(Press-News.org) Social media is a critical marketing tool to help raise awareness when firms launch new products. The platforms can help inform consumers about product characteristics and benefits relative to competitors’ products.
New research from the University of Notre Dame analyzes data from the motion picture industry, which often relies on social media promotion, in an effort to understand how marketers could better promote other new products.
“The Ripple Effect of Firm-Generated Content on New Movie Releases,” forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing Research from lead author Shijie Lu, the Howard J. and Geraldine F. Korth Associate Professor of Marketing at Notre Dame’s Mendoza College of Business, analyzes 145,502 firm-generated and 5.9 million user-generated Twitter posts associated with 159 movies.
Lu and co-authors Isaac Dinner from Indeed and Rajdeep Grewal from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill find a positive and significant ripple effect of firm-generated content (FGC) on movie sales. FGC increases user-generated content (UGC), which then drives movie consumption.
The conventional belief has been that social media allows marketers to influence the purchase behavior of their followers directly. However, the team’s findings show that the way FGC works in new product releases is indirectly — through the UGC or word of mouth spread by followers of firms’ social media accounts.
The team looked at Twitter posts about movies released by the top 20 U.S. studios between January 2014 and June 2015. The movies were associated with 486 unique Twitter handles, including 158 movie accounts, 310 actor and director accounts and 18 studio accounts. They conducted an econometric analysis to test the relationships between FGC, UGC and box office sales.
“Interestingly, even when multiple social media accounts from the movie’s actors, directors and studio are used to promote a new movie, the FGC from the main movie account is more effective than other firm-related accounts in driving sales,” Lu said. “But the UGC resulting from that main account sells even more. So, FGC from celebrity actors and directors who are active on social media does not improve box office performances nearly as much as UGC from the fans.”
Additionally, firms’ regular posts with a movie-specific hashtag are more effective than replies, retweets and posts without the hashtag.
“This suggests that movie executives should focus on creating FGC that sparks conversations among followers when new movies are released,” Lu said. “The Barbie movie’s recent retweet of a father who dressed in a Barbie costume when taking his daughter to watch the movie is a good example of getting followers to talk about the movie spontaneously.”
Although the study focused on movies, Lu said the findings can be generalized to other products, including TV shows, games, music and books.
Contact: Shijie Lu, 574-631-5883, slyu@nd.edu
END
Social media marketing most effective when it prompts consumers to start posting
2023-07-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study shows new stroke surgery eligibility criteria may dramatically increase lifesaving stroke surgery rates, with nationwide implications
2023-07-31
Study Shows New Stroke Surgery Eligibility Criteria May Dramatically Increase Lifesaving Stroke Surgery Rates, with Nationwide Implications
SAN DIEGO—A recent study presented today at the Society of NeuroInterventional Surgery’s (SNIS) 20th Annual Meeting noted that U.S. rates of endovascular thrombectomy, a lifesaving stroke treatment, are projected to increase dramatically based on new criteria.
In the study, endovascular thrombectomy was shown to improve clinical outcomes in patients with large ischemic strokes. This change has the ...
Lignin separation method could make renewable material profitable
2023-07-31
RICHLAND, Wash. – A novel method to extract lignin could help spin wheat straw into gold. Lignin produced using the new method was color-neutral, odorless and homogenous, an advance that could make this carbon-neutral material a more viable candidate for development of high-value products.
Reporting in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the Washington State University researchers extracted up to 93% lignin with up to 98% purity from wheat straw, producing a significant amount of material in a uniform way that could make ...
Hydrogen sulfide shows promise as healthy ageing therapeutic when specifically targeted within cells
2023-07-31
Future therapies to help people live healthy lives for longer could be developed from drugs that release tiny amounts of the gas hydrogen sulfide (H2S), new research has indicated.
A study from the University of Exeter, funded by the US Army and charity The United Mitochondrial Disease Foundation, found that targeting tiny amounts of H2S to specific areas of cells in adult worms using a H2S-releasing molecule called AP39, greatly improved health and activity as they aged. The research, published in PNAS, concludes that targeting ...
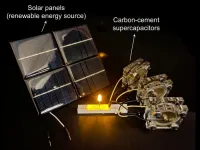
MIT engineers create an energy-storing supercapacitor from ancient materials
2023-07-31
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. -- Two of humanity's most ubiquitous historical materials, cement and carbon black (which resembles very fine charcoal), may form the basis for a novel, low-cost energy storage system, according to a new study. The technology could facilitate the use of renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and tidal power by allowing energy networks to remain stable despite fluctuations in renewable energy supply.
The two materials, the researchers found, can be combined with water to make a supercapacitor — an alternative to batteries — ...
How flies develop sight: Scientists use single-cell sequencing to identify cell types in the visual system
2023-07-31
New York University researchers have discovered new cell types in the visual system of flies, made possible by their creation of a tool that finds and labels neurons during development.
The study, published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), combines single-cell sequencing data with a novel algorithm to identify pairs of genes that point to previously unknown cells in the brains of fruit flies.
Fruit flies (also known as Drosophila) have long been used as a model organism to study fundamental ...
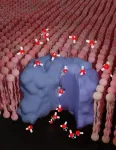
Study reveals long-debated makeup of the molecules that help organize your cells
2023-07-31
For years, we’ve known that a special kind of molecular assembly known as a “polyelectrolyte complex” helps your cells keep themselves organized. These complexes are very good at forming interfaces to keep two liquids separated: your cells use them to create compartments. These abilities have led scientists to consider them for technological applications, including filtering water, better batteries, and even underwater glue, as well as for better pharmaceutical drugs.
But for decades, no one knew exactly ...
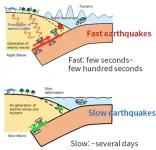
How to distinguish slow and fast earthquakes
2023-07-31
Researchers from the University of Tokyo and Stanford University show what differentiates slow and fast earthquakes and how their magnitudes vary with time.
Normally, earthquakes last up to a few minutes and radiate strong seismic waves. But around 23 years ago, scientists discovered an unusual slow-slip phenomena called slow earthquakes. Slow earthquakes last days or even months. Though they involve significant tectonic movement, you may never feel them. Since slow earthquakes could indicate future fast earthquakes, monitoring and ...
Research shows filter tip stent retrievers may allow neurointerventionalists to remove blood clots on the first try during stroke treatment
2023-07-31
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE: July 31, 2023, 12:00 P.M. PDT
CONTACT: Camille Jewell
cjewell@vancomm.com or 202-248-5460
Research Shows Filter Tip Stent Retrievers May Allow Neurointerventionalists to Remove Blood Clots on the First Try During Stroke Treatment
SAN DIEGO—Research presented today at the Society of NeuroInterventional Surgery’s (SNIS) 20th Annual Meeting shows that different types of stent retriever tips may result in improved patient outcomes when performing mechanical thrombectomy to treat stroke.
Ischemic stroke, one of the most common types of strokes, happens ...
Nuclear spin's impact on biological processes uncovered
2023-07-31
A research team led by Prof. Yossi Paltiel at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem with groups from HUJI, Weizmann and IST Austria new study reveals the influence of nuclear spin on biological processes. This discovery challenges long-held assumptions and opens up exciting possibilities for advancements in biotechnology and quantum biology.
Scientists have long believed that nuclear spin had no impact on biological processes. However, recent research has shown that certain isotopes behave differently due to their nuclear spin. The team focused on stable oxygen isotopes (16O, 17O, 18O) and found ...
Researchers use geospatial mapping to assist burn patients
2023-07-31
University of Texas at Dallas researchers are using geospatial mapping techniques to identify social and environmental obstacles in communities that might impede burn injury survivors’ reentry into society.
The project is designed to help patients with burn injuries better adapt to their lives after medical discharge, including improving patient access to transportation, employment, food and other necessities.
“Our study looks at how people who survive burn injuries reenter the community,” said Dr. Richard Scotch, program head of sociology and a professor of public policy and political economy in the School of ...