Keck Hospital of USC receives highest rating on national quality report
Hospital earns five stars from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) annual quality star rating report
2023-07-26
(Press-News.org) LOS ANGELES, CA — Keck Hospital of USC earned five stars, the highest rating possible, on the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) 2023 quality star rating report.
Only approximately 16% of hospitals across the country, 483 out of 3,076, received five stars out of a one-to-five-star rating system.
“This prestigious designation demonstrates our continuing commitment to patient safety and to best patient outcomes, and is the result of the hard work of every physician, nurse and staff member at the hospital,” said Stephanie Hall, MD, MHA, chief medical officer of Keck Hospital and USC Norris Cancer Hospital.
A hospital’s star rating is based on how well it performs across five different areas of quality measures:
Readmission — returns to the hospital following a hospitalization.
Mortality — death rates of patients in the 30 days following a hospitalization.
Safety of care — potentially preventable injury and complications due to care provided during a hospitalization.
Timely and effective care.
Patient experience — such as how effectively physicians and nurses communicate to the patient and if a patient would recommend the hospital to others.
“A five-star rating means that Keck Hospital outperforms the national average in readmission, mortality and complication rates as well as timely and effective care, which is a tremendous validation of our commitment to quality care,” said Marty Sargeant, MBA, CEO of Keck Hospital and USC Norris Cancer Hospital. “We’re also proud to have received five stars in the patient experience category, which reflects that more than 90% of our patients are likely to recommend our hospital to others.”
This quality designation is one of many recent national safety and quality recognitions the hospital has received, including earning a five-star ranking for excellence by Vizient, Inc., a leading health care performance improvement company. Keck Medicine of USC also recently underscored its commitment to safety by hiring a health system chief quality officer.
The CMS rating system was launched in 2016 to help patients and caregivers make informed decisions when selecting a hospital. Hospitals report quality data to the CMS through multiple reporting programs, and the data is then reviewed and standardized to calculate hospital star rankings.
For detailed information on how Keck Hospital scored on quality measures, please click here.
###
For more information about Keck Medicine of USC, please visit news.KeckMedicine.org.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-07-26
About 15 years ago, researchers reported that the timing of spring in high-Arctic Greenland had advanced at some of the fastest rates of change ever seen anywhere in the world. But, according to new evidence reported in the journal Current Biology on July 26, that earlier pattern has since been completely erased. Instead of coming earlier and earlier, it seems the timing of Arctic spring is now driven by tremendous climate variability with drastic differences from one year to the next.
“As scientists we are obliged to revisit previous ...
2023-07-26
The United States has more than 10 times the number of mass shooting incidents than other developed countries, yet little research has shown the distribution and types of shootings, geographically.
“I’m constantly asked, ‘What is public health doing about the rise in mass shootings?” says Leslie Barnard, MPH, a student working with the University of Colorado School of Medicine’s Firearm Injury Prevention Initiative.
Barnard, a doctoral candidate in the Department of Epidemiology in the Colorado School of Public Health at the CU Anschutz Medical Campus, wanted to find answers to address public ...
2023-07-26
Eighty-two percent of child deaths in low-income countries could be prevented, according to a study from the international CHAMPS network published in JAMA Network Open. The study, which used the minimally invasive autopsy technique developed by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), found an infectious agent in 87% of cases and identified malnutrition as the most common underlying cause of death.
Ninety-nine percent of deaths in children under five years of age occur in low- and middle-income countries. "If we want to prevent these deaths, we need to know the causes, but the problem is that we lack reliable data," says Quique Bassat, ...
2023-07-26
About The Study: The findings of this study including 268 counties in 22 states suggest that wastewater surveillance can provide an accurate assessment of county SARS-CoV-2 incidence and may be the best metric for monitoring amount of circulating virus as home testing increases and disease acuity decreases because of vaccination and treatment.
Authors: Meri R. J. Varkila, M.D., of Stanford University in Palo Alto, California, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.25591)
Editor’s Note: Please ...
2023-07-26
About The Study: This secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial including 19,000 older adults found a significant increase in intracranial bleeding with daily low-dose aspirin but no significant reduction of ischemic stroke. These findings may have particular relevance to older individuals prone to developing intracranial bleeding after head trauma (e.g., from falls).
Authors: John J. McNeil, Ph.D., of Monash University in Melbourne, Australia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.25803)
Editor’s ...
2023-07-26
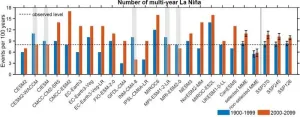
The El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is the Earth's most consequential interannual climate fluctuation. Alternating irregularly between warm El Niño and cold La Niña phases, it brings shifts in ocean surface temperature and disrupts wind and rainfall patterns across the tropics.
Unlike El Niño, which usually lasts one year, La Niña tends to develop after an El Niño and lasts for two consecutive years or more. This is known as a multiyear La Niña event and exerts prolonged and aggregated impacts, such as increased wildfires, flooding, and altered ...
2023-07-26
Earth is truly unique among our Solar System’s planets. It has vast water oceans and abundant life. But Earth is also unique because it is the only planet with plate tectonics, which shaped its geology, climate and possibly influenced the evolution of life.
Plate tectonics describes the movement and interaction of tectonic plates on Earth’s surface. This movement is driven by the very slow creeping motion of Earth's mantle, called convection, which carry heat from the interior to our planet's ...
2023-07-26
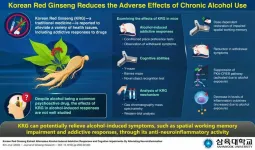
Alcohol is one of the most commonly used psychoactive drugs, with a growing number of users in many parts of the world. Despite the awareness regarding its adverse effects, individuals can get habituated to alcohol consumption, leading to a medical condition called alcohol use disorder (AUD). AUD is characterized by the abuse, dependency, and addiction of alcohol, leading to compromised social responses and interactions of the individual. Moreover, it impairs spatial working memory (memory that allows us to orient ourselves ...
2023-07-26
Researchers have found that people with obstructive sleep apnea have an increased cardiovascular risk due to reduced blood oxygen levels, largely explained by interrupted breathing. Obstructive sleep apnea has long been associated with increased risk of cardiovascular issues, including heart attack, stroke, and death, but the findings from this study, partially supported by the National Institutes of Health and published in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, show the mechanism mostly responsible ...
2023-07-26
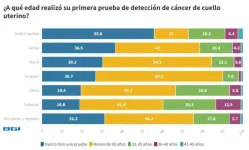
Research from the Registro Nacional de Cáncer notes that Uruguay has the highest cancer incidence and mortality rates in Latin America. In particular, cervical cancer is the third leading cause of cancer related morbidity among Uruguay's female population.
To further motivate action to combat cervical cancer, BGI Genomics today released its State of Cervical Cancer Awareness Report in Uruguay. This report assesses the level of knowledge, attitudes, and practices related to cervical cancer screening and the human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine. By examining these key areas, this survey seeks to highlight the associated barriers and opportunities. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Keck Hospital of USC receives highest rating on national quality report
Hospital earns five stars from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) annual quality star rating report