(Press-News.org) In an increasingly diverse, multicultural world, adolescents struggle academically in multicultural environments if they don’t receive consistent and positive messages at school, home and among their peers about cultures that are not their own, a University of California, Davis, study suggests.
In a survey of more than 700 teens at public schools in the Southwestern United States, researchers found that while these students attended ethnically diverse schools and reported learning about multiple cultures in school, they didn’t always get the same messages from friends and their families. This affected their academic engagement, such as participation and interest in school, and their goals for higher education.
“It can be emotionally taxing to adolescents to receive different messages, and it can affect their academic achievement,” said Maciel M. Hernández, assistant professor of human ecology and lead author of the study. “Youth need to successfully interact with and be socially connected to people from diverse backgrounds … it’s important to be full partakers in this fabric of society and appreciate cultural traditions that are not their own.”
Co-lead author of the article is M. Dalal Safa, Department of Psychology and Neuroscience, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
The study was published July 26 in the Journal of Youth and Adolescence.
Surveyed about getting consistent messages
Researchers surveyed sixth and ninth graders from multiple schools in the same region. Only 4% of those surveyed reported getting consistent and high levels of multicultural messaging and affirmation in their classroom, peer and family environments.
The questions asked of the teens in the study ranged from what they had learned about diverse cultures, to how much their friends and family encouraged their learning and appreciating what they learned.
For example, with regard to family interaction, the survey asked how often parents and caregivers encouraged their teens to read books about other racial/ethnic groups, talked to them about important people or events in the history of racial/ethnic groups other than their own, and expressed that all people are equal regardless of race/ethnicity.
Similar questions were posed about peer interaction, but researchers did not question students about where they interacted with peers, such as their involvement in extracurricular activities or participation in sports, clubs or worship.
Students also were asked how much they enjoyed school, learning and activities, and how far they intended to progress in school.
Hernández said that students who answered affirmatively about listening in school and liking school, not surprisingly, reported goals for higher education. “Beyond that, it’s important to have youth who like to go to school and are meaningfully engaged by their experiences in a culturally diverse world,” she said. “This affects many parts of their lives and their future success.”
The survey found that youth with at least one immigrant parent were more likely to experience higher degrees of multicultural socialization than those without immigrant parents, perhaps because their parents more intentionally worked to integrate into their diverse communities and passed these aspirations along to their children, researchers said.
Latinx (31.8 %) and multiethnic (31.5 %) made up the majority of respondents in the study. Whites made up 25.7 %, 7.3 % were Black, 1.4 % were Asian American or Pacific Islander, 1.4 % were American Indian or Alaska Native, and 1% were Middle Eastern or North African.
“Importantly, promoting multicultural socialization across school, peer and family settings is promising for improving adolescents’ academic functioning. Especially since only 4% of students are getting consistent messages, there is a lot of room to improve,” Hernández said.
Additional co-authors include Olga Kornienko, Department of Psychology, George Mason University; Adam A. Rogers, School of Family Life, Brigham Young University; and Thao Ha, Department of Psychology, Arizona State University.
This research was made possible by a grant from the Spencer Foundation.
END
Susan G. Komen®, the world’s leading breast cancer organization, announced the fourth MBC-focused research grant supported through the Komen Metastatic Breast Cancer Collaborative Research Initiative (MBCCRI), a collaboration between Komen, Duke Cancer Institute and the University of North Carolina Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center, which pairs researchers from each of the organizations to work together and address significant gaps in our knowledge about MBC to advance patient care and improve patient outcomes.
In 2021, Komen’s MBCCRI awarded $1.5 million for three research projects focused on finding ...
LA JOLLA, CA—Support for early career researchers is about to get a major boost, thanks to a new fellowship fund established by leaders at La Jolla Institute for Immunology (LJI) and Japan-based global pharmaceutical corporation, Kyowa Kirin, Inc.
The fellowship fund has been named in honor of LJI Professor Michael Croft, Ph.D., who has worked closely with Kyowa Kirin scientists through the years. The new Michael Croft Fellowship in Immunology Fund recognizes Croft’s commitment to training and mentoring the next generation ...
UT-Battelle, LLC, has appointed Stephen K. Streiffer to be the next director of Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL). He currently serves as interim director at SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory and will join ORNL in October.
“Stephen is a proven leader with diverse experience and a commitment to mission-driven research and development,” said Lou Von Thaer, CEO of Battelle and chair of UT-Battelle, which operates ORNL for the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE). “Throughout his career, Stephen has leveraged existing strengths to create new opportunities and partnerships that strengthen our nation’s ability to innovate ...
Researchers at NYU College of Dentistry’s Pain Research Center have developed a gene therapy that treats chronic pain by indirectly regulating a specific sodium ion channel, according to a new study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
The innovative therapy, tested in cells and animals, is made possible by the discovery of the precise region where a regulatory protein binds to the NaV1.7 sodium ion channel to control its activity.
“Our study represents a major step forward in understanding the underlying biology of the NaV1.7 sodium ion channel, which can be harnessed to provide relief from chronic pain,” said Rajesh ...
At first glance, the hexagonal cells build by honey bees and social wasps may seem similar, but they are significantly different. Honey bees build using wax, whereas wasps use paper. Honey bees build their double-sided combs vertically, whereas wasps build single-sided comb horizontally (i.e., the opening of each cell faces downward).
Indeed, the hexagonal cells built by these two groups have independent evolutionary origins. Just like sharks and whales have similar body plans due to their watery environment, bees and wasps build hexagonal cells because the shape maximizes strength and storage area, while minimizing building materials.
But what happens when perfectly ...
During the COVID-19 pandemic, governments changed rules and procedures related to Medicaid enrollment. These changes decreased many of the burdens eligible people face when signing up for programs and contributed to a 30 percent increase in Medicaid enrollment. However, the end of public health emergency declarations brings an end to these pandemic policies, which many fear could lead to eligible people losing public health insurance simply because they are unable to fulfill administrative requirements such as accurately filling out and submitting forms, renewing their enrollment ...
New research shows the importance of long-term commitment to the MIND diet for reaping the greatest benefit to brain health.
“The benefits within the new study’s three-year clinical trial weren’t as impressive as we’ve seen with the MIND diet observational studies in the past, but there were improvements in cognition in the short-term, consistent with the longer-term observational data,” said lead study author Lisa Barnes, PhD, associate director of the Alzheimer’s Disease Research Center at RUSH.
Results from the study, published in The New England Journal of Medicine, showed that within a three-year period, there was no significant ...
July 27, 2023 – Race/ethnicity is not an independent predictor of hospital readmission in patients undergoing breast reconstruction surgery, reports a study in the August issue of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®, the official medical journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
Among patients who have unplanned hospitalizations after breast reconstruction, costs are substantially higher for Black or Hispanic patients, according to the new research by ASPS ...
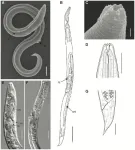
A soil nematode reanimated from Siberian permafrost had laid dormant for approximately 46,000 years, according to a study publishing July 27, 2023 in the open access journal PLOS Genetics by Anastasia Shatilovich at the Institute of Physicochemical and Biological Problems in Soil Science RAS in Russia, Vamshidhar Gade at the Max Planck Institute for Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics in Germany, and colleagues.
Some animals, such as tardigrades, rotifers, and nematodes, can survive harsh conditions by entering a dormant state known as “cryptobiosis”. Previously, nematode individuals were reanimated from samples collected from a fossilized burrow in silt deposits ...
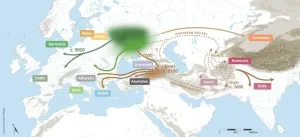
For over two hundred years, the origin of the Indo-European languages has been disputed. Two main theories have recently dominated this debate: the ‘Steppe’ hypothesis, which proposes an origin in the Pontic-Caspian Steppe around 6000 years ago, and the ‘Anatolian’ or ‘farming’ hypothesis, suggesting an older origin tied to early agriculture around 9000 years ago. Previous phylogenetic analyses of Indo-European languages have come to conflicting conclusions about the age of the family, due to the combined effects of inaccuracies and inconsistencies in the datasets they used and limitations in the way that phylogenetic methods analyzed ...