(Press-News.org) Okazaki, Japan – Although you might never have consciously considered it, it’s very likely that when you receive a reward, part of the value that you place on it depends on what other people have received as similar rewards. In a recent study published in Nature Communications, Japanese researchers have identified an important brain circuit for this specific process.
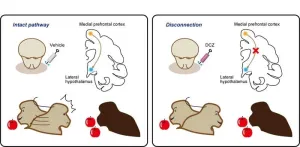
Although researchers have identified the brain regions that are important for deciding the value of a reward in relation to those of others (a process the authors termed ‘socially subjective reward valuation’), the connections between these regions have never been tested experimentally. The research team from the National Institute for Physiological Sciences (NIPS) decided to create a temporary disconnect between the medial prefrontal cortex, which is part of the social brain network, and the lateral hypothalamus, which is involved in social reward valuation.
“We used a relatively new technique that is commonly known as DREADD, or ‘designer receptor exclusively activated by designer drug’, in macaque monkeys,” says senior author of the study Masaki Isoda. “This method allowed us to temporarily block most of the connections from the brain’s medial prefrontal cortex to the lateral hypothalamus.”
To test the effects of functionally disconnecting two regions of the monkeys’ brains responsible for socially subjective reward valuation, the researchers used an existing experimental setup. Two monkeys were sat together and shown pictures on a screen. After seeing each picture, only one of the monkeys (or sometimes neither of the monkeys) received water as a reward. By varying the probability of reward for each monkey over a series of tests, the researchers were able to see what happened when the monkeys expected a reward for themselves (they made many licking motions with their tongues) versus a reward for the other monkey (they made fewer licking motions).
“Using this test, we were able to see the effects of disconnecting the medial prefrontal cortex from the lateral hypothalamus on the monkeys’ expectations of rewards,” says Isoda. “We were excited to see that, with this disconnect, the monkeys were much less susceptible to the prospect of others receiving rewards, but that their own expectations of a reward did not change, suggesting that this pathway is a key circuit in socially subjective reward valuation only.”
Together with recent research suggesting that the medial prefrontal cortex/lateral hypothalamus circuit is crucial for social rank information in mice, these results indicate that this circuit underlies many important social behaviors. A better understanding of this pathway will aid in the clinical diagnosis and treatment of injuries or alterations to the medial prefrontal cortex and lateral hypothalamus.
###
The article, “Chemogenetic dissection of a prefrontal-hypothalamic circuit for socially subjective reward valuation in macaques,” was published in Nature Communications at DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-40143-x.
END
They got more than me! The brain circuit for socially subjective reward valuation
Researchers from the National Institute for Physiological Sciences (NIPS) identify an important brain circuit for determining the value of your own reward in relation to others’ rewards
2023-08-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
ASBMB calls for student loan relief
2023-08-04
On June 20, the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology submitted public hearing testimony to the Department of Education expressing concerns about the growing burden of student loan debt. The society called for expanding debt-relief programs across all educational levels and allowing postdoctoral researchers to defer loan payments until after completion of their training.
“We are in the midst of a student debt crisis, and it's hurting the research enterprise and more importantly, the next generation of scientists,” Sarina Neote, ASBMB public affairs director, said. “The average student ...
Scientists develop novel method to synthesize azide compounds for wider industrial applications
2023-08-04
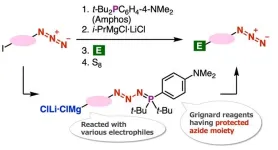
Azide compounds play a pivotal role for subsequent synthesis of organonitrogens such as amines and triazoles that are essential compounds in organic and materials chemistry. Triazoles that can be synthesized by the ‘click’ reaction have attracted attention in the development of pharmaceuticals and other industries. However, the azido groups are electrophilic and are susceptible to various nucleophiles such as carbanions. This poses a significant challenge for the synthesis of carbanions having azido groups.
To this end, a team of researchers from Japan, led by Associate Professor Suguru ...
Telehealth Week @ TTUHSC Conference to highlight digital health care
2023-08-04
Telehealth Week @ TTUHSC, a conference about digital innovation, will offer an immersive experience in digital health using technology for access to care. The free conference, which takes place Sept. 19-21 at the TTUHSC Academic Event Center located at 3601 Fourth St., is open to all clinicians, administrators, health care providers and stakeholders.
The conference aims to demonstrate how digital health enhances access to care and solves rural health disparities. Three goals of the conference include:
Exposing stakeholders to the broader goals of digital health at TTUHSC
Motivating stakeholders to go beyond telehealth and embrace the fullness of digital ...
A new technique offers improved diagnostic precision and a route to personalized therapy for a common arrhythmia that affects more than 10 million people in Europe
2023-08-04
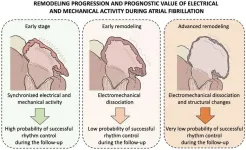
A multidisciplinary study led by scientists at the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC) presents a new method for assessing the structural and electrophysiological changes, called atrial remodeling, produced in the heart of patients with atrial fibrillation, one of the most frequent forms of cardiac arrhythmia. The new diagnostic method is based on the simultaneous assessment of electrical and mechanical (contractile) activity in the heart atria during atrial fibrillation. The study is published in Nature Communications (DOI 10.1038/s41467-023-40196-y).
Study leader David Filgueiras explained that, until now, “this was an unmet challenge,” because, on the one ...
Prenatal diagnosis matters: Linked to earlier surgery for congenital heart disease
2023-08-04
A study from Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago has shown that prenatal diagnosis, or diagnosis before a baby is born, is associated with earlier surgery for babies with congenital heart defects, the most common birth defects affecting nearly 1% of all live births. The association was demonstrated for critical defects (when heart surgery is required before the infant leaves the hospital) and certain types of noncritical defects, which constitute about 75% of all congenital heart defects.
The benefits of prenatal ...
Researchers find genetic cause of Raynaud’s phenomenon
2023-08-04
Researchers at Queen Mary University of London’s Precision Healthcare Research Institute (PHURI) and the Berlin Institute of Health (BIH) at Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin have identified the genetic causes of Raynaud’s phenomenon. Their findings, published today in Nature Communications, could lead to the first effective treatments for people with Raynaud’s.
Raynaud’s phenomenon (RP) is a heritable condition that affects blood circulation. It’s a vasopastic condition, which means ...
Consuming added sugars may increase risk of kidney stones
2023-08-04
Between 7% and 15% of people in North America, between 5% and 9% of people in Europe, and between 1% and 5% of people in Asia suffer from kidney stones. Common symptoms are severe pain, nausea, vomiting, fever, chills, and bloody urine. But kidney stones don’t just reduce the quality of life: in the long run, they may lead to infections, swollen kidneys (hydronephrosis), renal insufficiency, and end-stage renal disease. Known risk factors for developing kidney stones include being an adult male, obesity, chronic diarrhea, dehydration, and having inflammatory bowel disease, diabetes, or gout.
Now, a ...
Tropical plant native to China reveals antiobesity potential
2023-08-04
Obesity, a major risk factor for various lifestyle diseases such as diabetes and hypertension has become widespread worldwide, inherently demanding innovative solutions to combat it.
A multi-institutional research group led by Associate Professor Akiko Kojima of the Graduate School of Human Life and Ecology at Osaka Metropolitan University, has made significant progress in the fight against obesity. The group had previously conducted a study on the effects of the extract of Mallotus furetianus (MFE), a tropical plant native to Hainan Island, China, on the prevention of fatty liver, but the antiobesity effects of MFE and its mechanisms had not been ...
Parasites of viruses drive superbug evolution
2023-08-04
In a study published today in Cell, one of the most prominent peer-reviewed scientific journals in the field of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology, scientists from the National University of Singapore (NUS) and Imperial College London have discovered a new way by which bacteria transmit their genes, enabling them to evolve much faster than previously understood. Led by Assistant Professor John Chen from the Department of Microbiology and Immunology and the Infectious Diseases Translational Research Programme at the NUS Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine (NUS Medicine), ...
Geomagnetic field protects Earth from electron showers
2023-08-04
Understanding the ionosphere high in the Earth's atmosphere is important due to its effects on communications systems, satellites and crucial chemical features including the ozone layer. New insights into the activity of high energy electrons have come from a simulation study led by geophysicist Yuto Katoh at Tohoku University, reported in the journal Earth, Planets and Space.
"Our results clarify the unexpected role of the geomagnetic field surrounding the Earth in protecting the atmosphere from high energy electrons," says Katoh.
The ionosphere is a wide region between roughly ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
Plants pause, play and fast forward growth depending on types of climate stress
University of Minnesota scientists reveal how deadly Marburg virus enters human cells, identify therapeutic vulnerability
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
[Press-News.org] They got more than me! The brain circuit for socially subjective reward valuationResearchers from the National Institute for Physiological Sciences (NIPS) identify an important brain circuit for determining the value of your own reward in relation to others’ rewards