(Press-News.org) Scientists are looking for ways to use the low-value energy widely distributed in natural environments to generate electricity. A research team has created a power generator that collects the natural atmospheric humidity and produces continuous electrical signals. This is the first humidity generator designed using a nano-sized material called polyoxometalates. It holds the potential of being a new research direction for polyoxometalates in the sustainable utilization of low-value energy.
The team’s work is published in the journal Nano Research on August 01.
The team set out to solve the problem of the discontinuity in the operation of energy conversion devices. They sought to address the shortage of atmospheric humidity power generation materials and the limited designable performance of materials. “We wanted to understand the conversion process of atmospheric humidity energy to electrical energy and the role of polyoxometalates in the atmospheric humidity power generation,” said Weilin Chen, a professor in the Department of Chemistry at Northeast Normal University.
Polyoxometalates, known as POMs, have special morphology and functional properties, which make them very useful in controllable synthesis, assembly, and performance research. They are a versatile class of inorganic molecular materials. POM nanomaterials can self-assemble to form microporous structures that are capable of collecting atmospheric humidity. They are also environmentally friendly, with great stability in light, heat, and chemical environments. Scientists expect that POM nanomaterials are the materials with the potential to effectively utilize atmospheric humidity.
The team constructed POMs into organic ammonium-polyoxoanion clusters. The clusters were assembled into thin films power generators with tiny, nano-sized pores called micropores, that are capable of working in atmospheric humidity. Their tiny POM generator produced a voltage of 0.68 V, was stable, and worked continuously under almost all-natural environments, with atmospheric humidity ranging from 10 percent to 90 percent.
The POM atmospheric humidity generator works as the POM nanoclusters spontaneously absorb atmospheric humidity with the micropores in POM nanowires films. They form a distribution gradient of water which is the structural basis of power generation. The POM generator has proven to have high stability and continuous power generation performance.
The team determined that the POM power generator can effectively collect the natural atmospheric humidity and produce continuous electrical signals by the uneven distribution and directional movement of ions. This work provides new ideas for the continuous use of low-value energy and a new research angle for polyoxometalate chemistry.
There has been an urgent need to develop a continuous low-value energy in a natural environment. In past research, scientists have created devices that collect and use low-value energy. But these devices have been limited because low-value energy is intermittent and unstable. In recent years, scientists have made progress in their use of atmospheric humidity energy. But the team’s POM generator is the first humidity generator to produce continuous power.
This POM generator has many potential applications, such as the detection of human respiratory processes; the detection, recording, and alarm of environmental humidity; the integration with electrical appliances to achieve continuous power supply of equipment; and meeting the electricity needs of multiple scenarios.
“The most important message is that continuous power generation using atmospheric humidity has been achieved through the design and modification of POMs nanomaterials, and the mechanism of atmospheric humidity power generation has been deeply understood by using the characteristics of POMs nanomaterials,” said Chen.
Looking ahead, the team hopes to improve the efficiency of atmospheric humidity power generation by screening and optimizing materials. They want to achieve a deeper understanding the atmospheric humidity power generation process.
“The ultimate goal is achieving the efficient use of humidity generators to promote sustainable development of energy and the environment by exploring the mechanism that optimizes the efficiency of the humidity generator,” said Chen.
The Chinese research team includes Tuo Ji and Weilin Chen from the Northeast Normal University; Zhenhui Kang from Soochow University; and Liming Zhang from the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
The research is funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Science and Technology Research Project of the Education Department of Jilin Province, and the Natural Science Foundation of Jilin Province.
##
About Nano Research
Nano Research is a peer-reviewed, international and interdisciplinary research journal, publishes all aspects of nano science and technology, featured in rapid review and fast publishing, sponsored by Tsinghua University and the Chinese Chemical Society. It offers readers an attractive mix of authoritative and comprehensive reviews and original cutting-edge research papers. After 15 years of development, it has become one of the most influential academic journals in the nano field. In 2023 InCites Journal Citation Reports, Nano Research has an Impact Factor of 9.9, the total cites reached 35645, ranking first in China's international academic journals, and the number of highly cited papers reached 194, ranked among the top 1.8% of 8769 academic journals.
About Tsinghua University Press
Established in 1980, belonging to Tsinghua University, Tsinghua University Press (TUP) is a leading comprehensive higher education and professional publisher in China. Committed to building a top-level global cultural brand, after 42 years of development, TUP has established an outstanding managerial system and enterprise structure, and delivered multimedia and multi-dimensional publications covering books, audio, video, electronic products, journals and digital publications. In addition, TUP actively carries out its strategic transformation from educational publishing to content development and service for teaching & learning and was named First-class National Publisher for achieving remarkable results.
END
Researchers have developed a pair of modules that gives a boost to the use of artificial neural networks to identify potentially cancerous growths in colonoscopy imagery, traditionally plagued by image noise resulting from the colonoscopy insertion and rotation process itself.
A paper describing the approach was published in the journal CAAI Artificial Intelligence Research on June 30.
Colonoscopy is the gold standard for detecting colorectal growths or ‘polyps’ in the inner lining of your colon, also known as the large intestine. ...
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — In temperate climates, like North America and Europe, flu season starts in the fall, peaks in the winter and ends in the spring. While public health officials have generally assumed that influenza is also seasonal in tropical climates, new research led by Penn State has found little evidence of a repeatable pattern in influenza cases in Vietnam. The findings suggest that influenza is likely unpredictable throughout the tropics, posing substantial challenges for prevention and management of cases for the one-third of the global population living in tropical areas.
“The World ...
About The Study: In this study of Massachusetts schools, the secondary attack rate for SARS-CoV-2 among school-based contacts was low during two periods, and factors associated with transmission risk varied over time. These findings suggest that ongoing surveillance efforts may be essential to ensure that both targeted resources and mitigation practices remain optimal and relevant for disease prevention.
Authors: Sandra B. Nelson, M.D., of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2023.2310)
Editor’s ...
About The Study: In this study of 230,000 persons with second primary cancers in the U.S., the Black population had a higher risk of death from both cancer and cardiovascular disease compared with the white population, whereas the Hispanic population had a higher risk of death from cancer. These results suggest that research priorities to address survival disparities in the growing population of survivors of multiple primary cancers are warranted.
Authors: Hyuna Sung, Ph.D., of the American Cancer Society in Atlanta, is ...
ATLANTA, August 4, 2023 — In new findings from researchers at the American Cancer Society (ACS), non-Hispanic Black individuals diagnosed with a second primary cancer (SPC) experienced 21% higher cancer-related death rates and 41% higher cardiovascular-related death rates compared with their non-Hispanic White counterparts. The study also showed that Hispanic individuals diagnosed with a second primary cancer also experienced 10% higher cancer-related death rates compared with their non-Hispanic White counterparts, but 10% lower cardiovascular-related death rates. The paper was published ...
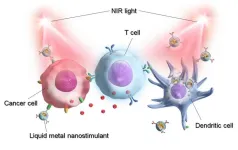
Ishikawa, Japan -- Liquid metals (LM) such as pure gallium (Ga) and Ga-based alloys are a new class of materials with unique physicochemical properties. One of the most prominent applications of LMs is photothermal therapy against cancer, in which functional LM nanoparticles convert light energy to heat energy, thus killing cancerous cells. LM-based phototherapy is superior to traditional cancer therapy owing to its high specificity, repeatability, and low side effects.
In a new cutting-edge study, Associate Professor Eijiro Miyako and his colleagues from Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (JAIST) synthesized multifunctional Ga-based nanoparticles that combine cancer ...
Breastfeeding for six months or more appears to reduce the risk of cardiovascular problems developing in mothers for at least three years after delivery, a new South Australian study has found.
The surprising cardio-metabolic benefit for maternal health is particularly important for women who experienced a complicated pregnancy, which can increase their chance of developing cardiovascular disease (CVD) later in life.
The new results – published this month in the International Breastfeeding Journal by experts from the University of Adelaide ...
Patient-reported outcome (PRO) data are collected in oncology trials to determine patients' perspectives of cancer treatment - unfortunately often too briefly, for example only up to the point when an x-ray shows tumour growth and treatment is discontinued. As a result, it is not possible, for example, to reliably assess the impact on patients' lives of disease progression seen on X-rays or the long-term side effects of cancer treatment. The reasons given for this are organizational difficulties or patients’ lack of interest in long-term follow-up. ...
A subpolar species associated with Atlantic water expanded far into the Arctic Ocean during the Last Interglacial, analysis of microfossil content of sediment cores reveals. This implies that summers in the Arctic were ice free during this period. The findings are published in Nature Geoscience.
Arctic sea ice, an important component of the Earth system, is disappearing fast under climate warming. Summer sea ice is anticipated to vanish entirely within this century. To gain a deeper understanding of the climate dynamics in a world without Arctic sea ice, researchers have turned to analogues from the geological past.
”The Last Interglacial, between ...
For several years now, women have been voting more left-wing than men. This trend first appeared in the 2017 German general election and intensified in 2021. This is shown by a study carried out by the sociologist Dr Ansgar Hudde from the Institute of Sociology and Social Psychology at the University of Cologne (UoC). The trend is most evident among the youngest voters aged 18 to 24: In this group, the Greens, the Left and the Social Democrats (SPD) are much more popular among women than among men; the radical right-wing AfD and, above all, the economically liberal FDP are much more popular among men. The Christian ...