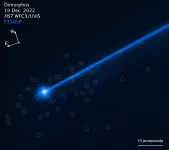
(Press-News.org) The popular 1954 rock song "Shake, Rattle and Roll," could be the theme music for the Hubble Space Telescope's latest discovery about what is happening to the asteroid Dimorphos in the aftermath of NASA's DART (Double Asteroid Redirection Test) experiment. DART intentionally impacted Dimorphos on September 26, 2022, slightly changing the trajectory of its orbit around the larger asteroid Didymos.
Astronomers using Hubble's extraordinary sensitivity have discovered a swarm of boulders that were possibly shaken off the asteroid when NASA deliberately slammed the half-ton DART impactor spacecraft into Dimorphos at approximately 14,000 miles per hour.
The 37 free-flung boulders range in size from three feet to 22 feet across, based on Hubble photometry. They are drifting away from the asteroid at little more than a half-mile per hour – roughly the walking speed of a giant tortoise. The total mass in these detected boulders is about 0.1% the mass of Dimorphos.
"This is a spectacular observation – much better than I expected. We see a cloud of boulders carrying mass and energy away from the impact target. The numbers, sizes, and shapes of the boulders are consistent with them having been knocked off the surface of Dimorphos by the impact," said David Jewitt of the University of California at Los Angeles, a planetary scientist who has been using Hubble to track changes in the asteroid during and after the DART impact. "This tells us for the first time what happens when you hit an asteroid and see material coming out up to the largest sizes. The boulders are some of the faintest things ever imaged inside our solar system."
Jewitt says that this opens up a new dimension for studying the aftermath of the DART experiment using the European Space Agency's upcoming Hera spacecraft, which will arrive at the binary asteroid in late 2026. Hera will perform a detailed post-impact survey of the targeted asteroid. "The boulder cloud will still be dispersing when Hera arrives," said Jewitt. "It's like a very slowly expanding swarm of bees that eventually will spread along the binary pair's orbit around the Sun."
The boulders are most likely not shattered pieces of the diminutive asteroid caused by the impact. They were already scattered across the asteroid's surface, as evident in the last close-up picture taken by the DART spacecraft just two seconds before collision, when it was only seven miles above the surface.
Jewitt estimates that the impact shook off two percent of the boulders on the asteroid's surface. He says the boulder observations by Hubble also give an estimate for the size of the DART impact crater. "The boulders could have been excavated from a circle of about 160 feet across (the width of a football field) on the surface of Dimorphos," he said. Hera will eventually determine the actual crater size.
Long ago, Dimorphos may have formed from material shed into space by the larger asteroid Didymos. The parent body may have spun up too quickly or could have lost material from a glancing collision with another object, among other scenarios. The ejected material formed a ring that gravitationally coalesced to form Dimorphos. This would make it a flying rubble pile of rocky debris loosely held together by a relatively weak pull of gravity. Therefore, the interior is probably not solid, but has a structure more like a bunch of grapes.
It's not clear how the boulders were lifted off the asteroid's surface. They could be part of an ejecta plume that was photographed by Hubble and other observatories. Or a seismic wave from the impact may have rattled through the asteroid – like hitting a bell with a hammer – shaking lose the surface rubble.
"If we follow the boulders in future Hubble observations, then we may have enough data to pin down the boulders' precise trajectories. And then we’ll see in which directions they were launched from the surface," said Jewitt.
The DART and LICIACube (Light Italian CubeSat for Imaging of Asteroids) teams have also been studying boulders detected in images taken by LICIACube’s LUKE (LICIACube Unit Key Explorer) camera in the minutes immediately following DART's kinetic impact.
The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and ESA. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Maryland, conducts Hubble and Webb science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, in Washington, D.C.
END
Hubble sees boulders escaping from asteroid dimorphos
2023-07-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The American Society for Nutrition appoints Xingen Lei, Ph as next editor-in-chief of The Journal of Nutrition
2023-07-20
Rockville, MD (July 20, 2023) Xingen Lei, PhD, professor of molecular nutrition and associate dean of research and innovation at Cornell University’s College of Agriculture and Life Sciences, has been named the next editor-in-chief of The Journal of Nutrition, effective January 1, 2024. Established in 1928, The Journal of Nutrition is the oldest journal devoted to publishing influential original research, reviews, and perspectives of molecular, cellular, animal, human, and population nutrition and mechanisms.
Dr. Lei has published extensively in The Journal of Nutrition ...
Sending the shoes back? How about this lovely gift card? Cross-selling can help retailers avoid lost revenue from returns
2023-07-20
https://www.rotman.utoronto.ca/Connect/MediaCentre/NewsReleases/20230720
Toronto - It’s become so darn easy to order stuff thanks to the miracles of online shopping. But it’s not so simple on the retailer end, especially when more than 16 per cent of those sales are later sent back. In the U.S., that adds up to a staggering $816 billion in lost revenue.
Cross-selling can help, say a pair of researchers. Their experiments show that once we’ve chosen to buy something, we tend to consider that money as already spent or gone, also called ...
ECOG-ACRIN adds a new treatment trial to the ComboMATCH precision medicine initiative
2023-07-20
The ECOG-ACRIN Cancer Research Group (ECOG-ACRIN) has enrolled the first patient in a new treatment trial to evaluate the effectiveness of adding nilotinib to standard paclitaxel chemotherapy. The trial (EAY191-E4) is for the treatment of adults with cancers that are getting worse after being treated with taxane-based chemotherapy. It is a new addition to the recently launched ComboMATCH precision medicine initiative, which uses tumor biology as a guiding point for testing new combinations of cancer drugs.
James M. Ford, MD, the ECOG-ACRIN Chair for ComboMATCH and Professor of Medicine (Oncology) and Genetics at Stanford University, ...
Climate science is catching up to climate change with predictions that could improve proactive response
2023-07-20
In Africa, climate change impacts are experienced as extreme events like drought and floods. Through the Famine Early Warning Systems Network (which leverages expertise from USG science agencies, universities, and the private sector) and the IGAD Climate Prediction and Applications Center, it has been possible to predict and monitor these climatic events, providing early warning of their impacts on agriculture to support humanitarian and resilience programming in the most food insecure countries of the world.
Science is beginning to catch up with and even ...
Detecting threats beyond the limits of human, sensor sight
2023-07-20
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. — Remember what it’s like to twirl a sparkler on a summer night? Hold it still and the fire crackles and sparks but twirl it around and the light blurs into a line tracing each whirl and jag you make.
A new patented software system developed at Sandia National Laboratories can find the curves of motion in streaming video and images from satellites, drones and far-range security cameras and turn them into signals to find and track moving objects as small as one pixel. The developers say this system can enhance the performance of any remote sensing application.
“Being able to track each pixel from a distance matters, ...
Nature inspires breakthrough achievement: hazard-free production of fluorochemicals
2023-07-20
For the first time, Oxford chemists have generated fluorochemicals – critical for many industries – without the use of hazardous hydrogen fluoride gas.
The innovative method was inspired by the biomineralization process that forms our teeth and bones.
The results are published today in the leading journal Science.
A team of chemists have developed an entirely new method for generating critically important fluorochemicals that bypasses the hazardous product hydrogen fluoride (HF) gas. ...
Could early induction of labor reduce inequities in pregnancy outcomes?
2023-07-20
Inducing labor at 39 weeks of pregnancy has the greatest benefit in risk reduction for women from more socioeconomically deprived areas, according to a new study published July 13th in the open access journal PLOS Medicine by Ipek Gurol-Urganci of the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, UK, and colleagues. The findings suggest that increased uptake of induction of labor at 39 weeks may help reduce inequities in adverse perinatal outcomes.
Adverse perinatal outcomes— which include stillbirths, neonatal ...
Ultra-flexible endovascular probe records deep-brain activity in rats, without surgery
2023-07-20
A new ultra-small and ultra-flexible electronic neural implant, delivered via blood vessels, can record single-neuron activity deep within the brains of rats, according to new study. “This technology could enable long-term, minimally invasive bioelectronic interfaces with deep-brain regions, writes Brian Timko in a related Perspective. Brain-machine interfaces (BMIs) enable direct electrical communication between the brain and external electronic systems. They allow brain activity to directly ...
Northwestern Greenland was ice-free 400,000 years ago, according to Camp Century sediments
2023-07-20
Sediments recovered from the base of the Camp Century ice core show that northwestern Greenland was ice-free during a period of history known to have exhibited some of the lowest global ice volumes -- the Marine Isotope Stage (MIS) 11 interglacial period. The absence of ice at that location means that the Greenland Ice Sheet must have contributed more 1.4 meters of sea-level equivalent to global sea level during the interglacial – a period in which average global air temperature was similar to what we’ll soon experience, given human-caused climate warming. The climate conditions of past interglacials – periods during Earth’s climatic history ...
Global GPS measurements indicate observable phase of fault slip two hours before large earthquakes
2023-07-20
Analysis of Global Positioning System (GPS) time-series data from nearly 100 large earthquakes worldwide has provided evidence for the existence of a precursory phase of fault slip occurring two hours before seismic rupture. “If it can be confirmed that earthquake nucleation often involves an hours-long precursory phase, and the means can be developed to reliably measure it, a precursor warning could be issued,” writes Roland Bürgmann in a related Perspective. The ability to predict large earthquakes has been a longstanding yet elusive goal. Short-term ...