(Press-News.org) UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Chemical structures called cyclopropanes can increase the potency and fine-tune the properties of many drugs, but traditional methods to create this structure only work with certain molecules and require highly reactive—potentially explosive—ingredients. Now, a team of researchers from Penn State has identified and demonstrated a safe, efficient and practical way to create cyclopropanes on a wide variety of molecules using a previously undescribed chemical process. With additional development, the new method—described in a paper publishing Aug. 4 in the journal Science—could transform how this important process occurs during drug development and creation.
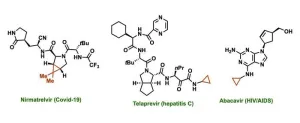
Cyclopropanes are a key feature in many drugs currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, including those used to treat COVID-19, asthma, hepatitis C, and HIV/AIDs. These structures can increase a drug’s potency, alter its ability to dissolve in the body, minimize its interactions with unintended targets, and otherwise fine-tune performance. Cyclopropanes are a ring of three connected carbon atoms, with one carbon attached to the rest of the drug molecule and the other two each attached to two hydrogen atoms.
“Cyclopropanes are an essential component of many drugs and adding them to drug candidates can be an important part of the drug discovery process,” said Ramesh Giri, professor of chemistry in the Eberly College of Science at Penn State and leader of the research team. “Previous efforts to improve the creation of cyclopropanes have focused on altering a mechanistic pathway devolved more than 60 years ago. We approached this from a different angle and identified a completely new pathway that is a simple, practical, and broadly applicable.”
The new method transforms a specific chemical structure on compounds called alkenes—used in the synthesis of many molecules—into cyclopropanes. The method takes advantage of “radical chemistry,” where intermediate steps of reactions leave some carbon atoms with unpaired electrons called free radicals that propel the reaction forward. This specific method uses visible light to initiate the reaction and uses common chemical ingredients, including oxygen.
Traditional methods to create cyclopropanes require highly reactive and difficult-to-acquire ingredients and must be conducted under controlled conditions, and the resulting compounds often have a very short shelf life. These unstable ingredients are critical to producing an intermediate compound in the process called a carbene—a highly reactive carbon atom with two unpaired electrons. The new method completely bypasses the carbene intermediate, producing the unpaired electrons one at a time as radicals.
“All of the ingredients used in this pathway are commercially available or easy to create in the lab and do not require any special safety precautions, and the end product can be stored for prolonged periods,” Giri said. “We can add all the ingredients together in one mixture while exposed to air with as little as 10% oxygen, and it proceeds in one step. The reaction is simple and safe enough that we are even planning to include it as part of an undergraduate chemistry lab.”
Another shortcoming of traditional methods is that they generally do not work with complex molecules. For this reason, cyclopropanes are typically installed early in the synthesis when the molecule is less complex, but following steps can cause the ring to open up, and later attempts to make derivatives of the molecule would require backtracking to those early steps. Using the new method, the researchers successfully transformed a variety of alkenes with a wide range of complexities into cyclopropanes, including pharmaceutically relevant compounds such as the steroid estrone, penicillin and vitamin B.
“We explored the entire range of molecule complexity that people might encounter during drug synthesis,” Giri said. “In some cases, traditional methods might be able to develop the same end product but in many more steps. In other cases, traditional methods would be unable to create these products, because the starting alkenes are too sensitive or too complex. The new method is not only safer, more efficient and more practical, but has a wider range of applications than traditional methods.”
Some of the ingredients in the reaction can also be swapped out to add additional chemical groups to the final product to achieve various therapeutic goals. One of the reaction’s ingredients is as a type of compound called a methylene. There are hundreds of different methylenes that are commercially available, each with a specific chemical group that makes it a methylene as well as other groups that differ and could theoretically be added to the alkene as a cyclopropane Is created. The researchers demonstrated the breadth of the new method using 19 different methylene compounds.
“The idea of using a visible light-based reaction and radical chemistry to transform alkenes into cyclopropanes using methylenes at first seems counterintuitive, which is why it was so important for us to thoroughly demonstrate this new catalytic method,” Giri said. “The key insight was introducing oxygen into the reaction, which helps create a radical that then interacts with the alkene. My lab has been studying other reactions that use alkenes to create a radical and wondered if the same idea could be applied to creating cyclopropanes.”
Next, Giri and his lab plan to scale up the method so that it is industrially viable.
“With future development and scaling up, this method has the potential to transform the way alkenes are cyclopropanated, which could have important implications for drug discovery, development, and creation,” he said.
In addition to Giri, the research team at Penn State includes postdoctoral researcher Dhruba Poudel, postdoctoral researcher at the time of the research Amrit Pokhrel, postdoctoral researcher at the time of the research Raj Kumar Tak, and postdoctoral research Majji Shankar. The U.S. National Institute of General Medical Sciences and Penn State supported this research.
END
New, simple and accessible method creates potency-increasing structure in drugs
Previously undescribed chemical process may offer safer, more practical way to create cyclopropanes—a key feature in many drugs and drug-candidates.
2023-08-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study finds a surprising new role for a major immune regulator
2023-08-03
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- A signaling protein known as STING is a critical player in the human immune system, detecting signs of danger within cells and then activating a variety of defense mechanisms.
STING is primarily on the lookout for DNA, which can indicate either a foreign invader such as a virus or damage to the host tissue or cell. When STING detects that danger signal, it can turn on at least three different pathways — one leading to interferon production, one to non-canonical autophagy (involved in recycling cell components and clearing pathogens), and a third to formation of the inflammasome, a complex of proteins that activates ...
Winter storms over Labrador Sea influence Gulf Stream system
2023-08-03
The Gulf Stream, which brings warm water from the Gulf of Mexico to Europe and keeps the climate mild, is only part of a larger system of oceanic currents called the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation, or AMOC for short. It runs through the Atlantic like a giant climate machine: as warm water from the tropics is transported northwards at the surface, the current reverses in the North Atlantic – the water cools, becomes heavier and flows south at depth.
Where exactly these sinking processes take place is the subject of current research, and recent measurement programmes have located them to the east of Greenland. ...
Doctors, medical professionals, and artificial intelligence: Innocent bystanders or vicious culprits? – a hot topic of the AI & Medicine 2024 World Congress in Paris, France
2023-08-03
Paris, France – August 3, 2023 – The First International Congress on Artificial Intelligence and Medicine, AI & Medicine 2024, is set to take place on April 11-12, 2024, in Paris, France. Building on the success of IA & Néphrologie 2023, the conference aims to bridge the gap between cutting-edge technology and health care.
AI & Medicine 2024 aims to inform medical professionals about the capabilities of advanced machine learning techniques, and simultaneously raise awareness within the tech industry regarding the unique challenges and requirements of the healthcare sector. The congress will offer a platform to discuss the current applications of AI in diagnostics, ...
A spinout’s biggest competitor may be the parent company, not other entrepreneurs
2023-08-03
Spinouts, or new ventures started by employees leaving a parent firm, often outperform other types of new firms. But a new study published in Strategic Management Journal finds that when parent firms identify and implement ideas internally, they outperform spinouts. For example, if employees at Microsoft leave the parent and start their own spinout in the competing industry, the spinout potentially needs to compete against a new establishment formed by Microsoft in the same industry.
New ventures by former employees often have an edge over competitors because of the knowledge transfer from their ...
FSU researcher finds potential new tool for early identification of dementia risk
2023-08-03
Research at the Florida State University College of Medicine has identified a potential low-cost method for predicting if a person is at risk of developing dementia.
By analyzing data from nearly 13,000 subjects who participated in a long-term aging study, researchers found that an interviewer’s rating of a cognitively healthy person’s memory successfully predicted the likelihood of developing dementia over a 15-year period. Their findings will be published in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease.
“Our findings show that interviewers ...
Current takes a surprising path in quantum material
2023-08-03
ITHACA, N.Y. -- Cornell researchers used magnetic imaging to obtain the first direct visualization of how electrons flow in a special type of insulator, and by doing so they discovered that the transport current moves through the interior of the material, rather than at the edges, as scientists had long assumed.
The finding provides new insights into the electron behavior in so-called quantum anomalous Hall insulators and should help settle a decades-long debate about how current flows in more general quantum Hall insulators. These insights will inform the development of topological materials for next-generation quantum devices.
The team’s paper, “Direct ...
Professor Deborah Laufer discusses barriers to cervical cancer screening in Uruguay – BGI Insights
2023-08-03
The recently released BGI Genomics 2023 Global State of Cervical Cancer Awareness Report highlights the level of knowledge, attitudes, and practices related to cervical cancer screening and the human papillomavirus (HPV) on a global scale.
Dr. Deborah Laufer, a gynecologist and Associate Professor at the Faculty of Medicine in the University of Montevideo, offers her insights on this report's findings and the steps needed to improve cervical cancer awareness in Uruguay.
Q: 40% of respondents worldwide did not choose HPV as the key cause of cervical cancer. 37% in Uruguay did not mention it either. ...
Researchers strengthen defenses against common cyberattack
2023-08-03
RICHLAND, Wash.—Scientists have developed a better way to recognize a common internet attack, improving detection by 90 percent compared to current methods.
The new technique developed by computer scientists at the Department of Energy’s Pacific Northwest National Laboratory works by keeping a watchful eye over ever-changing traffic patterns on the internet. The findings were presented on August 2 by PNNL scientist Omer Subasi at the IEEE International Conference on Cyber Security and Resilience, where the manuscript was recognized as the best research paper presented at the meeting.
The ...
Mussel-inspired membrane can boost sustainability and add value to industrial wastewater treatment
2023-08-03
Engineers have developed a new kind of membrane that separates chemicals within wastewater so effectively that they can be reused, presenting a new opportunity for industries to improve sustainability, while extracting valuable by-products and chemicals from wastewater.
Created for use in wastewater treatment, the thin-film composite nanoporous membrane known as a TFC NPM, exhibits an ‘unprecedented’ capability to separate salts and other chemical components from water, and could lead to more sustainable treatment and management of water in a range of industries.
A research ...
CAR-T immune therapy attacks ovarian cancer in mice with a single dose
2023-08-03
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — CAR-T immune therapies could be effective against solid tumors if the right targets are identified, a new study led by University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign researchers suggests. The researchers successfully deployed CAR-T in a mouse model of ovarian cancer, a type of aggressive, solid-tumor cancer that has eluded such therapies until now.
“Even with an advanced stage tumor model, even with a single dose, we saw strong anti-tumor effects,” said Diana Rose Ranoa, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
Plants pause, play and fast forward growth depending on types of climate stress
University of Minnesota scientists reveal how deadly Marburg virus enters human cells, identify therapeutic vulnerability
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
The gut can drive age-associated memory loss
Enhancing gut-brain communication reversed cognitive decline, improved memory formation in aging mice
Mothers exposure to microbes protect their newborn babies against infection
How one flu virus can hamper the immune response to another
Researchers uncover distinct tumor “neighborhoods”, with each cell subtype playing a specific role, in aggressive childhood brain cancer
Researchers develop new way to safely insert gene-sized DNA into the genome
Astronomers capture birth of a magnetar, confirming link to some of universe’s brightest exploding stars
New photonic device, developed by MIT researchers, efficiently beams light into free space
UCSB researcher bridges the worlds of general relativity and supernova astrophysics
Global exchange of knowledge and technology to significantly advance reef restoration efforts
[Press-News.org] New, simple and accessible method creates potency-increasing structure in drugsPreviously undescribed chemical process may offer safer, more practical way to create cyclopropanes—a key feature in many drugs and drug-candidates.