(Press-News.org) Researchers at Uppsala university have developed a new method to find mutations in brain tumors in children. They could also show that the mutations identified by them changes how cancer cells respond to a cancer drug. These findings could lead to better diagnostics and more individualized treatment of children with brain tumors. The study is published in the journal PNAS.
Medulloblastoma is the most common malignant brain tumor in children. It usually develops in the cerebellum and even if modern treatment has improved the prognosis so that over 70% live more than five years, not all patients can be cured. The aggressive cancer treatment also causes severe side effects such as balance problems and impaired learning abilities in cancer survivors.
Numerous studies have explored the less than two percent of human DNA which gives rise to proteins, and much less is known about the rest of the genome. In a cancer, such as medulloblastoma, 98% of the mutations thus occur in the less studied part of the genome. There could be thousands of mutations, and it is difficult to separate the ones driving the cancer from those without importance.
To gain a comprehensive view of what mutations are important in medulloblastoma, the researchers used a method that they recently developed as part of an international consortium. The method specifically looks at conserved positions in the genome, and builds on the assumption that DNA-sequences that has remained the same over millions of years of evolution are likely to have important functions.
“In the new study, mutations in patients with medulloblastoma were compared with information about how well an individual position in the genome has been kept throughout evolution. Mutations in areas that hardly changed at all can be assumed to be most important,” says Ananya Roy, researcher and shared first author of the new study.
Our of the 200 000 mutations found in 145 patients, a total of 114 mutations were found in conserved positions in the genome. Many of these mutations occurred in genes that were previously not reported to be mutated in this cancer, even though some of the genes had altered protein levels in medulloblastoma. The newly identified mutations are located in DNA that contains instructions about where, when and how much of proteins should be made. The results may therefore explain earlier observations of different protein levels in medulloblastoma.
“We focused on mutations at the best-preserved positions, as these are likely the most critical ones for gene regulation. This way we can sort out the most important mutations, which would otherwise not be possible, and then test their functionality”, says Karin Forsberg-Nilsson, one of the researchers who led the study.
The researchers found different mutations in different age groups and different subgroups of medulloblastoma, and that the mutations changed gene expression in medulloblastoma cell in culture.
“This shows that our method works, and can provide a clearer picture of how these mutations regulate protein levels in cancer cells”, says Kerstin Lindblad-Toh, who also led the study.
In the study, the researchers could also show that mutations found by the new method modified the cancer cells’ resistance to a cancer drug. This new way of analyzing mutations could therefore suggest individual treatment, so called precision medicine.
This means that the patient’s specific mutation pattern is used to select a drug which affects the gene that is mutated in that individual, something which is more and more used in cancer care.
For this to work, however, there must be an already existing drug, maybe utilized for another disease, which can be used to treat a few cancer patients with the “right mutation”. The new study can expand the number of treatable mutations, which in the long run gives more individualized therapies to offer to patients.
“To be able to use cancer mutation analysis for precision medicine, a lot of genetic information about each patient is needed. Since all children with brain tumors in Sweden are now offered whole genome sequencing analysis, i.e. the entire tumor genome is mapped, there are good possibilities to develop the analysis further to benefit patients”, says Forsberg-Nilsson.
END
New method to identify mutations in childhood brain tumors
2023-08-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Climate influences the spread of a life-threatening zoonotic disease in the Amazon
2023-08-07
Outbreaks of polycystic echicnococcosis, a life-threatening zoonotic disease, are driven by regional climate changes, according to a study led by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), an institution supported by “la Caixa” Foundation. The findings, published in PNAS, provide evidence of the impact of climate on neglected tropical diseases in the Amazon region, with implications for other zoonoses.
Polycystic echinococcosis (PE) is a neglected life-threatening zoonosis caused by an intestinal worm (Echinococcus vogeli) ...
Research discovers key cause of restricted blood flow to the brain in vascular dementia
2023-08-07
Groundbreaking new research has uncovered a potential route to developing the first ever drug treatments for vascular dementia, that directly target a cause of the condition. The research, funded by the British Heart Foundation and published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, [1] has shed light on how high blood pressure causes changes to arteries in the brain, a process that leads to the devastating condition.
High blood pressure is a main cause of vascular dementia, a condition characterised by poor blood flow to the brain. The reduced blood supply starves brain cells of nutrients and over time they become damaged ...
Latest in body art? ‘Tattoos’ for individual cells
2023-08-07
Engineers have developed nanoscale tattoos—dots and wires that adhere to live cells—in a breakthrough that puts researchers one step closer to tracking the health of individual cells.
The new technology allows for the first time the placement of optical elements or electronics on live cells with tattoo-like arrays that stick on cells while flexing and conforming to the cells’wet and fluid outer structure.
“If you imagine where this is all going in the future, we would like to have sensors to remotely monitor and ...
Georgia State Researcher awarded $3.6 million grant to help address mental health crisis in schools
2023-08-07
ATLANTA — Catherine Perkins, a clinical professor in the College of Education & Human Development at Georgia State University, has been awarded a five-year, $3.6 million grant by the U.S. Department of Education to expand quality school-based mental health (SBMH) services for underserved populations in high-need schools.
The Expanding Quality SBMH Services for Underserved Populations with Inclusive Practices (GSU-EQUIP) grant will have a direct impact in metro Atlanta by increasing access to school-based programs and strengthening the candidate pool of mental ...
Current estimates of Lake Erie algae toxicity may miss the mark
2023-08-07
COLUMBUS, Ohio – There is more to a harmful algal bloom than the green stuff in water that meets the eye – specifically, a changing hazard level of toxins produced by the microbes that make up the scummy mess.
A new study analyzing toxins produced by Microcystis, the main type of cyanobacteria that compose the annual harmful algal bloom (HAB) in Lake Erie, suggests that the toxicity of the bloom may be overestimated in earlier warm months and underestimated later in the summer.
The research is part of a large project, led by The Ohio State University, designed to develop a more accurate harmful algal bloom toxicity forecast ...
Dogs with less complex facial markings found to be more expressive in their communication with humans
2023-08-07
WASHINGTON (August 7, 2023) – The domestication of canines and their co-evolution with humans has fostered an incredibly unique relationship with these animals. Over time, our four-legged friends have adapted well to understanding human modes of communication, both verbal and nonverbal. However, researchers at the George Washington University say humans could do more to better understand our furry companions, and a dogs’ facial markings may be one key to meeting them halfway.
In a new paper published in the journal Animals, ...
Century-old coral reveals Pacific western boundary current strengthened as climate warmed, impacting El Niño
2023-08-07
Chestnut Hill, Mass. (8/7/2023) - The Pacific Ocean’s western boundary current, which forms a critical regulator of sea surface temperature and weather patterns, has significantly strengthened as the planet warms, according to a new study published in the journal Nature Geoscience.
The study provides the first evidence that the western boundary current in the South Pacific has significantly strengthened during the 20th century in response to global warming, contributing to an intensified equatorial undercurrent, according to Boston College Assistant Professor of Earth and Environmental Sciences Xingchen (Tony) Wang, a co-author ...
For Black teens, school belonging can be a matter of life and death
2023-08-07
Academic performance has long been linked to how supported students feel at school. Now, a Rutgers study suggests this sentiment is also essential to preventing suicides.
A Rutgers researcher found that having a strong sense of school belonging – the subjective feeling of being accepted, valued, included and encouraged in the school community – could mitigate suicidal tendencies among Black adolescents.
“Having a supportive teacher or other nonparent adult can change a child’s life because they will want to go to school,” said Adrian Gale, an assistant professor at the Rutgers School of Social Work and co-author of the study ...
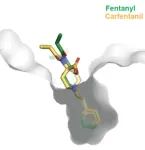
Human antibody that targets carfentanil, fentanyl and related opioids reverses overdose effects in preclinical study
2023-08-07
LA JOLLA, CA—An antibody in single-chain fragment variable (scFv) format that binds to the powerful opioid carfentanil was shown to reverse signs of carfentanil overdose in preclinical tests conducted by scientists at Scripps Research.
Carfentanil is a variant of the synthetic opioid fentanyl, and about 100 times as potent as its chemical cousin. Along with fentanyl and other fentanyl variants, it is commonly mixed with illegal drugs such as heroin and cocaine to enhance their euphoric effects, resulting in many fatal overdoses.
In the study, published in ACS ...
Midwest Integrated Center for Computational Materials renewed by U.S. Department of Energy
2023-08-07
The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) has announced the renewal of the Midwest Integrated Center for Computational Materials (MICCoM) for another three years at $3 million per year. Founded in 2015, the Center is headquartered at DOE’s Argonne National Laboratory. Partnering universities include the University of Chicago, University of Notre Dame and University of California, Davis.
“The MICCoM team has been at the forefront of developing simulation methods and codes and solving cutting-edge materials science problems,” said Center director Giulia Galli. She is also a senior scientist in Argonne’s Materials Science division and professor in the ...