(Press-News.org) Philadelphia, August 8, 2023 – There is a need to better deliver information on medical nutrition therapy for patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD). Findings of a new study in the Journal of Nutrition Education and Behavior, published by Elsevier, show digital health serves as an additional health service resource, which increases the healthcare provider’s abilities to collect current visual and objective data, thereby decreasing patient and caregiver burden and medical expenses.
Lead author Dara Lyn LoBuono, PhD, RD, assistant professor in health and exercise science at Rowan University, says, “People with PD are ideal candidates for using digital health platforms because of their decreased mobility, lack of transportation, the need for visual assessment by their health care team, and informal caregivers to be present at health appointments.”
LoBuono conducted the research as a PhD candidate at the University of Rhode Island under the advisement of Ingrid Lofgren, PhD, MPH, RD, professor in the department of nutrition. The study took place in the northeast US during home visits with individuals with PD and their caregivers. Semistructured dyadic interviews with 20 dyads (20 people with Parkinson’s disease and 20 caregivers) were conducted. Researchers used a technology acceptance model and transition theory to inform and guide their development and research. This model provides a basis for understanding external factors influencing end user perceptions, attitudes and intentions to use technology throughout usage.
The research showed that digital health platforms can successfully deliver nutrition services for patients with Parkinson’s disease (PwPD) and their caregivers by personalizing digital services to meet their needs (e.g., disease stage), clearly communicating the benefits of the digital service platforms, training people on how to effectively use the technology (while offering continuous support, when needed), and promoting social interaction with the nutrition expert and members of the PD community while using the digital platform. With the implementation of these findings, digital nutrition service platforms could improve the quality of life for those suffering with PD and their caregivers.
Despite the many benefits of digital health, barriers exist to using these platforms for PwPD. For example, cognitive changes and PD-related tremors can make the software and hardware interface difficult for PwPD.
The authors explain, “Sixteen patients interviewed revealed they did not have access to certain technologies…. [They] did not know how to use some technologies and/or were unsure how they could benefit from technology.”
Additional barriers include difficulties remembering how to operate the devices, concerns around the clarity of information provided, lack of added value, technology being time-consuming, compatibility issues, and privacy concerns.
The authors note, “Overall, findings from this research support developing, piloting, and examining the acceptability and feasibility of a digital health platform to deliver a nutrition service across diverse PD communities that are convenient, include informal caregivers, and minimize participant burden.”
END
Well-designed digital health platforms can improve the quality of life for people with Parkinson’s disease and their caregivers
Research published in the Journal of Nutrition Education and Behavior identified facilitators and barriers to using digital health platforms to inform future digital nutrition services
2023-08-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Bat activity lower at solar farm sites, study finds
2023-08-08
The activity level of six bat species was significantly reduced at solar farm sites, researchers have observed.
Their findings, published today in Journal of Applied Ecology, have the potential to impact and inform planning legislation and policy so that the benefits of solar power are reaped without impacting wildlife.
Renewable technologies are important in meeting energy demands sustainably. This is of vital importance given the roles of fossil fuels in producing carbon dioxide, a key driver of climate change. Renewable energy is growing at a rapid pace globally, with solar photovoltaic power ...
New model reduces bias and enhances trust in AI decision-making and knowledge organization
2023-08-08
University of Waterloo researchers have developed a new explainable artificial intelligence (AI) model to reduce bias and enhance trust and accuracy in machine learning-generated decision-making and knowledge organization.
Traditional machine learning models often yield biased results, favouring groups with large populations or being influenced by unknown factors, and take extensive effort to identify from instances containing patterns and sub-patterns coming from different classes or primary sources.
The medical field is one area where there are severe implications for biased machine learning results. Hospital staff and medical ...
Whale like filter-feeding discovered in prehistoric marine reptile
2023-08-08
A remarkable new fossil from China reveals for the first time that a group of reptiles were already using whale-like filter feeding 250 million years ago.
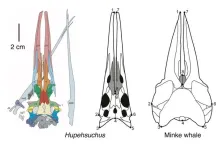
New research by a team from China and the UK has shown details of the skull of an early marine reptile called Hupehsuchus that indicate it had soft structures such as an expanding throat region to allow it to engulf great masses of water containing shrimp-like prey, and baleen whale-like structures to filter food items as it swam forward.
The team also found that the Hupehsuchus skulls show the same grooves and notches along the edges of its jaws similar to baleen whales, ...
New research shines light on how COVID-19 vaccination reduces severity and mortality after breakthrough infections
2023-08-08
In one of the largest studies of its kind, researchers provide answers to whether COVID-19 vaccinations reduce sickness and mortality following infection with SARS-CoV-2.
The study published today in The Lancet Microbe found among individuals recently infected with SARS-CoV-2, those who were fully vaccinated had lower concentrations of almost all inflammation markers (cytokines and chemokines) than those who were unvaccinated in the short-term and long-term after symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection.
While vaccinations don’t entirely prevent infection, this study demonstrates that vaccination significantly reduces morbidity and mortality by significantly reducing elevated levels ...
Air pollution linked to higher mental health service use by people with dementia
2023-08-08
Exposure to relatively high levels of air pollution is linked to increased use of community mental health services by people with dementia, finds a large long term study focusing on a large area of London with heavy traffic and published in the open access journal BMJ Mental Health.
Cutting levels of nitrogen dioxide and particulate matter might reduce demand in urban areas and help free up resources in overstretched psychiatric services, suggest the researchers.
An estimated 850,000 people are living with dementia in the UK, with the number projected to increase to 2 million by 2050, in tandem with the ageing of the population. Dementia is already the leading cause of death in the ...
Menstrual discs may be best for heavy monthly blood flow
2023-08-08
Amid widely differing capacities of available menstrual hygiene products, a menstrual disc—similar in shape to a diaphragm—may be best for dealing with heavy monthly blood flow as well as indicating excessive blood loss, suggests research published online in the journal BMJ Sexual & Reproductive Health.
Despite the fact that 800 million women around the globe will be on their period every day, menstruation remains something of a taboo subject—a stance that has hindered research and transformed a normal bodily process into something that is often associated with stigma and normalisation of pain, argue gynaecologists in a linked editorial.
Heavy ...
High level of heart attack protein linked to heightened risk of death from any cause
2023-08-08
A high level of troponin—a protein normally used to exclude the possibility of a heart attack in patients with chest pain—may signal a heightened risk of death from any cause within the next couple of years, even in the absence of known or suspected cardiovascular disease, suggests research published online in the journal Heart.
The finding prompts the researchers to suggest that troponin may therefore have a role as a more general indicator of medium term survival.
High cardiac troponin levels are often seen in hospital patients who don’t have ...
The Lancet Planetary Health: Antibiotic resistance increases may be linked to rising air pollution, first in-depth global analysis suggests
2023-08-08
Peer-reviewed / Observational and modelling study
Curbing levels of harmful air pollution could help reduce antibiotic resistance, according to the first in-depth global analysis of possible links between the two, published in The Lancet Planetary Health journal.
Findings from the study highlight that controlling air pollution could greatly reduce deaths and economic costs stemming from antibiotic-resistant infections.
The analysis indicates that increased air pollution is potentially linked with a higher risk of antibiotic resistance across global regions. It also indicates that the relationship between the two has strengthened over time, ...
Managing domestic and wildcats is likely to remain fraught, new research warns
2023-08-08
Current efforts to protect and restore native biodiversity is being threatened by difficulties in identifying wild and domestic cats, and categorisation is likely to remain fraught for the foreseeable future, experts have warned.
Efforts to restore the native wildcat (Felis sivestris) are ongoing in Britain and conservationists in New Zealand are also trying to protect native species. Domestic cats pose a threat to other species in both countries.
The study shows New Zealanders are much less sentimental about pest management to protect native species. As a result domestic cats are treated very differently in the two countries.
Dr Alexandra Palmer, ...
Brain’s ‘appetite control centre’ different in people who are overweight or living with obesity
2023-08-08
Cambridge scientists have shown that the hypothalamus, a key region of the brain involved in controlling appetite, is different in the brains of people who are overweight and people with obesity when compared to people who are a healthy weight.
The researchers say their findings add further evidence to the relevance of brain structure to weight and food consumption.
Current estimations suggest that over 1.9 billion people worldwide are either overweight or obese. In the UK, according to the Office for Health Improvement & Disparities, almost two-thirds ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Well-designed digital health platforms can improve the quality of life for people with Parkinson’s disease and their caregiversResearch published in the Journal of Nutrition Education and Behavior identified facilitators and barriers to using digital health platforms to inform future digital nutrition services