(Press-News.org) False claims and disinformation, especially in a social media-driven society, have become major problems with potentially severe consequences. Kash Barker, Ph.D., principal investigator and the Anadarko Presidential Professor in the School of Industrial and Systems Engineering, Gallogly College of Engineering at the University of Oklahoma, is leading a team of researchers examining indirect attacks targeting infrastructure systems via unwitting users, supported by a $599,947 grant from the National Science Foundation's Secure and Trustworthy Cyberspace program.
"We’ve seen an increase in the number of incidents of false claims in recent years, and studies suggest that a majority of online users tend to be initially fooled by fake news,” Barker said. “A potentially over-the-horizon problem could occur when these incidents are weaponized by an adversary against America’s infrastructure networks.”
Disinformation can be weaponized to disrupt underlying cyber-physical systems, human lives and economic productivity. Recent examples include tweets that trigger spikes in gasoline prices and false social media posts reporting impending water pumping station shutdowns due to cold temperatures. In these scenarios, chaos is caused because people, not systems or devices, are “hacked.”
"Certain utility companies are now using demand response management systems that allow consumers to play a role in the operation of the electric grid by shifting or reducing their usage,” Barker said. “You can imagine a situation where an adversary sends out information claiming that the electric company is giving away free power during the hottest hours of the day and enticing customers to use as much power as they’d like. This would likely overload the grid’s capacity and cause major problems.”
To combat these weaponized false claims, the researchers will examine the information layer – social media platforms, individual user interactions, etc., and the physical layer – utilities, transportation networks, and other critical infrastructure. Both layers are intrinsically linked but are also separately vulnerable to potential attacks.
“We can imagine a weaponized false claim attack through the information layer that causes humans to respond in a way that adversely alters the performance of the physical layer,” Barker said. “To combat these attacks and ensure secure cyber-physical systems, we must be able to offer a plan for integrating our research with the educational mission at our universities.”
Barker’s team will work with industry partners throughout this project to bring real-world insights into the research and disseminate findings. Additionally, they anticipate providing outreach activities for undergraduate and graduate students pursuing cyber-physical systems education and research. They are also planning educational offerings for the broader community.
Barker and his co-principal investigators, Andrés González, Ph.D., an assistant professor in the School of Industrial and Systems Engineering, Elena Bessarabova, Ph.D., an associate professor of communication in the Dodge Family College of Arts and Sciences, and Sridhar Radhakrishnan, Ph.D., a professor and the interim associate dean for partnerships for the Gallogly College of Engineering, received a supply chain research seed grant in 2022 for their project, “Securing Critical Networks from Weaponized Disinformation Attacks: Initial Surveys;” a precursor to this NSF-awarded research. John Jiang, Ph.D., a professor and the OG&E Endowed Chair Professor in the School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, while not involved in the seed grant, is also assisting on the NSF project, as are collaborators from Rutgers University, Stevens Institute of Technology, and Washington University in St. Louis.
Learn more about the project,” SaTC: CORE: Small: Socio-Technical Approaches for Securing Cyber-Physical Systems from False Claim Attacks Managing,” and Barker’s research by visiting the Risk-Based Systems Analytics Laboratory.
END
False claims attacks on infrastructure focus of NSF-funded research
2023-08-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New survey reveals British public generally think disruptive, non-violent protesters should not be imprisoned
2023-08-01
Despite this prevailing negative sentiment, results showed the public generally think the most suitable punishment for disruptive, non-violent protesters is a fine or lesser penalty than imprisonment.
The research, led by the University of Bristol, suggests public opinion may not be supportive of the Government’s recent legislative changes, through The Public Order Act 2023, which introduce harsher sentences for disruptive protesters.
The online poll, conducted by YouGov this month, surveyed 2,069 adults of all political viewpoints across Britain. ...
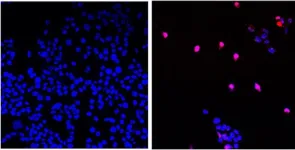
While resolving a key asthma challenge, Hamilton researchers also create a new method to detect proteins in body fluids and other materials
2023-08-01
HAMILTON, ON, Aug. 1, 2023 – Based on decades of work to uncover the underlying mechanisms of asthma and other respiratory conditions, researchers at McMaster University and St. Joseph’s Healthcare Hamilton have produced a simple, rapid test that can identify the presence of a key driver of severe asthma.
John Brennan, director of McMaster’s Biointerfaces Institute, and Parameswaran Nair, a respirologist at the St. Joseph’s-based Firestone Institute for Respiratory Health, led the creation of a new rapid test that can quickly and accurately identify white blood cells known as eosinophils, even when they are present in complex biological samples ...
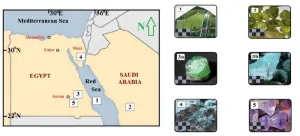
Using gemstones’ unique characteristics to uncover ancient trade routes
2023-08-01
WASHINGTON, Aug. 1, 2023 – Since ancient times, gemstones have been mined and traded across the globe, sometimes traveling continents from their origin. Gems are geologically defined as minerals celebrated for beauty, strength, and rarity. Their unique elemental composition and atomic orientation act as a fingerprint, enabling researchers to uncover the stones’ past, and with it, historical trade routes.
In AIP Advances, from AIP Publishing, Khedr et al. employed three modern spectroscopic techniques to rapidly analyze gems found in the Arabian-Nubian Shield and compare them with similar gems from around the world. Using ...
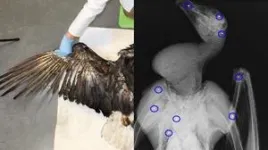
Illegal shooting kills most birds found dead near power lines
2023-08-01
Birds can be electrocuted if they come into contact with two energized parts of a power line at once—which can happen when they spread their wings to take off from or land on a power pole. Because of this, energy companies invest substantial time and money into making sure power lines are avian safe, installing safe perches and insulating energized elements. However, a recent study published on August 1 in the journal iScience presents a new priority for conservation, as it suggests that electrocution is no longer the only leading cause of death for ...
Male moth ‘aphrodisiac’ revealed
2023-08-01
Media contacts:
Coby Schal, coby@ncsu.edu
Mick Kulikowski, News Services, 919.218.5937 or mick_kulikowski@ncsu.edu
Aug 1, 2023
Male Moth ‘Aphrodisiac’ Revealed
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 11 A.M. EDT ON TUESDAY, AUG.1
North Carolina State University researchers have identified the specific blend of pheromone chemicals – including a newly revealed aphrodisiac – used by male moths during courtship as they attempt to entice females to mate. The findings provide more detail ...
USPSTF recommendation statement on folic acid supplementation to prevent neural tube defects
2023-08-01
Bottom Line: The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends that all persons planning to or who could become pregnant take a daily supplement containing 0.4 to 0.8 mg (400 to 800 μg) of folic acid. Neural tube defects are among the most common congenital malformations in the U.S., with an estimated 3,000 pregnancies affected each year. Many of these neural tube defects are caused by low folate levels in the body. The USPSTF routinely makes recommendations about the effectiveness ...
Race and treatment outcomes in patients with metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer
2023-08-01
About The Study: The results of this study suggest that providing fair and equal access to health care may reduce the disparities in treatment outcomes between Black and white patients with advanced prostate cancer.
Authors: Neeraj Agarwal, M.D., of the University of Utah in Salt Lake City, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.26546)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, ...
Effect of exercise on chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy among patients treated for ovarian cancer
2023-08-01
About The Study: The findings of this secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial suggest that exercise is a promising treatment for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) and incorporating exercise program referrals into the standard oncology care may reduce CIPN symptoms and increase quality of life for survivors of ovarian cancer.
Authors: Anlan Cao, M.B.B.S., of the Yale School of Public Health in New Haven, Connecticut, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.26463)
Editor’s ...
City of Hope scientists develop targeted chemotherapy able to kill all solid tumors in preclinical research
2023-08-01
LOS ANGELES — Researchers at City of Hope, one of the largest cancer research and treatment organizations in the United States, today published a new study explaining how they took a protein once thought to be too challenging for targeted therapy, proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), and developed a targeted chemotherapy that appears to annihilate all solid tumors in preclinical research. As the scientists continue to investigate the foundational mechanisms that make this cancer-stopping pill work in animal models, they note that ...
Millions of long-term smokers have lung disease that defies diagnosis
2023-08-01
Millions of Americans with tobacco-related lung disease have symptoms that do not fit any existing tobacco-related disease criteria – including the most common of those, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) – according to a new study led by researchers at UC San Francisco.
In a study publishing Aug. 1, 2023, in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA), the research team found that half of the participants with extensive tobacco exposure had a persistently high level of respiratory symptoms, including shortness of breath, daily cough and ...