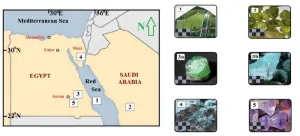
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, Aug. 1, 2023 – Since ancient times, gemstones have been mined and traded across the globe, sometimes traveling continents from their origin. Gems are geologically defined as minerals celebrated for beauty, strength, and rarity. Their unique elemental composition and atomic orientation act as a fingerprint, enabling researchers to uncover the stones’ past, and with it, historical trade routes.
In AIP Advances, from AIP Publishing, Khedr et al. employed three modern spectroscopic techniques to rapidly analyze gems found in the Arabian-Nubian Shield and compare them with similar gems from around the world. Using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, and Raman spectroscopy, the authors identified elements that influence gems’ color, differentiated stones found within and outside the region, and distinguished natural from synthetic.
The Arabian-Nubian Shield is an exposure of mineral deposits that sandwiches the Red Sea in current-day Egypt and Saudi Arabia. The deposits date back to the Earth’s earliest geological age, and the precious metals and gemstones have been harvested for thousands of years.
“We showed the main spectroscopic characteristics of gemstones from these Middle East localities to distinguish them from their counterparts in other world localities,” said author Adel Surour. “This includes a variety of silicate gems such as emerald from the ancient Cleopatra’s mines in Egypt, in addition to amethyst, peridot, and amazonite from other historical sites, which mostly date to the Roman times.”
The various spectroscopic techniques they employed revealed different information about the stones. LIBS quickly characterizes chemical composition, while FTIR determines functional groups connected to the structure and indicates the presence of water and other hydrocarbons. Even for chemically identical materials, Raman spectroscopy shows the unique crystalline structure of the gems’ atoms.
The authors identified that iron content correlates to amethysts’ signature purple hue, and other elements such as copper, chromium, and vanadium are also responsible for colorization. A signature water peak exposes lab-grown synthetic gems, which are useful for scientific purposes and identical to natural gems but are less expensive.
Crystalline structure differentiated amazonite beads from Mexico, Jordan, and Egypt.
“Gemstones such as emerald and peridot have been mined since antiquity,” Surour said. “Sometimes, some gemstones were brought by sailors and traders to their homelands. For example, royal crowns in Europe are decorated with peculiar gemstones that originate from either Africa or Asia. We need to have precise methods to distinguish the source of a gemstone and trace ancient trade routes in order to have correct information about the original place from which it was mined.”
###
The article “Characterization and discrimination of some gem silicate minerals adopting LIBS, FTIR and Raman spectroscopic techniques” is authored by Amal Abdelfattah Khedr, Adel A. Surour, Ahmed El-Hussein, and Mahmoud Abdelhamid. The article will appear in AIP Advances on Aug. 1, 2023 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0157623). After that date, it can be accessed at https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0157623.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
AIP Advances is an open access journal publishing in all areas of physical sciences—applied, theoretical, and experimental. The inclusive scope of AIP Advances makes it an essential outlet for scientists across the physical sciences. See https://pubs.aip.org/aip/adv.
###
END
Using gemstones’ unique characteristics to uncover ancient trade routes
Modern spectroscopy techniques can rapidly identify gemstone origins, distinguish natural from synthetic, and isolate elements that contribute to their quality
2023-08-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
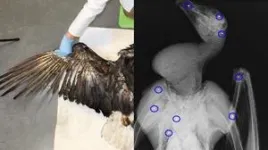
Illegal shooting kills most birds found dead near power lines
2023-08-01
Birds can be electrocuted if they come into contact with two energized parts of a power line at once—which can happen when they spread their wings to take off from or land on a power pole. Because of this, energy companies invest substantial time and money into making sure power lines are avian safe, installing safe perches and insulating energized elements. However, a recent study published on August 1 in the journal iScience presents a new priority for conservation, as it suggests that electrocution is no longer the only leading cause of death for ...
Male moth ‘aphrodisiac’ revealed
2023-08-01
Media contacts:
Coby Schal, coby@ncsu.edu
Mick Kulikowski, News Services, 919.218.5937 or mick_kulikowski@ncsu.edu
Aug 1, 2023
Male Moth ‘Aphrodisiac’ Revealed
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 11 A.M. EDT ON TUESDAY, AUG.1
North Carolina State University researchers have identified the specific blend of pheromone chemicals – including a newly revealed aphrodisiac – used by male moths during courtship as they attempt to entice females to mate. The findings provide more detail ...
USPSTF recommendation statement on folic acid supplementation to prevent neural tube defects
2023-08-01
Bottom Line: The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends that all persons planning to or who could become pregnant take a daily supplement containing 0.4 to 0.8 mg (400 to 800 μg) of folic acid. Neural tube defects are among the most common congenital malformations in the U.S., with an estimated 3,000 pregnancies affected each year. Many of these neural tube defects are caused by low folate levels in the body. The USPSTF routinely makes recommendations about the effectiveness ...
Race and treatment outcomes in patients with metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer
2023-08-01
About The Study: The results of this study suggest that providing fair and equal access to health care may reduce the disparities in treatment outcomes between Black and white patients with advanced prostate cancer.
Authors: Neeraj Agarwal, M.D., of the University of Utah in Salt Lake City, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.26546)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, ...
Effect of exercise on chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy among patients treated for ovarian cancer
2023-08-01
About The Study: The findings of this secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial suggest that exercise is a promising treatment for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) and incorporating exercise program referrals into the standard oncology care may reduce CIPN symptoms and increase quality of life for survivors of ovarian cancer.
Authors: Anlan Cao, M.B.B.S., of the Yale School of Public Health in New Haven, Connecticut, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.26463)
Editor’s ...
City of Hope scientists develop targeted chemotherapy able to kill all solid tumors in preclinical research
2023-08-01
LOS ANGELES — Researchers at City of Hope, one of the largest cancer research and treatment organizations in the United States, today published a new study explaining how they took a protein once thought to be too challenging for targeted therapy, proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), and developed a targeted chemotherapy that appears to annihilate all solid tumors in preclinical research. As the scientists continue to investigate the foundational mechanisms that make this cancer-stopping pill work in animal models, they note that ...
Millions of long-term smokers have lung disease that defies diagnosis
2023-08-01
Millions of Americans with tobacco-related lung disease have symptoms that do not fit any existing tobacco-related disease criteria – including the most common of those, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) – according to a new study led by researchers at UC San Francisco.
In a study publishing Aug. 1, 2023, in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA), the research team found that half of the participants with extensive tobacco exposure had a persistently high level of respiratory symptoms, including shortness of breath, daily cough and ...
Research team identifies human odorant receptor for horse stable odor
2023-08-01
Para-cresol is an aromatic compound with a strong horse stable-like odor. It contributes to the off-flavor of some foods, but it is also detectable as a characteristic odorant in whiskey and tobacco, as well as in the urine of various mammals. A research team led by the Leibniz Institute of Food Systems Biology at the Technical University of Munich has now discovered which odorant receptor humans use to perceive para-cresol.
Para-cresol (4-methylphenol) is formed during the microbial degradation of certain amino acids, but also during thermal ...
A natural experiment provides evidence of link between air pollution and childhood obesity
2023-08-01
A large natural experiment in Catalonia shows that moving to areas with higher levels of air pollution is associated with weight gain in young children. The study, led by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), an institution supported by ”la Caixa Foundation”, in collaboration with the IDIAP Jordi Gol, provides further evidence to support efforts to reduce air pollution.
Overweight and obesity in childhood result from the interaction of genes, lifestyle behaviours, physiological and social factors. Environmental exposures such as air pollution may ...
Cracking in lithium-ion batteries speeds up electric vehicle charging
2023-08-01
Aug. 1, 2023
Contact: Derek Smith, 734-546-3632, smitdere@umich.edu
Katherine McAlpine, 734-647-7087, kmca@umich.edu
Images
Cracking in lithium-ion batteries speeds up electric vehicle charging
Cracks in predominant lithium-ion electrodes shorten battery lifespans, but a neuroscience-inspired technique shows that they have an upside
ANN ARBOR—Rather than being solely detrimental, cracks in the positive electrode of lithium-ion batteries reduce battery charge time, research done at the University of Michigan shows.
This runs counter to the view of many ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Plants pause, play and fast forward growth depending on types of climate stress
University of Minnesota scientists reveal how deadly Marburg virus enters human cells, identify therapeutic vulnerability
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
The gut can drive age-associated memory loss
Enhancing gut-brain communication reversed cognitive decline, improved memory formation in aging mice
Mothers exposure to microbes protect their newborn babies against infection
How one flu virus can hamper the immune response to another
Researchers uncover distinct tumor “neighborhoods”, with each cell subtype playing a specific role, in aggressive childhood brain cancer
Researchers develop new way to safely insert gene-sized DNA into the genome
Astronomers capture birth of a magnetar, confirming link to some of universe’s brightest exploding stars
New photonic device, developed by MIT researchers, efficiently beams light into free space
UCSB researcher bridges the worlds of general relativity and supernova astrophysics
Global exchange of knowledge and technology to significantly advance reef restoration efforts
Vision sensing for intelligent driving: technical challenges and innovative solutions
To attempt world record, researchers will use their finding that prep phase is most vital to accurate three-point shooting
AI is homogenizing human expression and thought, computer scientists and psychologists say
Severe COVID-19, flu facilitate lung cancer months or years later, new research shows
Housing displacement, employment disruption, and mental health after the 2023 Maui wildfires
GLP-1 receptor agonist use and survival among patients with type 2 diabetes and brain metastases
Solid but fluid: New materials reconfigure their entire crystal structure in response to humidity
New research reveals how development and sex shape the brain
New discovery may improve kidney disease diagnosis in black patients
What changes happen in the aging brain?
Pew awards fellowships to seven scientists advancing marine conservation
Turning cancer’s protein machinery against itself to boost immunity
Current Pharmaceutical Analysis releases Volume 22, Issue 2 with open access research
Researchers capture thermal fluctuations in polymer segments for the first time
16-year study finds major health burden in single‑ventricle heart
Disposable vapes ban could lead young adults to switch to cigarettes, study finds
[Press-News.org] Using gemstones’ unique characteristics to uncover ancient trade routesModern spectroscopy techniques can rapidly identify gemstone origins, distinguish natural from synthetic, and isolate elements that contribute to their quality