(Press-News.org) About The Study: In this study of 230,000 persons with second primary cancers in the U.S., the Black population had a higher risk of death from both cancer and cardiovascular disease compared with the white population, whereas the Hispanic population had a higher risk of death from cancer. These results suggest that research priorities to address survival disparities in the growing population of survivors of multiple primary cancers are warranted.
Authors: Hyuna Sung, Ph.D., of the American Cancer Society in Atlanta, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.27429)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.27429?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=080423
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
Racial, ethnic disparities in survival among people with second primary cancer
JAMA Network Open
2023-08-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New study shows substantial racial and ethnic disparities among survivors of second primary cancers in the US
2023-08-04
ATLANTA, August 4, 2023 — In new findings from researchers at the American Cancer Society (ACS), non-Hispanic Black individuals diagnosed with a second primary cancer (SPC) experienced 21% higher cancer-related death rates and 41% higher cardiovascular-related death rates compared with their non-Hispanic White counterparts. The study also showed that Hispanic individuals diagnosed with a second primary cancer also experienced 10% higher cancer-related death rates compared with their non-Hispanic White counterparts, but 10% lower cardiovascular-related death rates. The paper was published ...
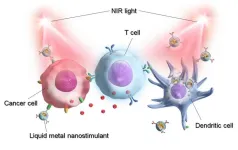
Novel liquid metal nanoparticles for cancer photoimmunotherapy
2023-08-04
Ishikawa, Japan -- Liquid metals (LM) such as pure gallium (Ga) and Ga-based alloys are a new class of materials with unique physicochemical properties. One of the most prominent applications of LMs is photothermal therapy against cancer, in which functional LM nanoparticles convert light energy to heat energy, thus killing cancerous cells. LM-based phototherapy is superior to traditional cancer therapy owing to its high specificity, repeatability, and low side effects.
In a new cutting-edge study, Associate Professor Eijiro Miyako and his colleagues from Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (JAIST) synthesized multifunctional Ga-based nanoparticles that combine cancer ...
Study finds breastfeeding helps mother’s cardio health for 3 years or more
2023-08-04
Breastfeeding for six months or more appears to reduce the risk of cardiovascular problems developing in mothers for at least three years after delivery, a new South Australian study has found.
The surprising cardio-metabolic benefit for maternal health is particularly important for women who experienced a complicated pregnancy, which can increase their chance of developing cardiovascular disease (CVD) later in life.
The new results – published this month in the International Breastfeeding Journal by experts from the University of Adelaide ...
Long-term collection of patient-reported outcome data in oncology trials: Important and feasible
2023-08-04
Patient-reported outcome (PRO) data are collected in oncology trials to determine patients' perspectives of cancer treatment - unfortunately often too briefly, for example only up to the point when an x-ray shows tumour growth and treatment is discontinued. As a result, it is not possible, for example, to reliably assess the impact on patients' lives of disease progression seen on X-rays or the long-term side effects of cancer treatment. The reasons given for this are organizational difficulties or patients’ lack of interest in long-term follow-up. ...
Invasion of the Arctic Ocean by Atlantic plankton species reveals a seasonally ice-free ocean during the last interglacial
2023-08-04
A subpolar species associated with Atlantic water expanded far into the Arctic Ocean during the Last Interglacial, analysis of microfossil content of sediment cores reveals. This implies that summers in the Arctic were ice free during this period. The findings are published in Nature Geoscience.
Arctic sea ice, an important component of the Earth system, is disappearing fast under climate warming. Summer sea ice is anticipated to vanish entirely within this century. To gain a deeper understanding of the climate dynamics in a world without Arctic sea ice, researchers have turned to analogues from the geological past.
”The Last Interglacial, between ...
In Germany, women vote more left-wing – but that was not always the case
2023-08-04
For several years now, women have been voting more left-wing than men. This trend first appeared in the 2017 German general election and intensified in 2021. This is shown by a study carried out by the sociologist Dr Ansgar Hudde from the Institute of Sociology and Social Psychology at the University of Cologne (UoC). The trend is most evident among the youngest voters aged 18 to 24: In this group, the Greens, the Left and the Social Democrats (SPD) are much more popular among women than among men; the radical right-wing AfD and, above all, the economically liberal FDP are much more popular among men. The Christian ...
They got more than me! The brain circuit for socially subjective reward valuation
2023-08-04
Okazaki, Japan – Although you might never have consciously considered it, it’s very likely that when you receive a reward, part of the value that you place on it depends on what other people have received as similar rewards. In a recent study published in Nature Communications, Japanese researchers have identified an important brain circuit for this specific process.
Although researchers have identified the brain regions that are important for deciding the value of a reward in relation to those of others (a process the authors termed ‘socially subjective reward valuation’), the connections between these regions have never been ...
ASBMB calls for student loan relief
2023-08-04
On June 20, the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology submitted public hearing testimony to the Department of Education expressing concerns about the growing burden of student loan debt. The society called for expanding debt-relief programs across all educational levels and allowing postdoctoral researchers to defer loan payments until after completion of their training.
“We are in the midst of a student debt crisis, and it's hurting the research enterprise and more importantly, the next generation of scientists,” Sarina Neote, ASBMB public affairs director, said. “The average student ...
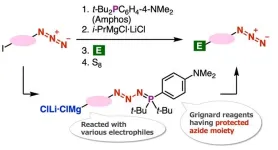
Scientists develop novel method to synthesize azide compounds for wider industrial applications
2023-08-04
Azide compounds play a pivotal role for subsequent synthesis of organonitrogens such as amines and triazoles that are essential compounds in organic and materials chemistry. Triazoles that can be synthesized by the ‘click’ reaction have attracted attention in the development of pharmaceuticals and other industries. However, the azido groups are electrophilic and are susceptible to various nucleophiles such as carbanions. This poses a significant challenge for the synthesis of carbanions having azido groups.
To this end, a team of researchers from Japan, led by Associate Professor Suguru ...
Telehealth Week @ TTUHSC Conference to highlight digital health care
2023-08-04
Telehealth Week @ TTUHSC, a conference about digital innovation, will offer an immersive experience in digital health using technology for access to care. The free conference, which takes place Sept. 19-21 at the TTUHSC Academic Event Center located at 3601 Fourth St., is open to all clinicians, administrators, health care providers and stakeholders.
The conference aims to demonstrate how digital health enhances access to care and solves rural health disparities. Three goals of the conference include:
Exposing stakeholders to the broader goals of digital health at TTUHSC
Motivating stakeholders to go beyond telehealth and embrace the fullness of digital ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
Rapid evolution can ‘rescue’ species from climate change
Molecular garbage on tumors makes easy target for antibody drugs
New strategy intercepts pancreatic cancer by eliminating microscopic lesions before they become cancer
Embryogenesis in 4D: a developmental atlas for genes and cells
CNIO research links fertility with immune cells in the brain
Why do lithium-ion batteries fail? Scientists find clues in microscopic metal 'thorns'
Surface treatment of wood may keep harmful bacteria at bay
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
[Press-News.org] Racial, ethnic disparities in survival among people with second primary cancerJAMA Network Open