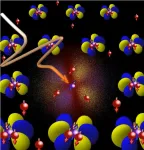
(Press-News.org) Using energy from light to activate natural enzymes can help scientists create new-to-nature enzymatic reactions that support eco-friendly biomanufacturing — the production of fuels, plastics, and valuable chemicals from plants or other biological systems.
Applying this photoenzymatic approach, researchers have developed a clean, efficient way to synthesize crucial chemical building blocks known as chiral amines, solving a longstanding challenge in synthetic chemistry.
The study, published in Nature Catalysis, included researchers from the Center for Advanced Bioenergy and Bioproducts Innovation (CABBI), a U.S. Department of Energy-funded Bioenergy Research Center; the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering (ChBE) at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign; and Xiamen University in China. It was led by CABBI’s Zhengyi Zhang, Postdoctoral Research Associate with ChBE Professor Huimin Zhao, CABBI’s Conversion Theme Leader and an affiliate of the Carl R. Woese Institute for Genomic Biology (IGB); and Jianqiang Feng and Binju Wang of the College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University.
Their work focused on hydroamination, a complex chemical reaction that can be used to produce chiral amines, which have wide applications in the synthesis of agrochemicals and other products. The team developed a photoenzymatic system that can control unstable nitrogen-centered radicals in a reaction known as enantioselective intermolecular radical hydroamination, which until now had been a major challenge in chemistry. Radicals are atoms or molecules with at least one unpaired electron, which makes them highly chemically reactive because electrons prefer to be in pairs.
Hydroamination involves adding an amino group (a nitrogen atom bonded to one or two hydrogen atoms) to an unsaturated organic compound. Currently, hydroamination reactions can be carried out by metal- or photo-catalysts, which are substances used to speed up chemical reactions. While photocatalysis has advantages over other methods, using light as the energy source and avoiding the need for expensive and poisonous metals, it has not been applied previously in intermolecular hydroamination reactions for chiral amines because of the difficulty of controlling the nitrogen-centered radicals — key intermediates in the catalytic process.
To address that problem, the research team turned to natural enzymes — proteins found in living organisms that catalyze reactions in a process called biocatalysis. Natural enzymes can generate and control radicals for various biological processes. And the high selectivity of biocatalysis allows researchers to deploy enzymes to act on specific substrates and create valuable target products. Zhao’s lab has had success steering that process with photocatalysis to produce new enzyme reactivity.
In this study, the CABBI researchers chose the ene-reductase enzyme, which they had previously used with other substrates to achieve different reactions. They successfully repurposed an ene-reductase with natural light to achieve intermolecular radical hydroamination with excellent enantioselectivity (the ability to target a mirror-image molecule known as an enantiomer).
“It’s a new reaction that is very hard to accomplish with a chemical catalyst because we are making chiral compounds, and there are no natural enzymes that can catalyze that reaction,” Zhao said. “In this work, we created an artificial enzyme that can achieve that unique reaction.”
Most biological compounds, including DNA molecules, amino acids, and many agrochemicals, are “chiral,” meaning a flipped or mirrored copy cannot be completely superimposed on top of the original molecule (like a left and right hand). Chirality is important in many agrochemical products; in some herbicides, for example, one enantiomer may have higher herbicidal activity and selectivity than the other. Therefore, it is important to develop methods to make chiral molecules efficiently.
The findings have practical applications for CABBI’s research to develop efficient methods for transforming leaves and stems from bioenergy grasses into high-value manufacturing products. Fatty acids that CABBI researchers derive from plant biomass can be readily converted into the unsaturated compounds used in this study, and therefore could potentially be upgraded into chiral amines.
More broadly, the discovery of this new photoenzymatic system demonstrates in principle that chiral amines — precursors for other valuable molecules — can be produced from fatty acid-derived material in the lab, thus offering a promising platform for biomanufacturing. It will enable further investigation into upgrading fatty acids into chiral amino acids, which can be used for production of agrochemicals and other molecules and materials.
By collaborating with researchers around the world, the CABBI team has taken a giant step toward understanding the fundamentals of this system, Zhang said. “I am excited to work with the team to study this reaction, which we believe will lead to new discoveries involving nitrogen-centered radicals.”
Zhao is hopeful that companies will use the novel method developed by the research team for making their products.
“We still want to continue to discover new reactions that can be catalyzed by enzymes, particularly using the biomass produced by CABBI,” he said.
Co-authors on this study included Wesley Harrison of CABBI, IGB, and ChBE; Haiyang Cui of IGB, ChBE, and the NSF Molecular Maker Lab Institute at Illinois; and Chao Yang and Dongping Zhong of Ohio State University.
END
CABBI develops eco-friendly enzyme to create key chemical building blocks
Photoenzymatic system can efficiently synthesize chiral amines, solving a persistent challenge in chemistry and advancing biomanufacturing
2023-07-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
When electrons slowly vanish during cooling
2023-07-31
Many substances change their properties when they are cooled below a certain critical temperature. Such a phase transition occurs, for example, when water freezes. However, in certain metals there are phase transitions that do not exist in the macrocosm. They arise because of the special laws of quantum mechanics that apply in the realm of nature’s smallest building blocks. It is thought that the concept of electrons as carriers of quantized electric charge no longer applies near these exotic phase transitions. Researchers at the University of Bonn and ETH Zurich have now ...
BU commentary: Including sexual and gender minority populations in medical research guarantees the health and well-being of all
2023-07-31
(Boston)—In the face of ongoing political threats to the rights and well-being of sexual and gender minority (SGM) populations, public health and health care institutions and practitioners must explicitly address the needs of marginalized populations while ensuring that those with multiple marginalized identities are well represented in research, according to a commentary in JAMA Network Open.
“If we continue to exclude SGM in research, we will remain oblivious to the troubles they face in achieving health and well-being,” said lead author Carl G. Streed, Jr., MD, MPH, FACP, ...
Luzio, who lived in São Paulo 10,000 years ago, was Amerindian like Indigenous people now, DNA reveals
2023-07-31
An article to be published on July 31 in Nature Ecology & Evolution reveals that Luzio, the oldest human skeleton found in São Paulo state (Brazil), was a descendant of the ancestral population that settled the Americas at least 16,000 years ago and gave rise to all present-day Indigenous peoples, such as the Tupi.
Based on the largest set of Brazilian archeological genomic data, the study reported in the article also offers an explanation for the disappearance of the oldest coastal communities, who built the icons of Brazilian archeology known as sambaquis, huge mounds of shells and fishbones used as dwellings, cemeteries and territorial boundaries. Archeologists often ...
Bees evolved from ancient supercontinent, diversified faster than suspected
2023-07-31
The first bees evolved on an ancient supercontinent more than 120 million years ago, diversifying faster and spreading wider than previously suspected, a new study shows.
Led by Washington State University researchers, the study provides a new best estimate for when and where bees first evolved. Newly published in the journal Current Biology, the project reconstructed the evolutionary history of bees, estimated their antiquity, and identified their likely geographical expansion around the world.
The results indicate their point of origin was in western Gondwana, an ancient supercontinent that at that time included today's continents of Africa and South America.
“There’s ...
New algorithm ensnares its first ‘potentially hazardous’ asteroid
2023-07-31
Link to Google Drive folder containing images, videos and caption/credit information:
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/19LP7UZbVKkTXSFds6DaKSy1lp014Hw4z?usp=sharing
Link to release:
https://www.washington.edu/news/2023/07/31/heliolinc3d/
FROM: James Urton
University of Washington
+1 206-543-2580
jurton@uw.edu
Ranpal Gill
Vera C. Rubin Observatory
+1 520-309-6195
rgill@lsst.org
Note: Researcher contact information at the end
For ...
Fascination of Science: 60 Encounters with Pioneering Researchers of Our Time
2023-07-31
What makes a brilliant scientist? Who are the people behind the greatest discoveries of our time? Connecting art and science, photographer Herlinde Koelbl seeks the answers in this English translation of the German book Fascination of Science, an indelible collection of portraits of and interviews with sixty pioneering scientists of the twenty-first century. Koelbl's approach is intimate and accessible, and her highly personal interviews with her subjects reveal the forces (as well as the personal quirks) that motivate the scientists' work; for example, one wakes up at 3 am because ...
Team identifies key driver of cancer cell death pathway that activates immune cells
2023-07-31
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Scientists have identified a protein that plays a pivotal role in the action of several emerging cancer therapies. The researchers say the discovery will likely aid efforts to fine-tune the use of immunotherapies against several challenging cancers. They report their findings in the journal Cancer Research.
“Most anticancer drugs cause cancer cells to shrivel up and die in a controlled process known as apoptosis. But apoptosis does not usually strongly activate immune cells,” said David Shapiro, a professor ...
Scrambler therapy may offer lasting relief for chronic pain, review paper suggests
2023-07-31
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
A new review paper co-authored by two Johns Hopkins pain experts suggests that scrambler therapy, a noninvasive pain treatment, can yield significant relief for approximately 80%–90% of patients with chronic pain, and it may be more effective than another noninvasive therapy: transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS). The write-up was published online July 13 in The New England Journal of Medicine.
Scrambler therapy, approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 2009, administers electrical stimulation through the skin via electrodes placed in areas of the body above and below where chronic pain is felt. The goal is to capture the nerve endings ...
Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai receives $11.5 million grant renewal to study the impact of psychosocial stress on cardiovascular disease
2023-07-31
New York, NY (July 31, 2023)—Psychosocial stress profoundly affects people’s lives globally, not least because it can be a critical risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Thanks to an $11.5 million award renewal from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) of the National Institutes of Health, distinguished researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and elsewhere aim to gain a deeper understanding of how stress influences cardiovascular health.
“To address residual cardiovascular risk in patients, our research program aims to bolster our mechanistic understanding ...
Way cool: UVA professor developing ‘freeze ray’ technology for the Air Force
2023-07-31
You know that freeze-ray gun that “Batman” villain Mr. Freeze uses to “ice” his enemies? A University of Virginia professor thinks he may have figured out how to make one in real life.
The discovery – which, unexpectedly, relies on heat-generating plasma – is not meant for weaponry, however. Mechanical and aerospace engineering professor Patrick Hopkins wants to create on-demand surface cooling for electronics inside spacecraft and high-altitude jets.
“That’s the primary problem right now,” Hopkins said. “A lot of electronics on board heat up, but they have no way to cool down.”
The U.S. Air Force likes the prospect of a freeze ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
Microbial clues uncover how wild songbirds respond to stress
Researchers develop AI tools for early detection of intimate partner violence
Researchers develop AI tool to predict patients at risk of intimate partner violence
New research outlines pathway to achieve high well-being and a safe climate without economic growth
How an alga makes the most of dim light
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
Inside the light: How invisible electric fields drive device luminescence
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
[Press-News.org] CABBI develops eco-friendly enzyme to create key chemical building blocksPhotoenzymatic system can efficiently synthesize chiral amines, solving a persistent challenge in chemistry and advancing biomanufacturing