(Press-News.org)
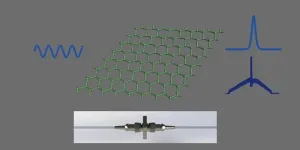
Saturable absorbers as passive modulators in passively mode-locked fiber lasers play a crucial role in the generation of ultrashort pulses. Germanene, a graphene-like two-dimensional material with fast carrier relaxation time and large nonlinear absorption coefficient comparable to that of graphene, is a saturable absorber material with very fast response.
Researchers led by Prof. Wei Xia at University of Jinan (UJN), are interested in modulation switches in fiber lasers, and two-dimensional material saturable absorbers have been a hot research topic in recent years. Two-dimensional materials make up for the disadvantages of traditional artificial saturable absorbers such as nonlinear polarization rotation and nonlinear amplification loop mirror with poor environmental stability and complex structure. And germanene, as an emerging two-dimensional material, has excellent nonlinear optical properties, and fully exploring its potential performance has a positive contribution to the development of passive modulators. The researchers predict its potential applications. Using it as a saturable absorber, the femtosecond pulse and higher energy noise-like pulse can be obtained.
The work entitled “Two types of ultrafast mode-locking operations generation from an Er-doped fiber laser based on germanene nanosheets” was published on Frontiers of Optoelectronics (published on Jun. 7, 2023).
###
Reference: Baohao Xu, Zhiyuan Jin, Lie Shi, Huanian Zhang, Qi Liu, Peng Qin, Kai Jiang, Jing Wang, Wenjing Tang, Wei Xia. Two types of ultrafast mode-locking operations from an Er-doped fiber laser based on germanene nanosheets. Front. Optoelectron., 2023, 16(2): 13 https://doi.org/10.1007/s12200-023-00068-1
About Higher Education Press
Founded in May 1954, Higher Education Press Limited Company (HEP), affiliated with the Ministry of Education, is one of the earliest institutions committed to educational publishing after the establishment of P. R. China in 1949. After striving for six decades, HEP has developed into a major comprehensive publisher, with products in various forms and at different levels. Both for import and export, HEP has been striving to fill in the gap of domestic and foreign markets and meet the demand of global customers by collaborating with more than 200 partners throughout the world and selling products and services in 32 languages globally. Now, HEP ranks among China's top publishers in terms of copyright export volume and the world’s top 50 largest publishing enterprises in terms of comprehensive strength.
The Frontiers Journals series published by HEP includes 28 English academic journals, covering the largest academic fields in China at present. Among the series, 12 have been indexed by SCI, 6 by EI, 2 by MEDLINE, 1 by A&HCI. HEP's academic monographs have won about 300 different kinds of publishing funds and awards both at home and abroad.
About Frontiers of Optoelectronics
Frontiers of Optoelectronics (FOE) aims at introducing the most recent research results and the cutting edge improvements in the area of photonics and optoelectronics. It is dedicated to be an important information platform for rapid communication and exchange between researchers in the related areas. The journal publishes review articles, research articles, letters, comments, special issues, and so on. The Editors-in-Chief are Academician Qihuang Gong from Peking University and Prof. Xinliang Zhang from Xidian University & Huazhong University of Science and Technology. FOE has been indexed by ESCI, EI, SCOPUS, DOAJ, PubMedCentral, CSCD, Source Journals for Chinese Scientific and Technical Papers and Citations, etc. FOE is fully open access since 2022.
END
About The Study: This study of more than 70 million births or spontaneous abortions showed the prevalence of hepatitis C (HCV)-positive pregnancies in the U.S. increased 16-fold between 1998 and 2018. Maternal HCV infection was associated with increased odds of preterm labor, poor fetal growth, or fetal distress. These data may support recent recommendations for universal HCV screening with each pregnancy.
Authors: Po-Hung Chen, M.D., Ph.D., of the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in Baltimore, ...
About The Study: The findings of this study of births to females ages 18 to 24 suggest that additional recommended cervical cancer screenings before birth were associated with an increased risk of preterm delivery. Cervical cancer screening guidelines should consider the downstream implications for preterm delivery risk when weighing the population-level costs of screenings against the benefits of reduced cervical cancer mortality.
Authors: Rebecca Bromley-Dulfano, M.S., of Harvard University Medical School in Cambridge, Massachusetts, is the corresponding author.
To ...
Francis Crick Institute press release
Under strict embargo: 16:00hrs BST 21 July 2023
Peer reviewed
Experimental study
Cells
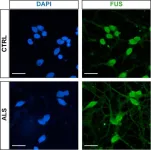
Research reveals the scale of disorder underpinning Motor Neurone Disease
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute and UCL have shown that hundreds of proteins and mRNA molecules are found in the wrong place in nerve cells affected by Motor Neuron Disease (MND), also known as Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS).
ALS is a rapidly progressing and devastating condition that causes paralysis by affecting ...
LA JOLLA, CA — Scripps Research scientists have developed a machine-learning system—a type of artificial intelligence (AI) application—that can track the detailed evolution of epidemic viruses and predict the emergence of viral variants with important new properties.
In a paper in Cell Patterns on July 21, 2023, the scientists demonstrated the system by using data on recorded SARS-CoV-2 variants and COVID-19 mortality rates. They showed that the system could have predicted the emergence of new SARS-CoV-2 “variants of concern” (VOCs) ahead of their official designations by the World Health Organization (WHO). Their ...
Researchers from the University of Liverpool have created a biomedical compound that has the potential to stop the spread of breast cancer. A recently published paper details these early findings.
Scientists from the Chemistry and Biochemistry Departments at the University of Liverpool and Nanjing Medical School in China have discovered a possible way to block proteins produced in the body when a patient has cancer and which causes its spread to other parts of the body. This process, called metastasis, is largely responsible for patient deaths.
The major problem hindering the successful treatment of commonly occurring cancers is not the primary tumour which can usually be removed by ...
Male crickets sing in unison to attract females – but stop singing if a rival gets too close, new research shows.
University of Exeter scientists watched more than 100 male field crickets, and measured how often they chirped at the same time (called “singing overlap”).
Singing by males one to five metres away from a listening male had a “stimulatory effect”, leading to a chorus of crickets singing together.
However, males were less likely to sing if another cricket chirped within one metre – possibly because the territorial insects instead chose to fight ...
Some people’s brain function still affected by Long COVID years after infection
UK researchers have found that people with longer-term COVID-19 symptoms including brain fog showed reduced performance in tasks testing different mental processes up to two years after infection with the virus.
Researchers from King’s College London looked at whether infection with COVID-19 affected performance in two rounds of online cognitive testing that took place in 2021 and 2022. Data was collected for over 3,000 participants of the COVID Symptom Study Biobank study, across 12 tasks that tested memory, attention, reasoning, processing speed and ...
A scientist from Northumbria University has been awarded almost half a million pounds to develop a new technology which could transform deep-space communication, radio astronomy, medical imaging and airport security scanning.
Dr Juna Sathian has received a grant from the government’s Engineering & Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) to develop a new type of MASER (Microwave Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation) device.
The forerunner to LASERs, MASERs were first discovered in the 1950s. But there has been ...
Benjamin Franklin may be best known as the creator of bifocals and the lightning rod, but a group of University of Notre Dame researchers suggest he should also be known for his innovative ways of making (literal) money.
During his career, Franklin printed nearly 2,500,000 money notes for the American Colonies using what the researchers have identified as highly original techniques, as reported in a study published this week in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The research team, led by Khachatur Manukyan, an associate research professor ...
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and collaborating institutions are developing a strategy to predict the response of triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) to chemotherapy, which would be a valuable tool for physicians deciding on the treatment with better probability of success on an individual basis. The study appears in Cancer Research Communications, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
“Multiple research innovations in cancer diagnostics are on display in this work,” said co-corresponding author Dr. Matthew Ellis, member of the Lester and Sue Smith Breast Center and the Dan ...