(Press-News.org)
As we age, our bodies undergo various changes that can impact our overall health and make us more susceptible to diseases. One common factor in the ageing process is low-grade inflammation, which contributes to age-related decline and impairment. However, the precise pathways responsible for this inflammation and their impact on natural ageing have remained elusive until now.
A new study led by Andrea Ablasser at EPFL now shows that a molecular signaling pathway called cGAS/STING, plays a critical role in driving chronic inflammation and functional decline during aging. By blocking the STING protein, the researchers were able to suppress inflammatory responses in senescent cells and tissues, leading to improvements in tissue function.
cGAS/STING is a molecular signaling pathway that detects the presence of DNA in cells. It involves two proteins, cyclic GMP–AMP synthase (cGAS) and Stimulator of Interferon Genes (STING). When activated, cGAS/STING triggers an immune response to defend against viral and bacterial infections.
Previous work by Ablasser and her colleagues has linked cGAS/STING to a number of biological processes, including cellular senescence, a hallmark of aging. Based on this, the researchers investigated whether it might underlie maladapted immune responses during ageing.
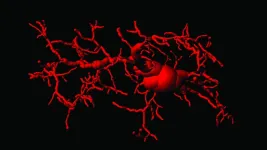
The research found that activating the STING protein triggers specific patterns of gene activity in microglia, the brain’s first-line-of-defense immune cells. These gene-activation patterns matched those arising in microglia in distinct neurodegenerative conditions, such as Alzheimer`s disease and ageing.
“In search for a mechanism that would engage the cGAS-STING pathway in ageing, we considered aberrant mitochondrial DNA species,” says Ablasser. “Mitochondria, the organelles that are responsible for energy production are well-known for disturbed functioning in ageing and disease. Indeed, in microglia from old, but not young mice, DNA from mitochondria accumulated in the cell cytoplasm, suggesting a possible mechanism by which the cGAS-STING pathway contributes to inflammation in the ageing brain.”
The researchers studied the effects of blocking the STING protein in aged mice. As expected by its central role in driving inflammation, inhibiting STING alleviated markers of inflammation both in the periphery and in the brain. More importantly, animals receiving STING inhibitors displayed significant enhancements in spatial and associative memory. STING blockade also affected physical function with improved muscle strength and endurance.
The study advances our understanding of ageing-related inflammation and also offers potential strategies for slowing cognitive deterioration in age-associated neurodegenerative conditions. The precise elucidation of the neuroimmune crosstalk governing microglial-dependent neurotoxicity also holds promise for the future study of neurodegenerative diseases.
Other contributors
EPFL Biological Electron Microscopy Core Facility
EPFL BioImaging and Optics Platform
Laboratory of Neuroepigenetics
University of Freiburg (Germany)
Lausanne University Hospital
The Netherlands Cancer Institute END
Cancer research centers conducting clinical trials could enroll more patients from underrepresented racial and ethnic groups by placing greater emphasis on relieving investigators of the costs of translating consent documents into languages other than English, according to a UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center study.
“We identified a readily addressable weakness in the clinical trial process, and we believe that overcoming this barrier, as we have begun to do, will ensure better representation of trial participants from traditionally underrepresented racial and ethnic groups, ...
Maillard reaction locks away 4 million tonnes of organic carbon a year
Process helped stabilise conditions for complex life to evolve
A chemical process used in the browning of food to give it its distinct smell and taste is probably happening deep in the oceans, where it helped create the conditions necessary for life.
Known as the Maillard reaction after the French scientist who discovered it, the process converts small molecules of organic carbon into bigger molecules known as polymers. In ...
An international team of researchers has found a genetic variant that may explain why some people of African ancestry have naturally lower viral loads of HIV, reducing their risk of transmitting the virus and slowing progress of their own illness.
Reported today in Nature, this is the first new genetic variant related to HIV infection discovered in nearly 30 years of research. It could, in the future, help direct the development of new treatments approaches for those living with HIV.
HIV remains a major threat to global health. According to UNAIDS, there were 38.4 million people living with HIV globally in 2021. A combination of pre-exposure drugs and medicines that dramatically ...
Building on the Middle East’s reputation as one of the historical birthplaces of cereal crop domestication, a KAUST-led team has compiled the first complete genome map of an ancient grain known as einkorn[1].
The 5.2-billion-letter-long sequence provides a window into the evolutionary origins of different wheat species. It could help farmers and crop breeders to develop bread wheat varieties with enhanced disease resistance, higher yields and improved hardiness.
“By understanding the genetic diversity and evolutionary history of einkorn, researchers can now leverage its potential for future ...
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that, although sexual minority women are at high risk of postpartum depression, their sexual identities are largely undocumented in medical records, highlighting the need for strategies to measure sexual orientation that can reliably capture this information.
Authors: Leiszle Lapping-Carr, Ph.D., of the Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine in Chicago, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at ...
About The Study: In this study of 6.3 million older U.S. adults, the mRNA-1273 (Moderna) vaccine was associated with a slightly lower risk of several adverse events compared with BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech), possibly due to greater protection against COVID-19. Future research should seek to formally disentangle differences in vaccine safety and effectiveness and consider the role of frailty in assessments of COVID-19 vaccine performance.
Authors: Daniel A. Harris, Ph.D., of the Brown University School of Public Health in Providence, Rhode Island, is the corresponding ...
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — While mRNA vaccines against COVID-19 have been found to be safe and effective for the general population, in-depth evidence about safety and effectiveness for older adults and individuals with chronic health conditions is more limited.
To address that gap, a team led by Brown University researchers conducted the largest head-to-head comparison study of the two mRNA vaccines approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration — the Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines. The results, published in JAMA Network Open, ...
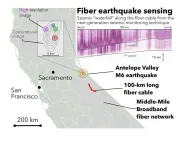
In California, thousands of miles of fiber optic cables crisscross the state, providing people with internet. But these underground cables can also have a surprising secondary function: they can sense and measure earthquakes. In a new study at Caltech, scientists report using a section of fiber optic cable to measure intricate details of a magnitude 6 earthquake, pinpointing the time and location of four individual asperities, the "stuck" areas of the fault, that led to the rupture.
For several years, Professor of Geophysics Zhongwen Zhan (PhD '14) ...
A non-opioid designer molecule for treating chronic neuropathic pain by calming hyperactive pain-sensing neurons in the peripheral nervous system has had promising results in a preclinical study conducted by researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine and the Burke Neurological Institute.
In the study, published Aug. 2 in the British Journal of Anaesthesia, the first-in-class drug conceptualized by lead author Dr. Gareth Tibbs was found to function according to its design at both the molecular level and as an apparently side-effect-free pain reliever in rats.
“With either a single dose or seven days of daily dosing, we saw a significant reversal of neuropathic pain signs in the ...
“We searched for human genetic variation that associates with spontaneous control of HIV and identified a novel region in the genome that is only variable in populations of African ancestries,” says Professor Jacques Fellay at EPFL’s School of Life Sciences. “We used a combination of computational and experimental approaches to explore the biological mechanism behind the genetic association and provide evidence that the gene CHD1L acts to limit HIV replication in a subset of white blood cells.”
HIV is still a problem
Despite significant advances in treatment and access to therapy, the ...