(Press-News.org)
Paris, France – August 3, 2023 – The First International Congress on Artificial Intelligence and Medicine, AI & Medicine 2024, is set to take place on April 11-12, 2024, in Paris, France. Building on the success of IA & Néphrologie 2023, the conference aims to bridge the gap between cutting-edge technology and health care.
AI & Medicine 2024 aims to inform medical professionals about the capabilities of advanced machine learning techniques, and simultaneously raise awareness within the tech industry regarding the unique challenges and requirements of the healthcare sector. The congress will offer a platform to discuss the current applications of AI in diagnostics, examine the role of AI in drug discovery, and highlight its contributions to personalized medicine. Moreover, the conference will also address the ethical and technical challenges of applying AI in medicine and explore opportunities to transform fundamental research into institutionalized practices.
Doctors, Medical Professionals and AI: Innocent Bystanders or Vicious Culprits
Doctors are neither innocent bystanders nor vicious culprits in the integration of AI in healthcare. Rather, they are vital actors. As healthcare practitioners, they have the potential to significantly influence how AI is used, ensuring that it is leveraged to enhance patient care, increase credibility and efficiency, and improve overall health outcomes. They are key to integrating these advancements in a manner that is ethical, responsible, and patient-centered.
Simultaneously, it's crucial that doctors are given adequate training and understanding of these technologies. This way, they can effectively interpret AI-generated information and make the best possible decisions for their patients.
Call for Innovations
A call has been issued for researchers, health care experts, Sociologists, startups, and industry leaders to participate in the AI & Medicine 2024 conference. Those interested can share their work through abstract submissions, project pitches, or innovation showcases, aligning with the objectives and themes of the conference.
AI & Medicine 2024 is an exciting platform that aims to drive innovation, collaboration, and advance healthcare progress. Attendees can expect insights from leading professionals in the field and the chance to network with global industry leaders.
To learn more about AI & Medicine 2024 and submit an abstract, visit our website at www.targeting-ai.com.
About AI & Medicine 2024
AI & Medicine 2024 is a congress that brings together the worlds of artificial intelligence and medical practice. The event, which follows the success of two previous editions held in France, stands as a beacon for innovation and collaboration in the healthcare sector. It provides an international platform for dialogue, sharing of best practices, and creating powerful connections. Building on the momentum of these past conferences, AI & Medicine 2024 continues to push the boundaries of technological advancements in healthcare, promoting a future where AI significantly improves patient care and outcomes.
END
Spinouts, or new ventures started by employees leaving a parent firm, often outperform other types of new firms. But a new study published in Strategic Management Journal finds that when parent firms identify and implement ideas internally, they outperform spinouts. For example, if employees at Microsoft leave the parent and start their own spinout in the competing industry, the spinout potentially needs to compete against a new establishment formed by Microsoft in the same industry.
New ventures by former employees often have an edge over competitors because of the knowledge transfer from their ...
Research at the Florida State University College of Medicine has identified a potential low-cost method for predicting if a person is at risk of developing dementia.
By analyzing data from nearly 13,000 subjects who participated in a long-term aging study, researchers found that an interviewer’s rating of a cognitively healthy person’s memory successfully predicted the likelihood of developing dementia over a 15-year period. Their findings will be published in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease.
“Our findings show that interviewers ...
ITHACA, N.Y. -- Cornell researchers used magnetic imaging to obtain the first direct visualization of how electrons flow in a special type of insulator, and by doing so they discovered that the transport current moves through the interior of the material, rather than at the edges, as scientists had long assumed.
The finding provides new insights into the electron behavior in so-called quantum anomalous Hall insulators and should help settle a decades-long debate about how current flows in more general quantum Hall insulators. These insights will inform the development of topological materials for next-generation quantum devices.
The team’s paper, “Direct ...
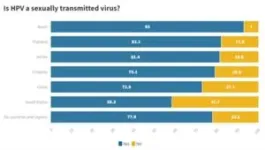
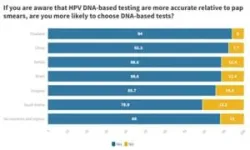
The recently released BGI Genomics 2023 Global State of Cervical Cancer Awareness Report highlights the level of knowledge, attitudes, and practices related to cervical cancer screening and the human papillomavirus (HPV) on a global scale.
Dr. Deborah Laufer, a gynecologist and Associate Professor at the Faculty of Medicine in the University of Montevideo, offers her insights on this report's findings and the steps needed to improve cervical cancer awareness in Uruguay.
Q: 40% of respondents worldwide did not choose HPV as the key cause of cervical cancer. 37% in Uruguay did not mention it either. ...
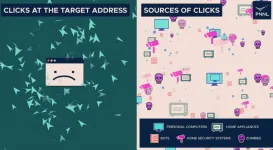
RICHLAND, Wash.—Scientists have developed a better way to recognize a common internet attack, improving detection by 90 percent compared to current methods.
The new technique developed by computer scientists at the Department of Energy’s Pacific Northwest National Laboratory works by keeping a watchful eye over ever-changing traffic patterns on the internet. The findings were presented on August 2 by PNNL scientist Omer Subasi at the IEEE International Conference on Cyber Security and Resilience, where the manuscript was recognized as the best research paper presented at the meeting.
The ...
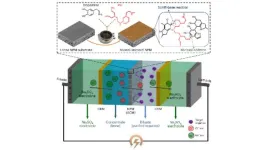
Engineers have developed a new kind of membrane that separates chemicals within wastewater so effectively that they can be reused, presenting a new opportunity for industries to improve sustainability, while extracting valuable by-products and chemicals from wastewater.
Created for use in wastewater treatment, the thin-film composite nanoporous membrane known as a TFC NPM, exhibits an ‘unprecedented’ capability to separate salts and other chemical components from water, and could lead to more sustainable treatment and management of water in a range of industries.
A research ...
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — CAR-T immune therapies could be effective against solid tumors if the right targets are identified, a new study led by University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign researchers suggests. The researchers successfully deployed CAR-T in a mouse model of ovarian cancer, a type of aggressive, solid-tumor cancer that has eluded such therapies until now.
“Even with an advanced stage tumor model, even with a single dose, we saw strong anti-tumor effects,” said Diana Rose Ranoa, ...
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Depression is a complex condition correlated with multiple differences in brain function and mechanisms. A new paper spanning known data about the neurotransmitter GABA and its principal receptors showcases evidence of the receptors’ importance in depression and potential as therapeutic targets.
Based on evidence from research on the receptors’ function in the brain and the drugs that can activate or inhibit them, the authors propose possible mechanisms by which GABA-modulating treatments could ...
DENVER/Aug. 3, 2023 – A newly funded study will evaluate the potential of a cancer drug to control tumor growth and improve outcomes for dogs with histiocytic sarcoma, an aggressive and typically fatal canine cancer.
The multi-center clinical trial is being conducted at Michigan State University, University of Florida, University of Wisconsin and Virginia Tech, and funded by the Bernese Mountain Dog Club of America through Morris Animal Foundation's Donor-Inspired Study program. Histiocytic sarcoma was ...
LA JOLLA, CA—Gastrointestinal and digestive issues impact roughly 3 million people across the United States alone, and that number is growing. A new study from Scripps Research scientists shows how sensory neurons control our gastrointestinal tracts—critical information that could shape our understanding of related diseases and disorders.
The study, published in the journal Cell on Aug. 3rd, 2023, used a combination of human clinical data and animal models to reveal that the receptor PIEZO2 controls gastrointestinal transit through the stomach, small intestine, and colon by sensing the presence of food and slowing the rate of gut motility accordingly. These ...