(Press-News.org) Oat is among the top ten cereal crop species in terms of global production. It can adapt to different climates, and farmers can grow it successfully even in harsh environments where other crops such as rice and corn fail. However, not all oat plants are the same. Based on their grains, two major oak varieties can easily be distinguished: hulled, grains that are covered in a non-edible husk, and naked, grains that have a soft outer casing that easily separates from the edible grain during threshing. To gain information on the origins of these different varieties, researchers in China have sequenced the genomes of over 100 oat plants from around the world. Their analyses indicate that, unlike what is the current belief — that the two varieties came from one domestication event, the hulled and naked oat were domesticated independently. The work is published in the Open Science journal GigaScience.
It is believed that the common oat (Avena sativa), which today is grown all over the world, was domesticated in Europe around 3,000 years ago. In contrast, the origins of naked oat, which today is grown mainly in China, remain unclear. Many researchers regard naked oat as a variant of hulled oat, speculating that a mutation occurred after hulled oat was introduced into China. However, new population genomic data generated and analyzed by the laboratory of Prof. Bing Han at Inner Mongolia Agricultural University (IMAU) tell a different story.
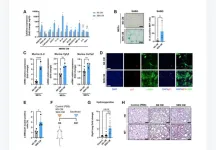
Rather than being a variant of common oat that separated relatively recently, the authors estimate that hulled oat and naked oat diverged around 51,000 years ago. They therefore speculate that the two varieties were domesticated independently a long time ago, rather than one being a recent derivative of the other. The analyses in the study include a set of whole genome sequences, including 89 naked oat and 22 hulled oat plants, as well as four other closely related hexaploid species from around the world.
Additional findings in this study arising from a deeper analysis of this large data set support this view. For example, if naked oat split recently from hulled oat, geneticists expected to see traces of a population bottleneck in the naked oat, which would have reduced the genetic diversity in the naked oat population. However, the scientists found the opposite: in their data, the genetic diversity of naked oat is higher than that of hulled oat, not the other way around.
The overall picture emerging from the data still remains rather complex, Prof. Bing Han explains: “The breeding of naked oat in China has gone through phases, including the direct collection and utilization of landraces, cross-breeding between naked oat varieties, and cross-breeding of naked oat with hulled oat.” All of this can increase the intricacy of the findings, leaving a great deal more to discover about the genetic history of naked oat.
The findings in this work demonstrate the power of large-scale genome sequencing to better understand the domestication history of one of the major crop species that is feeding the world today.
Further Reading:
Nan J; Ling Y; An J; Wang T; Chai M; Fu J; Wang G; Yang C; Yang Y; Han: B (2023): "Genome resequencing reveals independent domestication and breeding improvement of naked oat" GigaScience; https://doi.org/10.1093/gigascience/giad061
Article URL: https://academic.oup.com/gigascience/article-lookup/doi/10.1093/gigascience/giad061
Data Availability:
Nan J; Ling Y; An J; Wang T; Chai M; Fu J; Wang G; Yang C; Yang Y; Han: B (2023): Supporting data for "Genome resequencing reveals independent domestication and breeding improvement of naked oat" GigaScience Database. http://dx.doi.org/10.5524/102412
About GigaScience
GigaScience is co-published by GigaScience Press and Oxford University Press. Winner of the 2018 PROSE award for Innovation in Journal Publishing (Multidisciplinary), the journal covers research that uses or produces 'big data' from the full spectrum of the biological and biomedical sciences. It also serves as a forum for discussing the difficulties of and unique needs for handling large-scale data from all areas of the life and medical sciences. The journal has a completely novel publication format -- one that integrates manuscript publication with complete data hosting, and analyses tool incorporation. To encourage transparent reporting of scientific research as well as enable future access and analyses, it is a requirement of manuscript submission to GigaScience that all supporting data and source code be made available in the GigaScience database, GigaDB, as well as in publicly available repositories. GigaScience will provide users access to associated online tools and workflows, and has integrated a data analysis platform, maximizing the potential utility and re-use of data.
About GigaScience Press
GigaScience Press is BGI's Open Access Publishing division, which publishes scientific journals and data. Its publishing projects are carried out with international publishing partners and infrastructure providers, including Oxford University Press and River Valley Technologies. It currently publishes two award-winning data-centric journals: its premier journal GigaScience (launched in 2012), which won the 2018 American Publishers PROSE award for innovation in journal publishing, and its new journal GigaByte (launched 2020), which won the 2022 ALPSP Award for Innovation in Publishing. The press also publishes data, software, and other research objects via its GigaDB.org database. To encourage transparent reporting of scientific research and to enable future access and analyses, it is a requirement of manuscript submission to all GigaScience Press journals that all supporting data and source code be made openly available in GigaDB or in a community approved, publicly available repository.
END
Genome data rewrite the story of oat domestication in China
Genome analysis of 100 oat plants from around the world reveal that different oat varieties were developed in two different domestication events, challenging current plant research assumptions
2023-08-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Holding Trump accountable will not threaten American democracy
2023-08-01
With a Fulton County indictment of former President Donald Trump possible at any time, law enforcement in Atlanta is bracing for potential violence, with orange barricades restricting access to the entrance of the county courthouse.
With the anticipation of each new indictment has come threats of violence, decrease in trust in American justice and calls for retribution against the government. Just how concerned should Americans be that we may face another January 6th-type incident?
New data from the Polarization ...
Modifications to amino acids in sperm could be behind infertility
2023-07-31
Sperm play a critical role in the creation of new life, delivering essentially half of the genetic material required.
The success of this process relies on the generation of a developmentally competent sperm cell, which is often determined by shape. Indeed, during in vitro fertilization, the “best-looking” sperm is selected to fertilize an egg.
However, how this optimal shape translates to proper sperm function is difficult to assess because of many confounding factors.
Researchers at the University of Michigan are now delving into the molecular-level details of sperm formation, with a particular focus on how abnormalities in ...
Harnessing the power of light: Advancements in photonic memory for faster optical computing
2023-07-31
Technological advancements like autonomous driving and computer vision are driving a surge in demand for computational power. Optical computing, with its high throughput, energy efficiency, and low latency, has garnered considerable attention from academia and industry. However, current optical computing chips face limitations in power consumption and size, which hinders the scalability of optical computing networks.
Thanks to the rise of nonvolatile integrated photonics, optical computing devices can achieve in-memory computing while operating with zero static power consumption. Phase-change materials (PCMs) have emerged as promising candidates for achieving photonic memory and nonvolatile ...
Study raises possibility of immunotherapy treatment for ALS
2023-07-31
New research reveals a type of monoclonal antibody already tested in certain forms of cancer may be a promising treatment in stopping the progression of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, or ALS, a fatal neurodegenerative disease.
The study, led by scientists at Oregon Health & Science University, published today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The study, involving a mouse model and confirmed in the tissue of human brains affected by ALS and donated after death, revealed for the first time that modulating immune cells can slow the progression of the disease. Previous research suggested a role for immune cells in ALS, but researchers this time used a high-throughput ...
Multi-level international study explores anxiety, concerns of families with a child with a neurodevelopmental condition during the COVID-19 pandemic
2023-07-31
A peer-reviewed study published in the Journal of Global Health analyzed data from more than 6,600 families with a child with a neurodevelopmental condition (NDC)—autism, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, developmental language disorder, Down syndrome, Williams syndrome, and intellectual disability—from 70 countries, including the United States.
The study was led by Andrea Samson, associate professor of psychology at UniDistance Suisse and University of Fribourg, Switzerland, and Jo Van Herwegen, professor in developmental psychology and education at University College London’s ...
Human senescent fibroblasts cause lung fibrosis in mice
2023-07-31
“These observations support that accumulation of senescent cells may contribute to fibrotic lung disease [...]”
BUFFALO, NY- July 31, 2023 – A new research paper was published on the cover of Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 14, entitled, “Human senescent fibroblasts trigger progressive lung fibrosis in mice.”
Cell senescence has recently emerged as a potentially relevant pathogenic mechanism in fibrosing interstitial lung diseases (f-ILDs), particularly in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. In a new study, researchers Fernanda Hernandez-Gonzalez, ...
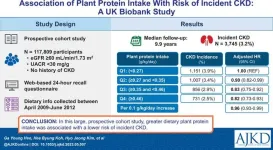
Plant-based protein intake may reduce kidney disease risk
2023-07-31
Plant-based diets confer various health benefits, including lowering the risk of cardiovascular disease and certain cancers. However, the relationship between plant protein intake and the risk of chronic kidney disease (CKD) remains unclear. This study led by Ga Young Heo aimed to investigate the association between plant protein intake and the development of CKD. Using the UK biobank study data, the researchers found that participants with a higher plant protein intake had a lower risk of developing CKD. This finding suggests that a higher dietary intake of plant-based protein may be beneficial for kidney health and provide insight into ...
Researchers identify two new subtypes of HPV-associated head and neck cancers
2023-07-31
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – Cases of human papillomavirus (HPV)-associated cancers of the head and neck, known as head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC), are rapidly increasing throughout the United States. Unfortunately, relatively little is known about the factors that contribute to these tumors and what makes some tumors more aggressive and treatment-resistant than others.
To determine why some patients respond better to radiation therapy than others, researchers in UNC School of Medicine’s Department of Otolaryngology/Head and Neck ...
Endocrine Society and Matchbox Virtual Media announce joint venture
2023-07-31
WASHINGTON—The Endocrine Society and Matchbox Virtual Media are pleased to announce today that the organizations formed a joint venture that will bring exciting new opportunities for medical, healthcare, and scientific associations to better customize the experiences of their customers relative to producing meetings, organizing communities, and disseminating educational products.
The new joint venture will benefit from the Endocrine Society’s initial financial investments and its robust networking within the medical and scientific fields. Matchbox Virtual Media brings its proven platform, technologies, ...
Scientist who expands chemists’ tools joins The Wertheim UF Scripps Institute
2023-07-31
JUPITER, Fla. — A new scientist joining The Herbert Wertheim UF Scripps Institute for Biomedical Innovation & Technology invents creative and efficient ways to build complex, potentially useful molecules, studying their activity so that compounds found in nature may eventually become useful products, such as medications.
Synthetic chemist and associate professor Masayuki Wasa, Ph.D., joins the institute from Boston College, where he was an assistant professor of chemistry. Synthetic chemists specialize in assembling larger molecules from smaller parts, like a child assembling a Lego spaceship from a basket of oddly shaped pieces.
But the work is far from child’s ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Public and patient involvement in research is a balancing act of power
Scientists discover “bacterial constipation,” a new disease caused by gut-drying bacteria
DGIST identifies “magic blueprint” for converting carbon dioxide into resources through atom-level catalyst design
COVID-19 vaccination during pregnancy may help prevent preeclampsia
Menopausal hormone therapy not linked to increased risk of death
Chronic shortage of family doctors in England, reveals BMJ analysis
Booster jabs reduce the risks of COVID-19 deaths, study finds
Screening increases survival rate for stage IV breast cancer by 60%
ACC announces inaugural fellow for the Thad and Gerry Waites Rural Cardiovascular Research Fellowship
University of Oklahoma researchers develop durable hybrid materials for faster radiation detection
Medicaid disenrollment spikes at age 19, study finds
Turning agricultural waste into advanced materials: Review highlights how torrefaction could power a sustainable carbon future
New study warns emerging pollutants in livestock and aquaculture waste may threaten ecosystems and public health
Integrated rice–aquatic farming systems may hold the key to smarter nitrogen use and lower agricultural emissions
Hope for global banana farming in genetic discovery
Mirror image pheromones help beetles swipe right
Prenatal lead exposure related to worse cognitive function in adults
Research alert: Understanding substance use across the full spectrum of sexual identity
Pekingese, Shih Tzu and Staffordshire Bull Terrier among twelve dog breeds at risk of serious breathing condition
Selected dog breeds with most breathing trouble identified in new study
Interplay of class and gender may influence social judgments differently between cultures
Pollen counts can be predicted by machine learning models using meteorological data with more than 80% accuracy even a week ahead, for both grass and birch tree pollen, which could be key in effective
Rewriting our understanding of early hominin dispersal to Eurasia
Rising simultaneous wildfire risk compromises international firefighting efforts
Honey bee "dance floors" can be accurately located with a new method, mapping where in the hive forager bees perform waggle dances to signal the location of pollen and nectar for their nestmates
Exercise and nutritional drinks can reduce the need for care in dementia
Michelson Medical Research Foundation awards $750,000 to rising immunology leaders
SfN announces Early Career Policy Ambassadors Class of 2026
Spiritual practices strongly associated with reduced risk for hazardous alcohol and drug use
Novel vaccine protects against C. diff disease and recurrence
[Press-News.org] Genome data rewrite the story of oat domestication in ChinaGenome analysis of 100 oat plants from around the world reveal that different oat varieties were developed in two different domestication events, challenging current plant research assumptions