(Press-News.org) Just as bacteria can develop antibiotic resistance, viruses can also evade drug treatments. Developing therapies against these microbes is difficult because viruses often mutate or hide themselves within cells. But by mimicking the way the immune system naturally deals with invaders, researchers reporting in ACS Infectious Diseases have developed a “peptoid” antiviral therapy that effectively inactivates three viruses in lab tests. The approach disrupts the microbes by targeting certain lipids in their membranes.
Viruses are almost like biological “zombies.” They are not quite living or nonliving, and are only able to multiply within a host, such as our body’s cells. Oftentimes, the immune system naturally destroys the pathogens with special molecules such as antibodies.
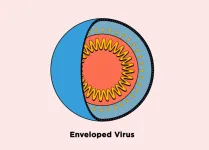
Less-well-known members of the immune system’s defense force are small protein-like molecules called antimicrobial peptides. These peptides aren’t good drug candidates, though, as they’re expensive to make, are quickly eliminated from the body and can cause side effects. Instead, some researchers have mimicked their function with lab-made molecules called peptoids that aren’t easily degraded by the body and are more economical to produce. Previously, Annelise Barron’s team showed that certain peptoids could pierce and destroy the SARS-CoV-2 and herpes viruses. This time, joined by Kent Kirshenbaum and colleagues, the group wanted to see if the peptoids could inactivate three other “enveloped” viruses enclosed within membranes — Zika, Rift Valley fever and chikungunya virus — as well as one that lacks a membrane envelope, coxsackie B3. No treatments currently exist for infections caused by these microbes.
The peptoids used in these experiments included three of the linear peptoids previously studied by Barron’s team, as well as four new circularized versions with increased antiviral activity. The researchers created model virus membranes using common lipids, including phosphatidylserine (PS). Membranes were disrupted most effectively when PS was present in higher concentrations, suggesting that the peptoids target it specifically. Though both human and viral membranes contain the lipid, it’s distributed differently in each instance, allowing an antiviral to preferentially attack the invader instead of the host. Next, the team incubated the peptoids with whole, infectious virus particles. Again, each worked to a different extent on the three enveloped viruses: some disrupted all three, some only one. However, none of the peptoids could inactivate the non-enveloped coxsackie B3 virus, showing that the mechanism of action hinges on the presence of the viral envelope. The team says that understanding this mechanism could inform the design of future peptoid-based antiviral treatments, and could be used to create drugs already armed against the next emerging viral threat.
The authors acknowledge funding from the National Science Foundation, the National Institutes of Health, Stanford University’s Discovery Innovation Fund, the Cisco University Research Program Fund, the Silicon Valley Community Foundation, and Dr. James Truchard and the Truchard Foundation. Kirshenbaum is the Chief Scientific Officer for and has material financial interests in Maxwell Biosciences, which is working to commercialize peptoid oligomers as anti-infective agents.
The paper’s abstract will be available on Aug. 2 at 8 a.m. Eastern time here: http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acsinfecdis.3c00063
For more of the latest research news, register for our upcoming meeting, ACS Fall 2023. Journalists and public information officers are encouraged to apply for complimentary press registration by completing this form.
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and all its people. The Society is a global leader in promoting excellence in science education and providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a leader in scientific information solutions, its CAS division partners with global innovators to accelerate breakthroughs by curating, connecting and analyzing the world’s scientific knowledge. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Follow us: Twitter | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram
END
Mimicking the body’s own defenses to destroy enveloped viruses
2023-08-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Novel molecules fight viruses by bursting their bubble-like membranes
2023-08-02
Antiviral therapies are notoriously difficult to develop, as viruses can quickly mutate to become resistant to drugs. But what if a new generation of antivirals ignores the fast-mutating proteins on the surface of viruses and instead disrupts their protective layers?
“We found an Achilles heel of many viruses: their bubble-like membranes. Exploiting this vulnerability and disrupting the membrane is a promising mechanism of action for developing new antivirals,” said Kent Kirshenbaum, professor of chemistry at NYU and the study’s senior author.
In a new study ...
More than 2,600 health care organizations recognized for commitment to high-quality cardiovascular care
2023-08-02
DALLAS, August 2, 2023 — The American Heart Association, a relentless force for a world of longer, healthier lives, has recognized 2,671 health care and emergency response organizations — nearly 145 more than in 2022 — for their commitment to improving health outcomes for cardiovascular patients through evidence-based efficient and coordinated care.
The American Heart Association’s Get With The Guidelines® and Mission: Lifeline® are hospital-based quality improvement recognition programs that use the latest evidence-based scientific guidelines to save lives and hasten health care recovery ...
Stalking a silent killer
2023-08-02
With a survival rate in the single digits, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is highly lethal. In fact, by the time PDAC is clinically diagnosed, it is already considered incurable via surgery or other means in up to 90% of patients.
Yangzom D. Bhutia, D.V.M., Ph.D., from the Department of Cell Biology and Biochemistry at the Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center (TTUHSC) School of Medicine, has for years focused her research on PDAC. To bolster her efforts, the National Cancer Institute at the National Institutes of Health recently awarded Bhutia a five-year, $1.76 million grant (“SLC6A14 as a unique ...
Many people feel their jobs are pointless
2023-08-02
A sociological study by the University of Zurich confirms that a considerable proportion of employees perceive their work as socially useless. Employees in financial, sales and management occupations are more likely to conclude that their jobs are of little use to society.
In recent years, research showed that many professionals consider their work to be socially useless. Various explanations have been proposed for the phenomenon. The much-discussed “bullshit jobs theory” by the American anthropologist David Graeber, for example, states that some jobs are objectively useless and that this occurs more frequently ...
Abortion facility access means long drives for 41.8% of women
2023-08-02
SPOKANE, Wash. – One year after the Dobbs decision, 41.8% of U.S. women of reproductive age have to drive 30 minutes or more to reach an abortion care facility, according to a study of data as of June 2, 2023. Researchers predicted that number would rise to 53.5% if other state bills under consideration are passed.
The study estimated longer drives as well, finding that 29.3% of women didn’t have access to a facility within a 60-minute drive and 23.6% lacked access even within a 90-minute drive. Those figures would jump to 45.6% ...
Unhappy family or trauma in youth leads to poor health in old age
2023-08-02
Adverse childhood experiences have impacts deep into old age, especially for those who experienced violence, and include both physical and cognitive impairments.
It’s known that a difficult childhood can lead to a host of health issues as a young or midlife adult, but now, for the first time, researchers at UC San Franciso have linked adverse experiences early in life to lifelong health consequences.
They found that older U.S. adults with a history of stressful or traumatic experiences as children were more likely to experience both physical and cognitive impairments in their senior years. Stressful childhood experiences could include exposure to ...
Extroverts more likely to resist vaccines, study shows
2023-08-02
EL PASO, Texas (Aug. 2, 2023) – Which types of personalities were more hesitant about COVID-19 vaccination during the pandemic’s peak? Extroverts — according to a new study on more than 40,000 Canadians.
“We expected that people who were especially high in extroversion would be more likely to get the vaccine,” said Melissa Baker, Ph.D., lead author and assistant professor at The University of Texas at El Paso. “We figured those people would want to get back out in the world and socialize, right? It’s actually the opposite.”
The findings, ...
UTokyo researchers imagine future see-through objects
2023-08-02
Researchers from the Institute of Industrial Science(IIS), The University of Tokyo, conducts a wide range of research, including physics, chemistry and biology. In this context, DLX Design Lab carries out activities aimed at fusing science, technology, and design. One of these activities is the Treasure Hunting Project, which aims to inform the general public about the value and potential of scientific research. As part of this project, in 2022-2023, DLX Design Lab produced a video introducing future ...
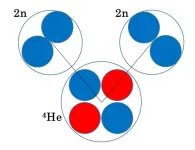
Correlation between neutron pairs observed in helium-8 nuclei
2023-08-02
Atomic nuclei consist of nucleons such as protons and neutrons, which are bound together by nuclear force or strong interaction. This force allows protons and neutrons to form bound states; however, when only two neutrons are involved, the attractive force is slightly insufficient to create such a state. This prompts the question: would four neutrons be adequate? This question has captivated atom physicists, who have actively sought to unlock this mystery in both the theoretical and experimental realms.
With ...
Training on LSA lifeboat operation using Mixed Reality
2023-08-02
Research Background
The International Maritime Organization (IMO) has identified the human element as one of the key attributes for the safety of life at sea and a contributing factor to most of the casualties in the shipping sector. The International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS) is an international maritime treaty which requires signatory flag states to ensure that ships flagged by them comply with minimum safety standards in construction, equipment and operation. As part of the SOLAS code, there is the requirement that all personnel on vessels at sea must undertake Standards of Training, ...