New insights into heterotopic ossification: Progenitor cells play a key role in aberrant bone formation
2023-08-01
(Press-News.org)
In a new study published on 21 July 2023 by the journal Bone Research, a team of researchers from Johns Hopkins University, using a combination of lineage tracing and single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq), delved into the contribution of synovial/tendon sheath progenitor cells to heterotopic bone formation. The researchers identified a distinct population of Tppp3+ tendon progenitor cells that actively participated in the formation of ectopic bone in vivo. Their findings provide new insights into the intricate cellular processes driving heterotopic ossification and offer potential therapeutic targets to prevent and treat this pathological condition.
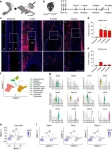
The study revealed that Tppp3+ progenitor cells, primarily located in the tendon sheath, rapidly expanded in response to HO induction, significantly contributing to the formation of heterotopic cartilage and bone in both tendon and joint-associated HO. Transcriptomic analysis indicated that Tppp3+ cells possess primitive progenitor properties and may regulate HO formation by releasing soluble molecules that promote osteogenic differentiation. Under normal conditions, Tppp3-tdT+ cells were mainly localized in the tendon sheath with minimal activity in the tendon body. However, upon HO induction, their numbers rapidly increased at the injury site. Tppp3 was predominantly expressed in mesenchymal cells, indicating a progenitor cell phenotype. Furthermore, scRNA-seq analysis revealed Tppp3 as an early progenitor cell marker for either tendon or osteochondral cells, offering insights into the dynamic behavior of Tppp3+ progenitor cells during injury. These cells were found to contribute significantly to heterotopic cartilage formation during the endochondral ossification phase, with around one-fifth of cartilage cells derived from Tppp3+ progenitors. Additionally, Tppp3+ cells played a crucial role in the osseous phase of heterotopic ossification in the Achilles tendon, contributing to the osteoblastic lineage at 9 weeks after injury. Notably, they also participated in tendon remodeling and the formation of a tendon-like matrix during the repair process. In the hip postarthroplasty HO model, Tppp3+ cells contributed to the formation of heterotopic cartilage in the synovium and expanded in the synovium and periosteum, acquiring an osteoprogenitor phenotype and contributing to ectopic bone formation. The presence and contribution of Tppp3+ cells in human pathological samples were confirmed, highlighting the relevance of these findings to human cases of HO.
The research contributes significantly to the field of regenerative medicine and sheds light on the regulatory role of Tppp3+ progenitor cells in HO formation and provides valuable insights for potential therapeutic strategies to target this pathological process. The identification of this newly defined population of tendon progenitors that contribute to ectopic bone formation may pave the way for the development of novel therapeutic approaches to prevent and treat HO.
###
References
Funding information
The NIH/NIAMS (R01 AR070773, R01 AR068316, R01 DE031028, R21 AR078919);
The Peer Reviewed Medical Research Program (W81XWH-18-1-0121, W81XWH-18-1-0336);
The Peer Reviewed Orthopaedic Research Program (W81XWH-20-10795);
Broad Agency Announcement (W81XWH-18-10613);
The American Cancer Society (Research Scholar Grant, RSG-18-027-01-CSM);
The Maryland Stem Cell Research Foundation;
The NIH (R01AR079171, R01 AR078324, and R01 AR071379).
DOI
10.1038/s41413-023-00272-x
About Bone Research
Bone Research was founded in 2013. As an open access English-language periodical, Bone Research focuses on basic and clinical aspects of bone biology, pathophysiology and regeneration, and supports the foremost discoveries resulting from basic investigations and clinical research related to bone. The aim of the Journal is to foster the worldwide dissemination of research in bone-related physiology, pathology, diseases and treatment.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-08-01
It’s easy to imagine that growing up in a neighborhood with safe and clean parks, little to no discrimination, and where people are not struggling financially makes for a lower-stress childhood. In contrast, neighborhoods with few community spaces, violence, and poverty create a higher-stress environment for a child to live in. Unfortunately, systemic and structural issues such as wealth inequality, residential segregation, barriers to home ownership, and environmental injustice in neighborhoods where Black American adolescents disproportionately reside make ...
2023-08-01
A type of soil called terra preta da Amazônia, or Amazon dark earth (ADE), promotes faster growth of trees and enhances their development in qualitative terms, according to an article published in the journal Frontiers in Soil Science.
The findings reported in the article resulted from studies supported by FAPESP (projects 20/08927-0, 18/19000-4 and 14/50320-4) under the aegis of its Biodiversity, Characterization, Conservation, Restoration and Sustainable Use Program (BIOTA).
“ADE is rich in nutrients and supports communities of microorganisms that help plants grow, among other things. Native people of the Amazon have ...
2023-08-01
Irvine, Calif., Aug. 1, 2023 — When a fragrance wafted through the bedrooms of older adults for two hours every night for six months, memories skyrocketed. Participants in this study by University of California, Irvine neuroscientists reaped a 226% increase in cognitive capacity compared to the control group. The researchers say the finding transforms the long-known tie between smell and memory into an easy, non-invasive technique for strengthening memory and potentially deterring dementia.
The team’s study appears in Frontiers in Neuroscience. ...
2023-08-01
Almost half of patients who experienced a stroke in the right cerebral hemisphere later develop a very unusual symptom: they lose the ability to perceive what is happening in the left side of space. As a result, they tend to eat only the right side of their plate, ignore people on their left, and have great difficulty finding their way around. This disorder, known as hemispatial neglect, does not involve basic visual abilities, which remain intact.
“These patients see very well. The problem ...
2023-08-01
PHILADELPHIA—A Penn Medicine and Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) team will seek to develop treatments for three rare, incurable genetic diseases with the help of a $26 million grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
The research will focus on three genetic diseases that impact newborns in the first weeks and months after birth: Phenylketonuria (PKU), hereditary tyrosinemia type 1 (HT1), and mucopolysaccharidosis type 1 (MPSI), commonly known as Hurler’s Syndrome. PKU causes an amino acid—called phenylalanine—to build up in the body, and as long as treatment begins at birth, PKU is ...
2023-08-01
False claims and disinformation, especially in a social media-driven society, have become major problems with potentially severe consequences. Kash Barker, Ph.D., principal investigator and the Anadarko Presidential Professor in the School of Industrial and Systems Engineering, Gallogly College of Engineering at the University of Oklahoma, is leading a team of researchers examining indirect attacks targeting infrastructure systems via unwitting users, supported by a $599,947 grant from the National Science Foundation's Secure ...
2023-08-01
Despite this prevailing negative sentiment, results showed the public generally think the most suitable punishment for disruptive, non-violent protesters is a fine or lesser penalty than imprisonment.
The research, led by the University of Bristol, suggests public opinion may not be supportive of the Government’s recent legislative changes, through The Public Order Act 2023, which introduce harsher sentences for disruptive protesters.
The online poll, conducted by YouGov this month, surveyed 2,069 adults of all political viewpoints across Britain. ...
2023-08-01
HAMILTON, ON, Aug. 1, 2023 – Based on decades of work to uncover the underlying mechanisms of asthma and other respiratory conditions, researchers at McMaster University and St. Joseph’s Healthcare Hamilton have produced a simple, rapid test that can identify the presence of a key driver of severe asthma.
John Brennan, director of McMaster’s Biointerfaces Institute, and Parameswaran Nair, a respirologist at the St. Joseph’s-based Firestone Institute for Respiratory Health, led the creation of a new rapid test that can quickly and accurately identify white blood cells known as eosinophils, even when they are present in complex biological samples ...
2023-08-01
WASHINGTON, Aug. 1, 2023 – Since ancient times, gemstones have been mined and traded across the globe, sometimes traveling continents from their origin. Gems are geologically defined as minerals celebrated for beauty, strength, and rarity. Their unique elemental composition and atomic orientation act as a fingerprint, enabling researchers to uncover the stones’ past, and with it, historical trade routes.
In AIP Advances, from AIP Publishing, Khedr et al. employed three modern spectroscopic techniques to rapidly analyze gems found in the Arabian-Nubian Shield and compare them with similar gems from around the world. Using ...
2023-08-01
Birds can be electrocuted if they come into contact with two energized parts of a power line at once—which can happen when they spread their wings to take off from or land on a power pole. Because of this, energy companies invest substantial time and money into making sure power lines are avian safe, installing safe perches and insulating energized elements. However, a recent study published on August 1 in the journal iScience presents a new priority for conservation, as it suggests that electrocution is no longer the only leading cause of death for ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New insights into heterotopic ossification: Progenitor cells play a key role in aberrant bone formation