(Press-News.org) The recently released BGI Genomics 2023 Global State of Cervical Cancer Awareness Report highlights the level of knowledge, attitudes, and practices related to cervical cancer screening and the human papillomavirus (HPV) on a global scale.
Dr. Deborah Laufer, a gynecologist and Associate Professor at the Faculty of Medicine in the University of Montevideo, offers her insights on this report's findings and the steps needed to improve cervical cancer awareness in Uruguay.
Q: 40% of respondents worldwide did not choose HPV as the key cause of cervical cancer. 37% in Uruguay did not mention it either. Why does this awareness gap exist?
Dr. Laufer: Undoubtedly, more education and awareness are needed in our country, mainly because cervical cancer is the third most common cancer among women. Without understanding HPV causes cervical cancer, increasing access to prevention via vaccination or other screening methods is very hard.
Furthermore, I think that in our country, there is a more significant lack of information since the HPV vaccine was very controversial, which means fewer people are aware of the vaccine's benefits and, ultimately, cervical cancer prevention.
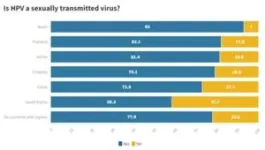
Q: 21% of Uruguayan women indicate HPV is not a sexually transmitted virus. Are you surprised by this finding?
Dr. Laufer: This data reveals a failure in our health system and sex education programs, not providing enough knowledge to the population that HPV is a sexually transmitted disease. What strikes me the most is the low percentage of awareness, yet I observe that this lack of awareness is reflected worldwide.
Q: Fear of results (40%) and embarrassment of meeting a male doctor performing a Pap smear (39%) are the top reasons keeping women from undertaking cervical cancer screening. The absence of symptoms is 56% in Uruguay, way higher than the global average (42%).
Dr. Laufer: In Uruguay, cervical cancer screening is mandatory to obtain occupational health certification. This leads to the majority of the female working-age population taking the test. But they are not aware of cervical cancer prevention.
The government health team should focus on educating the population about the importance of early prevention and explain that you don't have to wait for symptoms before getting a check-up done.
Q: 27% of Uruguay women never had a cervical cancer screening. What are the reasons for this gap in your country?
Dr. Laufer: Although pap smear coverage is required to work, and many Uruguayan women go for gynecological check-ups, much of the population is left out of the formal labor and health system. Investigating, educating these people, and understanding why they don't perform any screening is a priority.
Unfortunately, we also have lost opportunities for women who attend the health system and still do not have screening tests performed. I estimate that the latter group is less than 27%.
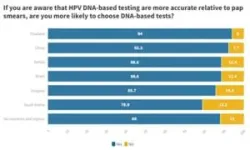
Q: In Uruguay, 86% of respondents will choose the HPV DNA test over a pap smear upon learning about its higher accuracy. How do you interpret this data?
Dr. Laufer: This response shows that if women receive clear and proper information about each of the tests and their scope, they are better placed to make more informed decisions.
About BGI Genomics:
BGI Genomics, headquartered in Shenzhen, China, is the world's leading integrated solutions provider of precision medicine. Our services cover more than 100 countries and regions, involving more than 2,300 medical institutions. In July 2017, as a subsidiary of BGI Group, BGI Genomics (300676.SZ) was officially listed on the Shenzhen Stock Exchange.
END
Professor Deborah Laufer discusses barriers to cervical cancer screening in Uruguay – BGI Insights
Dr. Laufer, Professor at the University of Montevideo, notes that 56% of women do not go for cervical cancer screening if they have no symptoms which is higher than global average of 42%
2023-08-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers strengthen defenses against common cyberattack
2023-08-03
RICHLAND, Wash.—Scientists have developed a better way to recognize a common internet attack, improving detection by 90 percent compared to current methods.
The new technique developed by computer scientists at the Department of Energy’s Pacific Northwest National Laboratory works by keeping a watchful eye over ever-changing traffic patterns on the internet. The findings were presented on August 2 by PNNL scientist Omer Subasi at the IEEE International Conference on Cyber Security and Resilience, where the manuscript was recognized as the best research paper presented at the meeting.
The ...
Mussel-inspired membrane can boost sustainability and add value to industrial wastewater treatment
2023-08-03
Engineers have developed a new kind of membrane that separates chemicals within wastewater so effectively that they can be reused, presenting a new opportunity for industries to improve sustainability, while extracting valuable by-products and chemicals from wastewater.
Created for use in wastewater treatment, the thin-film composite nanoporous membrane known as a TFC NPM, exhibits an ‘unprecedented’ capability to separate salts and other chemical components from water, and could lead to more sustainable treatment and management of water in a range of industries.
A research ...
CAR-T immune therapy attacks ovarian cancer in mice with a single dose
2023-08-03
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — CAR-T immune therapies could be effective against solid tumors if the right targets are identified, a new study led by University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign researchers suggests. The researchers successfully deployed CAR-T in a mouse model of ovarian cancer, a type of aggressive, solid-tumor cancer that has eluded such therapies until now.
“Even with an advanced stage tumor model, even with a single dose, we saw strong anti-tumor effects,” said Diana Rose Ranoa, ...
GABA receptors in brain could be targets to treat depression and its cognitive symptoms
2023-08-03
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Depression is a complex condition correlated with multiple differences in brain function and mechanisms. A new paper spanning known data about the neurotransmitter GABA and its principal receptors showcases evidence of the receptors’ importance in depression and potential as therapeutic targets.
Based on evidence from research on the receptors’ function in the brain and the drugs that can activate or inhibit them, the authors propose possible mechanisms by which GABA-modulating treatments could ...
New clinical trial to assess canine cancer treatment
2023-08-03
DENVER/Aug. 3, 2023 – A newly funded study will evaluate the potential of a cancer drug to control tumor growth and improve outcomes for dogs with histiocytic sarcoma, an aggressive and typically fatal canine cancer.
The multi-center clinical trial is being conducted at Michigan State University, University of Florida, University of Wisconsin and Virginia Tech, and funded by the Bernese Mountain Dog Club of America through Morris Animal Foundation's Donor-Inspired Study program. Histiocytic sarcoma was ...
How sensory neurons impact the gut
2023-08-03
LA JOLLA, CA—Gastrointestinal and digestive issues impact roughly 3 million people across the United States alone, and that number is growing. A new study from Scripps Research scientists shows how sensory neurons control our gastrointestinal tracts—critical information that could shape our understanding of related diseases and disorders.
The study, published in the journal Cell on Aug. 3rd, 2023, used a combination of human clinical data and animal models to reveal that the receptor PIEZO2 controls gastrointestinal transit through the stomach, small intestine, and colon by sensing the presence of food and slowing the rate of gut motility accordingly. These ...
Study finds hallmarks of T cell exhaustion within hours of tumor exposure
2023-08-03
Immune system T cells that should be able to kill cancer cells become dysfunctional or “exhausted” within hours of encountering a tumor, according to a study reported Aug. 3 in Nature Immunology.
The surprising findings have implications for cancer immunotherapies that aim to harness the tumor-killing power of T cells, and they challenge existing ideas about how T cells become exhausted, said Mary Philip, MD, PhD, assistant professor of Medicine in the Division of Hematology and Oncology ...
New research casts doubt on role of fungus in driving pancreatic cancer
2023-08-03
DURHAM, N.C. – Four years ago, a report that a common species of fungus might fuel pancreatic cancer offered a promising new view of the deadly disease.
But in working to validate the finding, Duke Health researchers have found no such association. In a study appearing online Aug. 3 in the journal Nature, the Duke researchers conducted a multi-pronged analysis of data from the earlier study and found no link between the pancreatic microbiome and the development of pancreatic cancer.
“We were intrigued by the original finding, as were ...
Dopamine controls movement, not just rewards
2023-08-03
Dopamine: It’s not just for rewards anymore.
In a new Northwestern University-led study, researchers identified and recorded from three genetic subtypes of dopamine neurons in the midbrain region of a mouse model.
Although there is a long-standing, common assumption that most — if not all — dopamine neurons solely respond to rewards or reward-predicting cues, the researchers instead discovered that one genetic subtype fires when the body moves. And, even more surprisingly, these neurons curiously do not respond to rewards at all.
Not only ...
Study uncovers epigenetic source of resistance to targeted therapy in EGFR-mutant lung cancer
2023-08-03
RESEARCH SUMMARY
Study Title: Mammalian SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complexes promote tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance in EGFR-mutant lung cancer
Publication: Cancer Cell
Dana-Farber Cancer Institute Senior and Lead Authors: Cigall Kadoch, PhD; Claudia Gentile, PhD; Akshay Sankar
Study Summary:
When lung cancers driven by mutations in the EGFR gene become resistant to osimertinib or other targeted therapies, epigenetic changes, rather than genetic changes, are often to blame. In a new study in Cancer Cell, researchers at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Yale Cancer Center show that the main source of these changes are ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
A clinical reveals that aniridia causes a progressive loss of corneal sensitivity
Fossil amber reveals the secret lives of Cretaceous ants
Predicting extreme rainfall through novel spatial modeling
The Lancet: First-ever in-utero stem cell therapy for fetal spina bifida repair is safe, study finds
Nanoplastics can interact with Salmonella to affect food safety, study shows
Eric Moore, M.D., elected to Mayo Clinic Board of Trustees
NYU named “research powerhouse” in new analysis
New polymer materials may offer breakthrough solution for hard-to-remove PFAS in water
Biochar can either curb or boost greenhouse gas emissions depending on soil conditions, new study finds
Nanobiochar emerges as a next generation solution for cleaner water, healthier soils, and resilient ecosystems
Study finds more parents saying ‘No’ to vitamin K, putting babies’ brains at risk
Scientists develop new gut health measure that tracks disease
Rice gene discovery could cut fertiliser use while protecting yields
Jumping ‘DNA parasites’ linked to early stages of tumour formation
Ultra-sensitive CAR T cells provide potential strategy to treat solid tumors
Early Neanderthal-Human interbreeding was strongly sex biased
North American bird declines are widespread and accelerating in agricultural hotspots
Researchers recommend strategies for improved genetic privacy legislation
How birds achieve sweet success
More sensitive cell therapy may be a HIT against solid cancers
Scientists map how aging reshapes cells across the entire mammalian body
Hotspots of accelerated bird decline linked to agricultural activity
How ancient attraction shaped the human genome
NJIT faculty named Senior Members of the National Academy of Inventors
[Press-News.org] Professor Deborah Laufer discusses barriers to cervical cancer screening in Uruguay – BGI InsightsDr. Laufer, Professor at the University of Montevideo, notes that 56% of women do not go for cervical cancer screening if they have no symptoms which is higher than global average of 42%