(Press-News.org) Skin, the largest organ of the human body, is home to a vast array of bacteria, fungi, and viruses – microorganisms that compose the skin microbiota. Among other things, these microbial populations, which are organized in complex community structures, protect against pathogens.
Prolonged exposure to UVR is associated with damage to DNA in skin cells, inflammation, and premature skin aging, yet intentional sun-seeking behaviors remain common.
Due to a lack of studies focusing on how individual behavior influences UVR-associated microbiota shifts, and how this may relate to skin health, researchers in the UK have now examined the effects of sun-seeking behaviors on the skin microbiota composition of holidaymakers.
“Here we show in a cohort of holidaymakers that their sun exposure behavior significantly affects the diversity and composition of their skin microbiota,” said Dr Abigail Langton, principal investigator at The University of Manchester and corresponding author of the study published in Frontiers in Aging.
“We have demonstrated that the development of a tan is associated with lower Proteobacteria abundance immediately post-holiday. However, the microbiota of all holidaymakers was recovered a few weeks after they stopped spending extended time periods in the sun.”
Sun-seeking harms skin bacteria
Prior to vacations to sunny destinations, which lasted at least seven days, the researchers analyzed participants’ skin. The skin microbiota is largely made up of three bacterial communities on the surface: Actinobacteria, Proteobacteria, and Firmicutes. On day one, 28, and 84 post-holiday, participants’ skin microbiota was assessed again.
Additionally, each holidaymaker was assigned a group based on individual tanning response. Eight out of 21 participants, who picked up a tan while on holiday, were deemed ‘seekers.’ The ‘tanned’ group was made up of seven individuals who already had a tan at departure and kept it throughout their holiday. These two groups were classified as ‘sun-seekers.’ The remaining six participants were deemed ‘avoiders;’ their skin tone was the same pre- and post-holiday.
“This study was performed in real-life holidaymakers and provides important insights into how sun exposure resulting in a tanning response – even over a relatively short sunny period – can lead to an acute reduction in Proteobacteria abundance, which decreased skin microbiota diversity,” Dr Thomas Willmott, the study’s first author and researcher at the University of Manchester, explained.
Despite the rapid reduction of Proteobacteria and the accompanying shift in skin microbiota diversity, the bacterial community structure had recovered 28 days after individuals had returned from vacation. “This indicates that UV exposure on holiday has an acute effect on the skin microbiota, but recovery is relatively rapid once the person returns to a less sunny climate,” Willmott continued.
Microbiota disturbance can cause health problems
“Proteobacteria dominate the skin microbiota. Accordingly, it is not surprising that there would be rapid recovery of the microbiota to re-establish optimal functioning conditions for the skin,” Langton pointed out. The authors state that what might be more concerning is the rapid alteration of microbiota diversity, which has been linked to disease states. A decrease in skin bacterial richness, for example, has been previously associated with dermatitis. Fluctuation in Proteobacteria diversity specifically has been associated with skin problems like eczema and psoriasis.
Future studies should examine why Proteobacteria seem to be particularly sensitive to UVR and how this change in diversity impacts skin health in the longer term, the researchers noted. “Ideally, such studies will aim to increase the number of participants to allow further insights,” Langton said.
END
Holidaymakers be warned: Short, intense sun-seeking trips can disrupt skin’s microbiome
Researchers have shown that too much sun exposure negatively affects short-term diversity and composition of the skin’s bacterial make-up
2023-08-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New Antarctic extremes ‘virtually certain’ as world warms
2023-08-08
Extreme events in Antarctica such as ocean heatwaves and ice loss will almost certainly become more common and more severe, researchers say.
With drastic action now needed to limit global warming to the Paris Agreement target of 1.5°C, the scientists warn that recent extremes in Antarctica may be the tip of the iceberg.
The study reviews evidence of extreme events in Antarctica and the Southern Ocean, including weather, sea ice, ocean temperatures, glacier and ice shelf systems, and biodiversity on land and sea.
It concludes that Antarctica’s fragile environments “may well be subject to considerable stress and ...
Three-dimensional printing achieves precision light control for structural coloration
2023-08-08
The world's first 3D printing technology that can be used in transparent displays and AR devices has been developed, which implements the physical phenomenon of chameleon's changing skin color or peacock's beautiful feather color.
Dr. Jaeyeon Pyo’s team at KERI has succeeded in realizing a three-dimensional diffraction grating that can precisely control the path of light based on 'nanoscale 3D printing technology'. This is a novel technology that can utilize the principle of structural color observed in nature ...
Well-designed digital health platforms can improve the quality of life for people with Parkinson’s disease and their caregivers
2023-08-08
Philadelphia, August 8, 2023 – There is a need to better deliver information on medical nutrition therapy for patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD). Findings of a new study in the Journal of Nutrition Education and Behavior, published by Elsevier, show digital health serves as an additional health service resource, which increases the healthcare provider’s abilities to collect current visual and objective data, thereby decreasing patient and caregiver burden and medical expenses.
Lead author Dara Lyn LoBuono, PhD, RD, assistant professor in health and exercise science at Rowan ...
Bat activity lower at solar farm sites, study finds
2023-08-08
The activity level of six bat species was significantly reduced at solar farm sites, researchers have observed.
Their findings, published today in Journal of Applied Ecology, have the potential to impact and inform planning legislation and policy so that the benefits of solar power are reaped without impacting wildlife.
Renewable technologies are important in meeting energy demands sustainably. This is of vital importance given the roles of fossil fuels in producing carbon dioxide, a key driver of climate change. Renewable energy is growing at a rapid pace globally, with solar photovoltaic power ...
New model reduces bias and enhances trust in AI decision-making and knowledge organization
2023-08-08
University of Waterloo researchers have developed a new explainable artificial intelligence (AI) model to reduce bias and enhance trust and accuracy in machine learning-generated decision-making and knowledge organization.
Traditional machine learning models often yield biased results, favouring groups with large populations or being influenced by unknown factors, and take extensive effort to identify from instances containing patterns and sub-patterns coming from different classes or primary sources.
The medical field is one area where there are severe implications for biased machine learning results. Hospital staff and medical ...
Whale like filter-feeding discovered in prehistoric marine reptile
2023-08-08
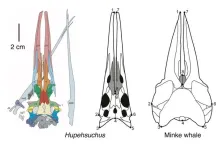
A remarkable new fossil from China reveals for the first time that a group of reptiles were already using whale-like filter feeding 250 million years ago.
New research by a team from China and the UK has shown details of the skull of an early marine reptile called Hupehsuchus that indicate it had soft structures such as an expanding throat region to allow it to engulf great masses of water containing shrimp-like prey, and baleen whale-like structures to filter food items as it swam forward.
The team also found that the Hupehsuchus skulls show the same grooves and notches along the edges of its jaws similar to baleen whales, ...
New research shines light on how COVID-19 vaccination reduces severity and mortality after breakthrough infections
2023-08-08
In one of the largest studies of its kind, researchers provide answers to whether COVID-19 vaccinations reduce sickness and mortality following infection with SARS-CoV-2.
The study published today in The Lancet Microbe found among individuals recently infected with SARS-CoV-2, those who were fully vaccinated had lower concentrations of almost all inflammation markers (cytokines and chemokines) than those who were unvaccinated in the short-term and long-term after symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection.
While vaccinations don’t entirely prevent infection, this study demonstrates that vaccination significantly reduces morbidity and mortality by significantly reducing elevated levels ...
Air pollution linked to higher mental health service use by people with dementia
2023-08-08
Exposure to relatively high levels of air pollution is linked to increased use of community mental health services by people with dementia, finds a large long term study focusing on a large area of London with heavy traffic and published in the open access journal BMJ Mental Health.
Cutting levels of nitrogen dioxide and particulate matter might reduce demand in urban areas and help free up resources in overstretched psychiatric services, suggest the researchers.
An estimated 850,000 people are living with dementia in the UK, with the number projected to increase to 2 million by 2050, in tandem with the ageing of the population. Dementia is already the leading cause of death in the ...
Menstrual discs may be best for heavy monthly blood flow
2023-08-08
Amid widely differing capacities of available menstrual hygiene products, a menstrual disc—similar in shape to a diaphragm—may be best for dealing with heavy monthly blood flow as well as indicating excessive blood loss, suggests research published online in the journal BMJ Sexual & Reproductive Health.
Despite the fact that 800 million women around the globe will be on their period every day, menstruation remains something of a taboo subject—a stance that has hindered research and transformed a normal bodily process into something that is often associated with stigma and normalisation of pain, argue gynaecologists in a linked editorial.
Heavy ...
High level of heart attack protein linked to heightened risk of death from any cause
2023-08-08
A high level of troponin—a protein normally used to exclude the possibility of a heart attack in patients with chest pain—may signal a heightened risk of death from any cause within the next couple of years, even in the absence of known or suspected cardiovascular disease, suggests research published online in the journal Heart.
The finding prompts the researchers to suggest that troponin may therefore have a role as a more general indicator of medium term survival.
High cardiac troponin levels are often seen in hospital patients who don’t have ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
[Press-News.org] Holidaymakers be warned: Short, intense sun-seeking trips can disrupt skin’s microbiomeResearchers have shown that too much sun exposure negatively affects short-term diversity and composition of the skin’s bacterial make-up