(Press-News.org) Researchers at Queen Mary University of London’s Precision Healthcare Research Institute (PHURI) and the Berlin Institute of Health (BIH) at Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin have identified the genetic causes of Raynaud’s phenomenon. Their findings, published today in Nature Communications, could lead to the first effective treatments for people with Raynaud’s.
Raynaud’s phenomenon (RP) is a heritable condition that affects blood circulation. It’s a vasopastic condition, which means that small blood vessels near the surface of the skin have spasms that can limit blood flow. People with Raynaud’s often experience pain in their fingers and toes, often alongside changes of colour in their skin, due a lack of blood flow during attacks when they’re cold or emotionally stressed. In more serious cases, it can cause severe pain or ulcers.
Around 2-5% of the population are affected by Raynaud’s. Despite it being a common condition, it’s under-investigated and little is understood about the genetic cause of the condition.
There are limited treatments available for RP. Doctors usually advise that the patient use 'self-management' strategies such as keeping warm and avoiding triggers of attacks. In severe cases medications can be prescribed, these are 'repurposed drugs', usually medicines to lower high blood pressure. These often cause severe side effects in patients. A better understanding of the underlying genetic mechanisms that cause RD is needed to develop safe and effective treatments.
Researchers led by Professor Claudia Langenberg and Professor Maik Pietzner, working across PHURI and the BIH, carried out the largest genome-wide association study (GWAS) for Raynaud’s phenomenon. The team used electronic health records from the UK Biobank, a large-scale biomedical database and research resource containing genetic and health information from half a million UK participants, to identify more than 9,000 people affected by Raynaud’s. The team also used electronic health records from Queen Mary’s Genes & Health study.
The findings
The researchers discovered variation in two genes that predisposed participants to Raynaud's phenomenon: One was the alpha-2A-adrenergic receptor for adrenaline, ADRA2A, a classic stress receptor that causes the small blood vessels to contract.
"This makes sense when it's cold or dangerous, because the body has to supply the inside of the body with blood," explains Maik Pietzner, Health Data Chair of PHURI and co-lead of the Computational Medicine Group at BIH.
"In Raynaud's patients, however, this receptor seemed to be particularly active, which could explain the vasospasms, especially in combination with the second gene that we found: This gene is the transcription factor IRX1, which may regulate the ability of blood vessels to dilate.
If its production is increased, it may activate genes that prevent constricted vessels from relaxing as they would normally do. Together with the overactive adrenaline receptor, this may then lead to the vessels not suppling enough blood for a longer period of time, which leads to the observed white fingers and toes.”
The researchers were also able to replicate parts of their findings using data from participants of British Bangladeshi and Pakistani origin from Queen Mary’s Genes & Health study.
The researchers’ findings also help to understand for the first time why the small vessels react so strongly in patients, even apparently without external stimuli, such as exposure to cold.
Dr Emma Blamont, Head of Research for Scleroderma and Raynaud's UK (SRUK), said:
"Raynaud's is a painful, chronic condition that affects around one in ten people in the UK. We know that attacks can be brought on by certain triggers like cold and stress, but relatively little is known about why some people experience Raynaud’s and others don’t. For the millions of people living with this condition, simple everyday tasks can be a challenge, so research like this, which significantly advances our understanding of Raynaud's and the role that genetics may play in causing it, is crucial.
"The next step is to confirm these important findings in more diverse population groups and validate the results through functional studies. If successful, these findings could help us unlock more new therapeutic avenues for Raynaud’s leading to better, more targeted and kinder treatments."
The findings could lead to recommendations for patients to help manage the condition. For example, the researchers showed that people with a genetic predisposition to low blood sugar levels have an increased risk of Raynaud's phenomenon and therefore patients should possibly avoid longer episodes of low blood sugar. Their findings may even point to novel treatment options as Claudia Langenberg explained “For example, already approved drugs that more or less specifically inhibit the function of ADRA2A could be an alternative, such as the antidepressant mirtazapine.
"I am convinced that our findings provide a path to novel effective medications.”
ENDS
END
Between 7% and 15% of people in North America, between 5% and 9% of people in Europe, and between 1% and 5% of people in Asia suffer from kidney stones. Common symptoms are severe pain, nausea, vomiting, fever, chills, and bloody urine. But kidney stones don’t just reduce the quality of life: in the long run, they may lead to infections, swollen kidneys (hydronephrosis), renal insufficiency, and end-stage renal disease. Known risk factors for developing kidney stones include being an adult male, obesity, chronic diarrhea, dehydration, and having inflammatory bowel disease, diabetes, or gout.
Now, a ...
Obesity, a major risk factor for various lifestyle diseases such as diabetes and hypertension has become widespread worldwide, inherently demanding innovative solutions to combat it.
A multi-institutional research group led by Associate Professor Akiko Kojima of the Graduate School of Human Life and Ecology at Osaka Metropolitan University, has made significant progress in the fight against obesity. The group had previously conducted a study on the effects of the extract of Mallotus furetianus (MFE), a tropical plant native to Hainan Island, China, on the prevention of fatty liver, but the antiobesity effects of MFE and its mechanisms had not been ...
In a study published today in Cell, one of the most prominent peer-reviewed scientific journals in the field of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology, scientists from the National University of Singapore (NUS) and Imperial College London have discovered a new way by which bacteria transmit their genes, enabling them to evolve much faster than previously understood. Led by Assistant Professor John Chen from the Department of Microbiology and Immunology and the Infectious Diseases Translational Research Programme at the NUS Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine (NUS Medicine), ...
Understanding the ionosphere high in the Earth's atmosphere is important due to its effects on communications systems, satellites and crucial chemical features including the ozone layer. New insights into the activity of high energy electrons have come from a simulation study led by geophysicist Yuto Katoh at Tohoku University, reported in the journal Earth, Planets and Space.
"Our results clarify the unexpected role of the geomagnetic field surrounding the Earth in protecting the atmosphere from high energy electrons," says Katoh.
The ionosphere is a wide region between roughly ...
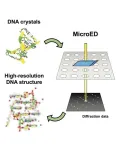
Function and form are deeply intertwined in biology. Knowing how organisms grow, adapt and reproduce requires understanding their physical structures. Hence the transformative power of the microscope across the past four centuries of science.
Microscopy, or the field of microscope use, can now reveal the tiniest of structures through techniques such as microcrystal electron diffraction, or MicroED. Instead of passing light through a cell like an optical microscope, MicroED bombards crystalline samples with a stream of electrons to produce detailed information about their atomic configuration.
“The method was developed ...
Korean researchers have unveiled a novel signaling pathway that fosters aging-related chronic metabolic disorders.
A research team led by Professor Jong Kyoung Kim from the Department of Life Sciences at POSTECH along with Professor Seung-Hoi Koo from the Division of Life Sciences at Korea University and principal researcher Geum-Sook Hwang from Korea Basic Science Institute (KBSI) announced the discovery of a new mechanism where BCAA metabolic pathway becomes impaired due to aging, resulting in dysfunctions of adipose cells and chronic metabolic disorders. The research findings were published in Nature Aging (IF=16.6) ...
Leesburg, VA, August 4, 2023—An accepted manuscript published in the American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR) found that deploying a radiomic-based model with T2-weighted MRI data could increase diagnostic accuracy for pediatric Crohn disease (CD).
Noting that ileal-wall radiomic features were strongly predictive of CD—and that model performance improved when ensembled with clinical data—“a radiomic machine learning model predicted CD diagnosis with better performance than two of three expert radiologists,” wrote corresponding author and AJR Pediatric Imaging Section Editor Jonathan R. Dillman, MD, MSc.
Dillman et al.’s manuscript ...
Childhood trauma, such as abuse, emotional neglect, and exposure to domestic violence, may heighten a woman’s subsequent risk of pregnancy complications, and of giving birth to a low birthweight or premature baby, finds a pooled data analysis of the available evidence, published in the open access journal BMJ Open.
The risks of pregnancy related diabetes, high blood pressure, depression/anxiety and of giving birth to underweight and or premature babies may all be significantly higher, the analysis suggests.
While previously ...
The use of essential peppermint oil aromatherapy may ease pain severity after open heart surgery and enhance sleep quality as well, suggest the results of a small comparative clinical trial, published online in the journal BMJ Supportive & Palliative Care.
Heart surgery is a major procedure, necessitating the separation of the breastbone (sternum) as well as mechanical breathing support, both of which are associated with a high risk of severe pain, stress, and sleeplessness, note the researchers.
Effective pain relief allows patients to recover more quickly and may reduce the risk of postoperative complications, ...
SEATTLE, Wash. August 3, 2023 – An analysis of 19 causes of death in the United States revealed persistent disparities and a familiar pattern across five racial-ethnic groups and 3,110 counties from 2000 to 2019. That’s according to the most comprehensive peer-reviewed research published today in The Lancet.
The mortality rates among American Indian or Alaska Native (AIAN) and Black populations were substantially higher than among White populations nationally and in most counties. For example, mortality was higher among the AIAN population than the White population in nearly all counties for skin and ...