New research casts doubt on role of fungus in driving pancreatic cancer
2023-08-03
(Press-News.org) DURHAM, N.C. – Four years ago, a report that a common species of fungus might fuel pancreatic cancer offered a promising new view of the deadly disease.
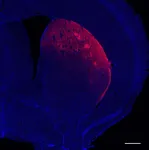
But in working to validate the finding, Duke Health researchers have found no such association. In a study appearing online Aug. 3 in the journal Nature, the Duke researchers conducted a multi-pronged analysis of data from the earlier study and found no link between the pancreatic microbiome and the development of pancreatic cancer.
“We were intrigued by the original finding, as were many research teams,” said senior author Peter Allen, M.D., professor in the Department of Surgery and chief of the Division of Surgical Oncology at Duke University School of Medicine.
“There is a growing body of literature connecting the human microbiome to disease, and this was particularly compelling for pancreatic cancer,” Allen said. “But our findings did not support an association between fungi and the development of pancreatic cancer in humans.”
Allen and colleagues worked to recreate the 2019 findings published in Nature by a different research team. The original study raised hopes that there might be a possible method of preventing pancreatic cancer with the use of antifungals or some other approach to protect from infection.
Focusing on the research team’s original raw sequencing data, the Duke researchers were unable to reproduce the findings. Additional studies, using pancreatic cancer tissue in Duke repositories, also failed to produce the original results.
“We believe our findings highlight the challenges of using low biomass samples for microbiome sequencing studies,” Allen said. “The inclusion of appropriate negative controls and efforts to identify and remove sequencing contaminants is critical to the interpretation of microbiome data.”
In addition to Allen, study authors include Ashley A. Fletcher, Matthew S. Kelly, and Austin M. Eckhoff.
The work was funded by the Duke University School of Medicine through a grant from the Duke Microbiome Center. Kelly and Eckhoff receive funding from the National Institutes of Health (K23-AI135090, T32-CA093245).
###
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-08-03
Dopamine: It’s not just for rewards anymore.
In a new Northwestern University-led study, researchers identified and recorded from three genetic subtypes of dopamine neurons in the midbrain region of a mouse model.
Although there is a long-standing, common assumption that most — if not all — dopamine neurons solely respond to rewards or reward-predicting cues, the researchers instead discovered that one genetic subtype fires when the body moves. And, even more surprisingly, these neurons curiously do not respond to rewards at all.
Not only ...
2023-08-03
RESEARCH SUMMARY
Study Title: Mammalian SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complexes promote tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance in EGFR-mutant lung cancer
Publication: Cancer Cell
Dana-Farber Cancer Institute Senior and Lead Authors: Cigall Kadoch, PhD; Claudia Gentile, PhD; Akshay Sankar
Study Summary:
When lung cancers driven by mutations in the EGFR gene become resistant to osimertinib or other targeted therapies, epigenetic changes, rather than genetic changes, are often to blame. In a new study in Cancer Cell, researchers at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Yale Cancer Center show that the main source of these changes are ...
2023-08-03
About 55 million years ago, the Atlantic Ocean was born. Until then, Europe and America were connected. As the continents began to move apart, the Earth’s crust between them ruptured, releasing large volumes of magma. This rift volcanism has led to the formation of large igneous provinces (LIPs) in several places around the world. One such LIP was formed between Greenland and Europe and now lies several kilometres below the ocean surface. An international drilling campaign led by Christian Berndt from the GEOMAR ...
2023-08-03
NASA's James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has recorded breath-taking new images of the iconic Ring Nebula, also known as Messier 57.
The images, released today by an international team of astronomers led by Professor Mike Barlow (UCL, UK) and Dr Nick Cox (ACRI-ST, France), with Professor Albert Zijlstra of The University of Manchester, showcase the nebula's intricate and ethereal beauty in unprecedented detail, providing scientists and the public with a mesmerizing view of this celestial wonder.
For many sky enthusiasts, the Ring Nebula is a well-known object that is visible all summer long and is located in the constellation ...
2023-08-03
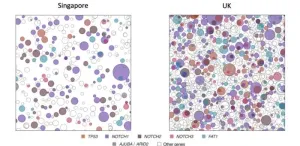
SKIN CANCER-RELATED MUTATIONS HIGHER IN THE UK THAN SINGAPORE
A new study has shown how, on average, people in the UK have facial skin that is far more DNA damaged from the sun than people in Singapore, explaining the far higher risk of developing the most common skin cancers in the UK.
This study looked at keratinocyte cancers - basal and squamous cell carcinomas - rather than melanoma, a rarer and sometimes fatal form of skin cancer, finding Northern European skin types in the UK were less able to protect themselves from UV damage.
Researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute and their collaborators at ...
2023-08-03
UK researchers are calling on higher education institutes and research funders to adopt a new set of recommended actions to address the substantial under-representation of PhD students from ethnic minority backgrounds.
Black, Asian and minority ethnic students have a markedly lower representation in postgraduate research compared with undergraduate or taught postgraduate study in the UK. For instance, in 2020/21, around 26.5% of UK undergraduates were from ethnic minority backgrounds, compared with around 19% for postgraduate students.
The ...
2023-08-03
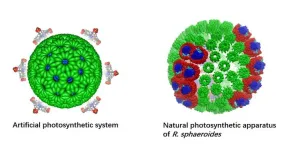
A joint research team from City University of Hong Kong (CityU) and collaborators recently developed a stable artificial photocatalytic system that is more efficient than natural photosynthesis. The new system mimics a natural chloroplast to convert carbon dioxide in water into methane, a valuable fuel, very efficiently using light. This is a promising discovery, which could contribute to the goal of carbon neutrality.
Photosynthesis is the process by which chloroplasts in plants and some organisms use sunlight, water and carbon dioxide to create food or energy. In past decades, many scientists have tried to develop artificial photosynthesis processes to turn ...
2023-08-03
About The Study: In this study of 1.4 million birthing person–infant pairs in the U.S., most pregnancy-specific alcohol policies were not associated with decreased odds of infant injuries or morbidities. Policy makers should not assume that pregnancy-specific alcohol policies improve infant health.
Authors: Sarah C. M. Roberts, Dr.P.H., of the University of California, San Francisco, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.27138)
Editor’s ...
2023-08-03
Digital Science, a technology company serving stakeholders across the research ecosystem, is pleased to announce that Nottingham Trent University has chosen Altmetric Explorer from Digital Science’s flagship products to improve the measurement and reporting of social media and alternative metrics.
Nottingham Trent University (NTU) has signed a deal to utilise Altmetric to report on societal impact and dissemination of research.
Using Digital Science’s products and tools, NTU will be able to support its research strategy, impact development, dissemination ...
2023-08-03
Seven entrepreneurs will embark on a two-year fellowship as the seventh cohort of Innovation Crossroads kicks off this month at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory. Representing a range of transformative energy technologies, Cohort 7 is a diverse class of innovators with promising new companies.
New to Innovation Crossroads’ sponsorship this year are DOE’s Office of Electricity and Office of Science Advanced Scientific Computing Research program, which join DOE’s Advanced Materials and Manufacturing Technologies Office, DOE’s Building Technologies Office, and the Tennessee ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New research casts doubt on role of fungus in driving pancreatic cancer