Perinatal depression screening among sexual minority women
JAMA Psychiatry
2023-08-02
(Press-News.org)
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that, although sexual minority women are at high risk of postpartum depression, their sexual identities are largely undocumented in medical records, highlighting the need for strategies to measure sexual orientation that can reliably capture this information.
Authors: Leiszle Lapping-Carr, Ph.D., of the Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine in Chicago, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2023.2619)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamapsychiatry/fullarticle/10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2023.2619?guestAccessKey=c193495c-7077-4548-8393-d7ab3cac07ae&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=080223
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-08-02
About The Study: In this study of 6.3 million older U.S. adults, the mRNA-1273 (Moderna) vaccine was associated with a slightly lower risk of several adverse events compared with BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech), possibly due to greater protection against COVID-19. Future research should seek to formally disentangle differences in vaccine safety and effectiveness and consider the role of frailty in assessments of COVID-19 vaccine performance.
Authors: Daniel A. Harris, Ph.D., of the Brown University School of Public Health in Providence, Rhode Island, is the corresponding ...
2023-08-02
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — While mRNA vaccines against COVID-19 have been found to be safe and effective for the general population, in-depth evidence about safety and effectiveness for older adults and individuals with chronic health conditions is more limited.
To address that gap, a team led by Brown University researchers conducted the largest head-to-head comparison study of the two mRNA vaccines approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration — the Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines. The results, published in JAMA Network Open, ...
2023-08-02
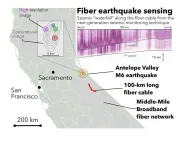
In California, thousands of miles of fiber optic cables crisscross the state, providing people with internet. But these underground cables can also have a surprising secondary function: they can sense and measure earthquakes. In a new study at Caltech, scientists report using a section of fiber optic cable to measure intricate details of a magnitude 6 earthquake, pinpointing the time and location of four individual asperities, the "stuck" areas of the fault, that led to the rupture.
For several years, Professor of Geophysics Zhongwen Zhan (PhD '14) ...
2023-08-02
A non-opioid designer molecule for treating chronic neuropathic pain by calming hyperactive pain-sensing neurons in the peripheral nervous system has had promising results in a preclinical study conducted by researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine and the Burke Neurological Institute.
In the study, published Aug. 2 in the British Journal of Anaesthesia, the first-in-class drug conceptualized by lead author Dr. Gareth Tibbs was found to function according to its design at both the molecular level and as an apparently side-effect-free pain reliever in rats.
“With either a single dose or seven days of daily dosing, we saw a significant reversal of neuropathic pain signs in the ...
2023-08-02
“We searched for human genetic variation that associates with spontaneous control of HIV and identified a novel region in the genome that is only variable in populations of African ancestries,” says Professor Jacques Fellay at EPFL’s School of Life Sciences. “We used a combination of computational and experimental approaches to explore the biological mechanism behind the genetic association and provide evidence that the gene CHD1L acts to limit HIV replication in a subset of white blood cells.”
HIV is still a problem
Despite significant advances in treatment and access to therapy, the ...
2023-08-02
Owing to human activities and climate change, many animal species have invaded new habitats. Such biological invasion comes with devastating impacts on the local biodiversity and ecosystems. The red swamp crayfish—known to the scientific world as Procambarus clarkii (P. clarkii)— is no exception. P. clarkii is a freshwater crayfish native to the tropical regions of southern USA and northeastern Mexico. After their introduction to different parts of the world, they have become one of the most widespread and invasive animal species. They are known for their adaptability and aggressive behavior that ensure their survival in a wide range of environments, ...
2023-08-02
Breast cancer survival rates have improved considerably in the last few decades in Colombia, but factors that increase the likelihood of patients experiencing cardiovascular side effects, like cardiotoxicity, are not well-known or well-treated. A recent study in the North-East region of Colombia found 11.94% of patients with a high BMI being treated for breast cancer at a regional center experienced heart damage, or cardiotoxicity, during chemotherapy. The study will be presented at the American College of Cardiology (ACC) Latin America 2023 Together with Asociación Costarricense ...
2023-08-02
AUSTIN, Texas – A new statistical tool can help researchers get meaningful results when a randomized experiment, considered the gold standard, is not possible.
Randomized experiments split participants into groups by chance, with one undergoing an intervention and the other not. But in real-world situations, they can’t always be done. Companies might not want to use the method, or such experiments might be against the law.
Developed by a researcher at The University of Texas at Austin, the new tool called two-step synthetic control adapts an existing research workaround, known as the synthetic control method.
The ...
2023-08-02
The first-ever study to look at drivers of both marine heatwaves and cold spells in the shallow nearshore along the California Current —coordinated by California Polytechnic State University, San Luis Obispo (Cal Poly) and the Virginia Institute of Marine Science, William & Mary — found that certain environmental conditions and the state of the ocean can lead to an enhanced risk for ocean temperature extremes.
The findings were recently published in Nature Scientific Reports in an article titled “Effects of basin-scale climate modes and upwelling on nearshore marine heatwaves and cold spells in the California Current.”
Extreme ...
2023-08-02
Just as bacteria can develop antibiotic resistance, viruses can also evade drug treatments. Developing therapies against these microbes is difficult because viruses often mutate or hide themselves within cells. But by mimicking the way the immune system naturally deals with invaders, researchers reporting in ACS Infectious Diseases have developed a “peptoid” antiviral therapy that effectively inactivates three viruses in lab tests. The approach disrupts the microbes by targeting certain ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Perinatal depression screening among sexual minority women
JAMA Psychiatry