Nematode resurrected from Siberian permafrost laid dormant for 46,000 years
Genome analysis shows new nematode species shares molecular toolkit for survival with C. elegans
2023-07-27
(Press-News.org)
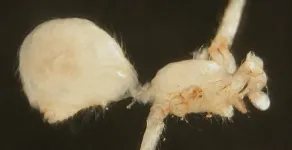
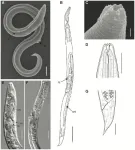
A soil nematode reanimated from Siberian permafrost had laid dormant for approximately 46,000 years, according to a study publishing July 27, 2023 in the open access journal PLOS Genetics by Anastasia Shatilovich at the Institute of Physicochemical and Biological Problems in Soil Science RAS in Russia, Vamshidhar Gade at the Max Planck Institute for Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics in Germany, and colleagues.
Some animals, such as tardigrades, rotifers, and nematodes, can survive harsh conditions by entering a dormant state known as “cryptobiosis”. Previously, nematode individuals were reanimated from samples collected from a fossilized burrow in silt deposits in the northeastern Arctic. In this study, radiocarbon analysis of plant material from the burrow revealed that these frozen deposits, 40 meters below the surface, had not thawed since the late Pleistocene, between 45,839 and 47,769 years ago.
Using genome sequencing, assembly, and phylogenetic analysis of the nematode’s relationship to modern species, the researchers determined that it belongs to a previously undescribed species, Panagrolaimus kolymaensis. They compared its genome with the model organism, Caenorhabditis elegans, and identified genes in common that are involved in cryptobiosis. When mildly desiccated in the laboratory, both species increased production of a sugar called trehalose, which may help them to survive harsh desiccation and freezing. They tested the survival capabilities of P. kolymaensis and found that exposure to mild desiccation before freezing helped prepare the worms for cryptobiosis and improved survival at -80°C. This treatment also benefitted C. elegans dauer larvae, which then survived 480 days at -80°C with no reductions in viability or reproduction after thawing.
This study extends the longest reported cryptobiosis in nematodes by tens of thousands of years. By adapting to cope with extreme conditions, such as permafrost, for short periods of time, the nematodes might have gained the potential to remain dormant over geological timescales.
The authors add, “This work also suggests that fluctuations in the environment also determine the time an organism can remain in a cryptobiotic state.”
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS Genetics: http://journals.plos.org/plosgenetics/article?id=10.1371/journal.pgen.1010798
Citation: Shatilovich A, Gade VR, Pippel M, Hoffmeyer TT, Tchesunov AV, Stevens L, et al. (2023) A novel nematode species from the Siberian permafrost shares adaptive mechanisms for cryptobiotic survival with C. elegans dauer larva. PLoS Genet 19(7): e1010798. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1010798
Author Countries: Germany, Ireland, Russia, UK
Funding: This work was supported by the Russian Foundation fr Basic Research (19-29-05003-mk) to AS and ER. VRG and TVK acknowledge the financial support from the Volkswagen Foundation (Life research grant 92847). PHS and TTH are supported by a DFG ENP grant to PHS (DFG project 434028868). GMH is funded by a UCD Ad Astra Fellowship. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-07-27
For over two hundred years, the origin of the Indo-European languages has been disputed. Two main theories have recently dominated this debate: the ‘Steppe’ hypothesis, which proposes an origin in the Pontic-Caspian Steppe around 6000 years ago, and the ‘Anatolian’ or ‘farming’ hypothesis, suggesting an older origin tied to early agriculture around 9000 years ago. Previous phylogenetic analyses of Indo-European languages have come to conflicting conclusions about the age of the family, due to the combined effects of inaccuracies and inconsistencies in the datasets they used and limitations in the way that phylogenetic methods analyzed ...
2023-07-27
Some organisms, such as tardigrades, rotifers, and nematodes, can survive harsh conditions by entering a dormant state known as “cryptobiosis.” In 2018, researchers from the Institute of Physicochemical and Biological Problems in Soil Science RAS in Russia found two roundworms (nematode) species in the Siberian Permafrost. Radiocarbon dating indicated that the nematode individuals have remained in cryptobiosis since the late Pleistocene, about 46,000 years ago. Researchers from the Max Planck Institute of Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics (MPI-CBG) in ...
2023-07-27
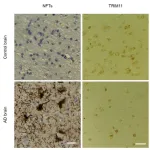
PHILADELPHIA – A gene encoding a protein linked to tau production—tripartite motif protein 11 (TRIM11)—was found to suppress deterioration in small animal models of neurodegenerative diseases similar to Alzheimer’s disease (AD), while improving cognitive and motor abilities, according to new research from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. Additionally, TRIM11 was identified as playing a key role in removing the protein tangles that cause neurodegenerative diseases, like AD. The findings are published today in Science. ...
2023-07-27
Cognitive and computer scientists at the University of Toronto, Universitat Pompeu Fabra and the Catalan Institution for Research and Advanced Studies have found child language development and the historical evolution of the world’s languages share a common cognitive foundation—a core knowledge base where patterns of children’s language innovation can predict patterns of language evolution, and vice versa.
Published today in Science, the paper is a first-of-its-kind step toward a unified theory of the lexicon and the mind examined across timescales. The result may also help predict how a word’s meaning may change ...
2023-07-27
People often debate whether social media creates "echo chambers" by showing users content that matches their politics and in turn increases polarization. A new study published today in the journal Nature reports that reducing Facebook users' exposure to content from politically "like-minded" sources had no measurable effect on their political beliefs or attitudes during the 2020 U.S. presidential election.
The findings are part of a broader research project examining the role of ...
2023-07-27
Australia’s rich and diverse fauna never fails to surprise us, as a new spider species has been documented from the continent.
The novel species, a blind daddy long-legs, was found in boreholes in the arid Pilbara of Western Australia. It is the first cave-adapted daddy long-legs spider reported from the continent, with other blind species of its genus so far only found in Thailand, Laos, and Vietnam.
“It represents a subfamily that was previously thought to be restricted to the tropical north and east of the continent,” says Bernhard Huber, one of the authors of a recent study published ...
2023-07-27
27 July 2023
Geological Society of America
Release No. 23-28
Contact: Justin Samuel
+1-303-357-1026
jsamuel@geosociety.org
Boulder, Colo., USA: GSA is pleased to welcome three exceptional new Fellows who will join us in our mission to advance geoscience knowledge and discovery through excellent writing, research, and advocacy.
GSA’s 2023–2024 Science Communication Fellow is Arianna Soldati.
Soldati is an assistant professor of volcanology at North Carolina State University. Her lab group works on a variety of topics, ranging from effusive eruptions to critical minerals. She received her Ph.D. in geological sciences from the University of ...
2023-07-27
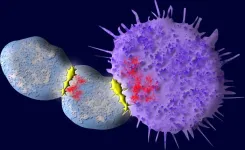
New Haven, Conn. — In a promising form of immunotherapy known as CAR T-cell (chimeric antigen receptor) therapy, the patient’s T cells are engineered to better recognize and attack antigens on the surface of cancer cells. In treatments currently approved for use in battling lymphoma and leukemia, however, the therapy has a drawback: Amidst the cancer-killing frenzy, many engineered T cells become tainted with the remnants of cancer antigens, which causes them to turn on other T cells. This eventually depletes the body of cancer-fighting cells ...
2023-07-27
Digital Science, a technology company serving stakeholders across the research ecosystem, is pleased to announce that the Research Corporation for Science Advancement (RCSA) has chosen Symplectic Grant Tracker from Digital Science’s suite of flagship products to advance its aims of providing catalytic funding for innovative scientific research and the development of academic scientists.
RCSA joins the 50+ foundations, charities and funders worldwide who manage their end-to-end grant lifecycle using Symplectic Grant Tracker. Designed from the outset to meet research funding needs, Grant Tracker includes features to assist applicants, reviewers, committees and ...
2023-07-27
PHILADELPHIA (July 27, 2023) – Two decades ago, the Practice Environment Scale of the Nursing Work Index was published to measure the nursing practice environment. Although the instrument's use has resulted in advances in science and quality improvement efforts, its potential may be limited by the availability and quality of translations into different languages.
Researchers from the University of Pennsylvania School of Nursing (Penn Nursing) investigated published translations of the instrument and have identified ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Nematode resurrected from Siberian permafrost laid dormant for 46,000 years
Genome analysis shows new nematode species shares molecular toolkit for survival with C. elegans