, which enables the addition of substituents to specific positions on aromatic compounds ...
Omega-3 fatty acids appear promising for maintaining lung health
2023-07-20
Omega-3 fatty acids appear promising for maintaining lung health
NIH-funded study supports new role for nutrient found in fish, dietary supplements
Omega-3 fatty acids, which are abundant in fish and fish oil supplements, appear promising for maintaining lung health, according to new evidence from a large, multi-faceted study in healthy adults supported by the National Institutes of Health. The study provides the strongest evidence to date of this association and underscores the importance of including omega-3 fatty acids in the diet, especially given that many Americans do not meet current guidelines. Funded largely by the National Heart, ...
Engineering plants for a changing climate
2023-07-20
Climate change is affecting the types of plant varieties we can cultivate, as well as how and where we can do so. A new collection of articles in the open access journal PLOS Biology explores the twin challenges of engineering plants for resilience to climate change and enhancing their carbon-capture potential. PLOS Biology Editors Pamela Ronald & Joanna Clarke provide a summary editorial, and details regarding the other papers may be found below.
To meet the agricultural challenges caused by climate change and a growing population, we need to improve crop production. This Perspective from industry leaders including Catherine Feuillet calls for more and better ...
Precision measurement of polarization
2023-07-20
NEWPORT NEWS, VA – A doctoral dissertation examining the most precise measurement of electron beam polarization ever made was just awarded the prestigious 2022 Jefferson Science Associates (JSA) Thesis Prize. Since 2017, award-winner Allison Zec has been part of a collaboration that ran experiments at the U.S. Department of Energy's Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility.
The goal of both the CREX and PREX-II experiments was to run an experiment and its mirror opposite simultaneously to determine ...
New study shows Black cancer survivors face increased mortality from heart disease; neighborhood socioeconomic status and insurance contributing factors
2023-07-20
ATLANTA, July 20, 2023 – A new study from researchers at the American Cancer Society (ACS) found that Black cancer survivors in the United States experience a higher risk of dying from cardiovascular disease (CVD) compared with White cancer survivors. The research showed Black cancer survivors carry from 30% up to a three-fold higher mortality risk from CVD, depending on the type of cancer that was diagnosed. Differences in neighborhood socioeconomic status and health insurance between Black and White cancer survivors explained the disparities in cardiovascular death rates between populations, according to the study authors. ...
High body temperature increases resistance to pathogenic viral infections, new study finds
2023-07-20
Researchers from The University of Tokyo unravel the connection between high body temperature and increased viral resistance.
Clinical evidence suggests that elderly individuals are at a higher risk of contracting viral infections. Quite notably, the older people also have lower mean body temperatures. However, the effects of increased body temperature on fighting viral infections remain largely unexplored. A team of Japanese researchers has now been able to bridge the gap by linking higher body temperature with an increased infection-fighting capability of the gut microorganisms or "microbiota." Their study was published in Volume 14 ...
New research sheds light on factors influencing trust and bias in societies
2023-07-20
People with more positive perceptions of their nation’s institutions are more likely to show favoritism toward fellow citizens, according to new research in Social Psychological and Personality Science. This research suggests that support for national institutions could pose a challenge for establishing trust across borders.
Researchers also found that people who identify strongly with their own nation are likely to favor their fellow citizens, which aligns with previous studies. The possible role of trust in national institutions, however, was an unexpected development for researchers.
“We observed greater favoritism in trust toward fellow citizens ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
A clinical reveals that aniridia causes a progressive loss of corneal sensitivity
Fossil amber reveals the secret lives of Cretaceous ants
[Press-News.org] New catalyst could dramatically cut methane pollution from millions of enginesResearchers demonstrate a way to remove the potent greenhouse gas from the exhaust of engines that burn natural gas.