(Press-News.org) July 27, 2023 – Race/ethnicity is not an independent predictor of hospital readmission in patients undergoing breast reconstruction surgery, reports a study in the August issue of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®, the official medical journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
Among patients who have unplanned hospitalizations after breast reconstruction, costs are substantially higher for Black or Hispanic patients, according to the new research by ASPS Member Surgeon Kevin C. Chung, MD, MS, of University of Michigan and colleagues. Dr. Chung comments, "Our study lends new insights into healthcare disparities for an important reconstructive surgery and points to possible strategies to foster more equitable care." Dr. Chung is Editor-in-Chief of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery.
Study looks at disparities in readmission and costs after breast reconstruction
The researchers evaluated potential racial/ethnic disparities in a sample of more than 17,000 patients who underwent breast reconstruction from 2006 to 2015. Data were drawn from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality's Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project, representing five states in four US regions.
The analysis focused on differences in unplanned emergency department visits and hospitalizations within 30 days after breast reconstruction. Differences in costs incurred during hospital readmissions were compared as well.
White patients accounted for 70% of the study sample, Black patients for 11%, Hispanic patients for 8%, and patients of "other" race/ethnicity for 11%. Rates of unplanned hospital visits were six percent for Black patients and seven percent for Hispanic patients, compared to five percent for White patients and those in "other" racial/ethnic categories.
However, after adjustment for other variables, race/ethnicity was not an independent risk factor for unplanned readmission. The presence of up to four comorbidities (other medical conditions) was a significant factor, associated with a 27% increase in readmission risk.
Non-White patients 'bear a higher cost burden' from unplanned readmissions
In contrast, non-White patients had higher costs for hospital readmission. Average costs were about $12,800 for Black patients, $12,350 for Hispanic patients, and $18,000 for patients in the "other" category, compared to $10,000 for White patients. In adjusted analyses, Black and Hispanic patients were about 35% more likely to experience an increased cost for their readmission and "other" patients about 70% more likely, compared to White patients.
"Racial disparities in postoperative plastic surgery care are well documented," Dr. Chung and colleagues write. "[H]owever, little is known about the consequences of this disparity as it related to unplanned hospital visits and associated costs." Breast reconstruction has benefits in restoring form and function in women who have undergone mastectomy for breast cancer.
"Although race is not an independent predictor of an unplanned hospital visit after surgery, racial minorities bear a higher cost burden after controlling for insurance status, further stimulating healthcare disparities," Dr. Chung and coauthors conclude. They highlight the need for further studies to determine the reasons for racial disparities in costs and what strategies can be followed to mitigate them, such as adjusted payment models. Additionally, the authors recognize the limitations of using an administrative database to study such a phenomenon and state that prospective studies are needed to better evaluate differences in cost for readmission among racial minorities.
Read [Racial Disparities in the Cost of Unplanned Hospitalizations After Breast Reconstruction]
Wolters Kluwer provides trusted clinical technology and evidence-based solutions that engage clinicians, patients, researchers and students in effective decision-making and outcomes across healthcare. We support clinical effectiveness, learning and research, clinical surveillance and compliance, as well as data solutions. For more information about our solutions, visit https://www.wolterskluwer.com/en/health and follow us on LinkedIn and Twitter @WKHealth.
###
About Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
For over 75 years, Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery® (http://www.prsjournal.com/) has been the one consistently excellent reference for every specialist who uses plastic surgery techniques or works in conjunction with a plastic surgeon. The official journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons, Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery® brings subscribers up-to-the-minute reports on the latest techniques and follow-up for all areas of plastic and reconstructive surgery, including breast reconstruction, experimental studies, maxillofacial reconstruction, hand and microsurgery, burn repair and cosmetic surgery, as well as news on medico-legal issues.
About ASPS
The American Society of Plastic Surgeons is the largest organization of board-certified plastic surgeons in the world. Representing more than 7,000 physician members, the society is recognized as a leading authority and information source on cosmetic and reconstructive plastic surgery. ASPS comprises more than 94 percent of all board-certified plastic surgeons in the United States. Founded in 1931, the society represents physicians certified by The American Board of Plastic Surgery or The Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada.
About Wolters Kluwer
Wolters Kluwer (EURONEXT: WKL) is a global leader in professional information, software solutions, and services for the healthcare, tax and accounting, financial and corporate compliance, legal and regulatory, and corporate performance and ESG sectors. We help our customers make critical decisions every day by providing expert solutions that combine deep domain knowledge with specialized technology and services.
Wolters Kluwer reported 2022 annual revenues of €5.5 billion. The group serves customers in over 180 countries, maintains operations in over 40 countries, and employs approximately 20,000 people worldwide. The company is headquartered in Alphen aan den Rijn, the Netherlands.
For more information, visit www.wolterskluwer.com, follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, and YouTube.
END
Race/ethnicity isn't associated with unplanned hospitalizations after breast reconstruction
However, Black and Hispanic patients have higher readmission costs, reports study in Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®
2023-07-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
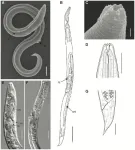
Nematode resurrected from Siberian permafrost laid dormant for 46,000 years
2023-07-27
A soil nematode reanimated from Siberian permafrost had laid dormant for approximately 46,000 years, according to a study publishing July 27, 2023 in the open access journal PLOS Genetics by Anastasia Shatilovich at the Institute of Physicochemical and Biological Problems in Soil Science RAS in Russia, Vamshidhar Gade at the Max Planck Institute for Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics in Germany, and colleagues.
Some animals, such as tardigrades, rotifers, and nematodes, can survive harsh conditions by entering a dormant state known as “cryptobiosis”. Previously, nematode individuals were reanimated from samples collected from a fossilized burrow in silt deposits ...
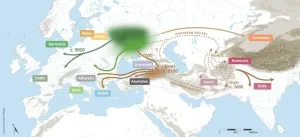
New insights into the origin of the Indo-European languages
2023-07-27
For over two hundred years, the origin of the Indo-European languages has been disputed. Two main theories have recently dominated this debate: the ‘Steppe’ hypothesis, which proposes an origin in the Pontic-Caspian Steppe around 6000 years ago, and the ‘Anatolian’ or ‘farming’ hypothesis, suggesting an older origin tied to early agriculture around 9000 years ago. Previous phylogenetic analyses of Indo-European languages have come to conflicting conclusions about the age of the family, due to the combined effects of inaccuracies and inconsistencies in the datasets they used and limitations in the way that phylogenetic methods analyzed ...
Genome analysis of 46,000-year-old roundworm from Siberian permafrost reveals novel species
2023-07-27
Some organisms, such as tardigrades, rotifers, and nematodes, can survive harsh conditions by entering a dormant state known as “cryptobiosis.” In 2018, researchers from the Institute of Physicochemical and Biological Problems in Soil Science RAS in Russia found two roundworms (nematode) species in the Siberian Permafrost. Radiocarbon dating indicated that the nematode individuals have remained in cryptobiosis since the late Pleistocene, about 46,000 years ago. Researchers from the Max Planck Institute of Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics (MPI-CBG) in ...
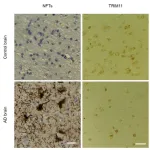
Tau-regulating protein identified as a promising target for developing Alzheimer’s disease treatment
2023-07-27
PHILADELPHIA – A gene encoding a protein linked to tau production—tripartite motif protein 11 (TRIM11)—was found to suppress deterioration in small animal models of neurodegenerative diseases similar to Alzheimer’s disease (AD), while improving cognitive and motor abilities, according to new research from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. Additionally, TRIM11 was identified as playing a key role in removing the protein tangles that cause neurodegenerative diseases, like AD. The findings are published today in Science. ...
A unified theory of the lexicon and the mind: Researchers find common cognitive foundation for child language development and language evolution
2023-07-27
Cognitive and computer scientists at the University of Toronto, Universitat Pompeu Fabra and the Catalan Institution for Research and Advanced Studies have found child language development and the historical evolution of the world’s languages share a common cognitive foundation—a core knowledge base where patterns of children’s language innovation can predict patterns of language evolution, and vice versa.
Published today in Science, the paper is a first-of-its-kind step toward a unified theory of the lexicon and the mind examined across timescales. The result may also help predict how a word’s meaning may change ...
Exposure to like-minded sources on Facebook is prevalent but did not increase polarization during the 2020 U.S. election
2023-07-27
People often debate whether social media creates "echo chambers" by showing users content that matches their politics and in turn increases polarization. A new study published today in the journal Nature reports that reducing Facebook users' exposure to content from politically "like-minded" sources had no measurable effect on their political beliefs or attitudes during the 2020 U.S. presidential election.
The findings are part of a broader research project examining the role of ...
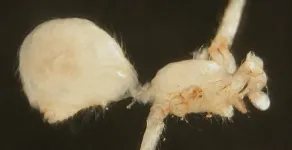
From Down Under to Underground: surprising daddy long-legs spiders discovered in Australia and Réunion
2023-07-27
Australia’s rich and diverse fauna never fails to surprise us, as a new spider species has been documented from the continent.
The novel species, a blind daddy long-legs, was found in boreholes in the arid Pilbara of Western Australia. It is the first cave-adapted daddy long-legs spider reported from the continent, with other blind species of its genus so far only found in Thailand, Laos, and Vietnam.
“It represents a subfamily that was previously thought to be restricted to the tropical north and east of the continent,” says Bernhard Huber, one of the authors of a recent study published ...
Geological Society of America announces 2023–2024 Fellows for Science Policy and Communication
2023-07-27
27 July 2023
Geological Society of America
Release No. 23-28
Contact: Justin Samuel
+1-303-357-1026
jsamuel@geosociety.org
Boulder, Colo., USA: GSA is pleased to welcome three exceptional new Fellows who will join us in our mission to advance geoscience knowledge and discovery through excellent writing, research, and advocacy.
GSA’s 2023–2024 Science Communication Fellow is Arianna Soldati.
Soldati is an assistant professor of volcanology at North Carolina State University. Her lab group works on a variety of topics, ranging from effusive eruptions to critical minerals. She received her Ph.D. in geological sciences from the University of ...
Tail spin: Study reveals new way to reduce friendly fire in cell therapy
2023-07-27
New Haven, Conn. — In a promising form of immunotherapy known as CAR T-cell (chimeric antigen receptor) therapy, the patient’s T cells are engineered to better recognize and attack antigens on the surface of cancer cells. In treatments currently approved for use in battling lymphoma and leukemia, however, the therapy has a drawback: Amidst the cancer-killing frenzy, many engineered T cells become tainted with the remnants of cancer antigens, which causes them to turn on other T cells. This eventually depletes the body of cancer-fighting cells ...
Research Corporation for Science Advancement (RCSA) chooses Symplectic Grant Tracker to manage funding for innovative scientific research
2023-07-27
Digital Science, a technology company serving stakeholders across the research ecosystem, is pleased to announce that the Research Corporation for Science Advancement (RCSA) has chosen Symplectic Grant Tracker from Digital Science’s suite of flagship products to advance its aims of providing catalytic funding for innovative scientific research and the development of academic scientists.
RCSA joins the 50+ foundations, charities and funders worldwide who manage their end-to-end grant lifecycle using Symplectic Grant Tracker. Designed from the outset to meet research funding needs, Grant Tracker includes features to assist applicants, reviewers, committees and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
[Press-News.org] Race/ethnicity isn't associated with unplanned hospitalizations after breast reconstructionHowever, Black and Hispanic patients have higher readmission costs, reports study in Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®