(Press-News.org) DENVER/Aug. 3, 2023 – A newly funded study will evaluate the potential of a cancer drug to control tumor growth and improve outcomes for dogs with histiocytic sarcoma, an aggressive and typically fatal canine cancer.
The multi-center clinical trial is being conducted at Michigan State University, University of Florida, University of Wisconsin and Virginia Tech, and funded by the Bernese Mountain Dog Club of America through Morris Animal Foundation's Donor-Inspired Study program. Histiocytic sarcoma was first described in Bernese mountain dogs in the late 1970s but has since been noted in many other breeds.
“Histiocytic sarcoma is a devastating disease, and traditional chemotherapeutic drugs have shown limited success in improving treatment outcomes, especially with the disseminated form of the disease,” said Dr. Vilma Yuzbasiyan-Gurkan, Principal Investigator of the study and Professor of Microbiology, Molecular Genetics and Small Animal Clinical Sciences at Michigan State University. “Based on our studies of the molecular pathways driving tumor growth, we now have an opportunity to use a targeted approach in the treatment of this deadly cancer.”
According to Yuzbasiyan-Gurkan, the drug trametinib targets and inhibits the molecular pathway responsible for tumor growth. Extensive testing has demonstrated the drug’s effectiveness against canine histiocytic sarcoma cell lines and in mouse models replicating canine tumors, as well as its safety and tolerability in dogs.
“We are hopeful that the treatment will have a significant and positive impact on the affected dogs,” Yuzbasiyan-Gurkan said. “We are always guided by data and look forward to seeing what the study will show.”
About Morris Animal Foundation
Morris Animal Foundation’s mission is to bridge science and resources to advance the health of animals. Founded in 1948 and headquartered in Denver, it is one of the largest nonprofit animal health research organizations in the world, funding nearly $160 million in more than 3,000 critical studies across a broad range of species. Learn more at morrisanimalfoundation.org.
Media Contact: Annie Mehl
END
New clinical trial to assess canine cancer treatment
Bernese Mountain Dog Club of America funds study evaluating novel treatment for histiocytic sarcoma
2023-08-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How sensory neurons impact the gut
2023-08-03
LA JOLLA, CA—Gastrointestinal and digestive issues impact roughly 3 million people across the United States alone, and that number is growing. A new study from Scripps Research scientists shows how sensory neurons control our gastrointestinal tracts—critical information that could shape our understanding of related diseases and disorders.
The study, published in the journal Cell on Aug. 3rd, 2023, used a combination of human clinical data and animal models to reveal that the receptor PIEZO2 controls gastrointestinal transit through the stomach, small intestine, and colon by sensing the presence of food and slowing the rate of gut motility accordingly. These ...
Study finds hallmarks of T cell exhaustion within hours of tumor exposure
2023-08-03
Immune system T cells that should be able to kill cancer cells become dysfunctional or “exhausted” within hours of encountering a tumor, according to a study reported Aug. 3 in Nature Immunology.
The surprising findings have implications for cancer immunotherapies that aim to harness the tumor-killing power of T cells, and they challenge existing ideas about how T cells become exhausted, said Mary Philip, MD, PhD, assistant professor of Medicine in the Division of Hematology and Oncology ...
New research casts doubt on role of fungus in driving pancreatic cancer
2023-08-03
DURHAM, N.C. – Four years ago, a report that a common species of fungus might fuel pancreatic cancer offered a promising new view of the deadly disease.
But in working to validate the finding, Duke Health researchers have found no such association. In a study appearing online Aug. 3 in the journal Nature, the Duke researchers conducted a multi-pronged analysis of data from the earlier study and found no link between the pancreatic microbiome and the development of pancreatic cancer.
“We were intrigued by the original finding, as were ...
Dopamine controls movement, not just rewards
2023-08-03
Dopamine: It’s not just for rewards anymore.
In a new Northwestern University-led study, researchers identified and recorded from three genetic subtypes of dopamine neurons in the midbrain region of a mouse model.
Although there is a long-standing, common assumption that most — if not all — dopamine neurons solely respond to rewards or reward-predicting cues, the researchers instead discovered that one genetic subtype fires when the body moves. And, even more surprisingly, these neurons curiously do not respond to rewards at all.
Not only ...
Study uncovers epigenetic source of resistance to targeted therapy in EGFR-mutant lung cancer
2023-08-03
RESEARCH SUMMARY
Study Title: Mammalian SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complexes promote tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance in EGFR-mutant lung cancer
Publication: Cancer Cell
Dana-Farber Cancer Institute Senior and Lead Authors: Cigall Kadoch, PhD; Claudia Gentile, PhD; Akshay Sankar
Study Summary:
When lung cancers driven by mutations in the EGFR gene become resistant to osimertinib or other targeted therapies, epigenetic changes, rather than genetic changes, are often to blame. In a new study in Cancer Cell, researchers at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Yale Cancer Center show that the main source of these changes are ...
Past climate warming driven by hydrothermal vents
2023-08-03
About 55 million years ago, the Atlantic Ocean was born. Until then, Europe and America were connected. As the continents began to move apart, the Earth’s crust between them ruptured, releasing large volumes of magma. This rift volcanism has led to the formation of large igneous provinces (LIPs) in several places around the world. One such LIP was formed between Greenland and Europe and now lies several kilometres below the ocean surface. An international drilling campaign led by Christian Berndt from the GEOMAR ...
James Webb Space Telescope captures stunning images of the Ring Nebula
2023-08-03
NASA's James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has recorded breath-taking new images of the iconic Ring Nebula, also known as Messier 57.
The images, released today by an international team of astronomers led by Professor Mike Barlow (UCL, UK) and Dr Nick Cox (ACRI-ST, France), with Professor Albert Zijlstra of The University of Manchester, showcase the nebula's intricate and ethereal beauty in unprecedented detail, providing scientists and the public with a mesmerizing view of this celestial wonder.
For many sky enthusiasts, the Ring Nebula is a well-known object that is visible all summer long and is located in the constellation ...
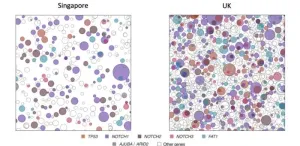
Wellcome Sanger Institute: Skin cancer-related mutations higher in the UK than Singapore
2023-08-03
SKIN CANCER-RELATED MUTATIONS HIGHER IN THE UK THAN SINGAPORE
A new study has shown how, on average, people in the UK have facial skin that is far more DNA damaged from the sun than people in Singapore, explaining the far higher risk of developing the most common skin cancers in the UK.
This study looked at keratinocyte cancers - basal and squamous cell carcinomas - rather than melanoma, a rarer and sometimes fatal form of skin cancer, finding Northern European skin types in the UK were less able to protect themselves from UV damage.
Researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute and their collaborators at ...
Researchers release action plan to boost diversity in postgraduate science students
2023-08-03
UK researchers are calling on higher education institutes and research funders to adopt a new set of recommended actions to address the substantial under-representation of PhD students from ethnic minority backgrounds.
Black, Asian and minority ethnic students have a markedly lower representation in postgraduate research compared with undergraduate or taught postgraduate study in the UK. For instance, in 2020/21, around 26.5% of UK undergraduates were from ethnic minority backgrounds, compared with around 19% for postgraduate students.
The ...
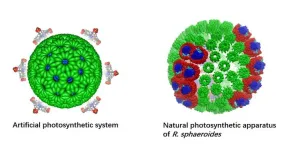
New photocatalytic system converts carbon dioxide to valuable fuel more efficiently than natural photosynthesis
2023-08-03
A joint research team from City University of Hong Kong (CityU) and collaborators recently developed a stable artificial photocatalytic system that is more efficient than natural photosynthesis. The new system mimics a natural chloroplast to convert carbon dioxide in water into methane, a valuable fuel, very efficiently using light. This is a promising discovery, which could contribute to the goal of carbon neutrality.
Photosynthesis is the process by which chloroplasts in plants and some organisms use sunlight, water and carbon dioxide to create food or energy. In past decades, many scientists have tried to develop artificial photosynthesis processes to turn ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Does online sports gambling affect substance use behaviors?
How do rapid socio-environmental transitions reshape cancer risk?
Do abortion bans affect birth rates and food-assistance costs?
Can artificial intelligence help reduce the carbon footprint of weather forecasting models?
Mangrove forests are short of breath
Low testosterone, high fructose: A recipe for liver disaster
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
[Press-News.org] New clinical trial to assess canine cancer treatmentBernese Mountain Dog Club of America funds study evaluating novel treatment for histiocytic sarcoma