(Press-News.org) The world's first 3D printing technology that can be used in transparent displays and AR devices has been developed, which implements the physical phenomenon of chameleon's changing skin color or peacock's beautiful feather color.
Dr. Jaeyeon Pyo’s team at KERI has succeeded in realizing a three-dimensional diffraction grating that can precisely control the path of light based on 'nanoscale 3D printing technology'. This is a novel technology that can utilize the principle of structural color observed in nature for advanced display technology.
When light encounters a microstructure at the wavelength level (1/100 to 1/1000 of the thickness of a human hair), it diffracts* and changes its path. In cases where the microstructure possesses reularity, specific wavelengths of light undergo strong reflection due to diffraction, resulting in distinct colors known as ‘structural color’. For instance, in nature, the skin color of chameleons doesn't arise from a mixture of multiple pigments; rather, it emerges from changes in the microstructure, which lead to the production of structural colors. Similarly, the beautiful colors seen in peacock feathers are a result of the specific arrangement of their internal microstructure.
* Diffraction: A phenomenon in which light bends or spreads widely through a hole (gap) when it encounters an obstacle.
KERI's achievement is the realization of 'diffraction grating', which can precisely control structural color, with nanoscale 3D printing technology. A diffraction grating is a device with a regularly arranged microstructure for the purpose of controlling the diffraction of light. When light is shined on it, the light is reflected in different paths depending on the wavelength, creating a specific structural color or spectrum. In other words, it is a 3D printing technology that enables precise control of light for vivid coloration without dyes.
A very fine diffraction grating is needed to control the diffraction of light whose wavelength is only 1/1000th the thickness of a human hair. KERI, which has the world's best nanoscale 3D printing technology, succeeded in printing high-density nanowire diffraction gratings with a new approach called 'lateral printing'. This is done by moving the 3D printing nozzle as if it were sewing to print the bridge shape(﹇).
The demonstrated diffraction grating is expected to be used in a variety of advanced display applications. Noting the transparency of the diffraction grating itself, it can be used in a variety of future transparent displays such as smart windows, mirrors, and heads-up displays in automobiles. There are also many applications for this technology in AR devices that already utilize diffraction gratings as a key component. Furthermore, diffraction gratings can be designed to emit different colors depending on their deformation, making the technology usable in mechanical engineering and biomedical applications where deformation detection is required, and the diffraction grating itself can be used in a variety of optical physics research.
Dr. Jaeyeon Pyo of KERI said that this is "the world's first 3D printing technology that accurately implements the desired structural color in the desired location without restrictions on the material or shape of the substrate." He added that this technology will be able to overcome the formulaic 'Form-Factor' limitations of display devices and bring about diversification of shapes.
The research was recognized for its excellence and published as a cover article in ACS Nano, a top-tier SCI journal in materials science published by the American Chemical Society. The JCR Impact Factor, which measures the impact of a journal, is 17.100, placing it in the top 5.7% of its field.
KERI, which has completed the patent application of the original technology, expects this achievement to receive a lot of attention from display-related companies, and plans to promote technology transfer by identifying companies that need this technology.
Meanwhile, KERI is a government-funded research institute under the National Science and Technology Research Council of the Ministry of Science and ICT. This research was developed through KERI's basic project, 'Development of 4D printing technology for circuit/housing integrated devices'. Dr. Jaeyeon Pyo is also an adjunct associate professor at the University of Science and Technology (UST). <KERI>
END
Three-dimensional printing achieves precision light control for structural coloration
Dr. Jaeyeon Pyo's team at KERI developed a method for printing structural colors through nanoscale 3D printing of diffraction gratings, selected as a cover article for ACS Nano
2023-08-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Well-designed digital health platforms can improve the quality of life for people with Parkinson’s disease and their caregivers
2023-08-08
Philadelphia, August 8, 2023 – There is a need to better deliver information on medical nutrition therapy for patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD). Findings of a new study in the Journal of Nutrition Education and Behavior, published by Elsevier, show digital health serves as an additional health service resource, which increases the healthcare provider’s abilities to collect current visual and objective data, thereby decreasing patient and caregiver burden and medical expenses.
Lead author Dara Lyn LoBuono, PhD, RD, assistant professor in health and exercise science at Rowan ...
Bat activity lower at solar farm sites, study finds
2023-08-08
The activity level of six bat species was significantly reduced at solar farm sites, researchers have observed.
Their findings, published today in Journal of Applied Ecology, have the potential to impact and inform planning legislation and policy so that the benefits of solar power are reaped without impacting wildlife.
Renewable technologies are important in meeting energy demands sustainably. This is of vital importance given the roles of fossil fuels in producing carbon dioxide, a key driver of climate change. Renewable energy is growing at a rapid pace globally, with solar photovoltaic power ...
New model reduces bias and enhances trust in AI decision-making and knowledge organization
2023-08-08
University of Waterloo researchers have developed a new explainable artificial intelligence (AI) model to reduce bias and enhance trust and accuracy in machine learning-generated decision-making and knowledge organization.
Traditional machine learning models often yield biased results, favouring groups with large populations or being influenced by unknown factors, and take extensive effort to identify from instances containing patterns and sub-patterns coming from different classes or primary sources.
The medical field is one area where there are severe implications for biased machine learning results. Hospital staff and medical ...
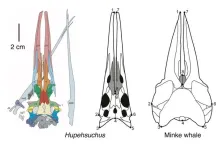
Whale like filter-feeding discovered in prehistoric marine reptile
2023-08-08
A remarkable new fossil from China reveals for the first time that a group of reptiles were already using whale-like filter feeding 250 million years ago.
New research by a team from China and the UK has shown details of the skull of an early marine reptile called Hupehsuchus that indicate it had soft structures such as an expanding throat region to allow it to engulf great masses of water containing shrimp-like prey, and baleen whale-like structures to filter food items as it swam forward.
The team also found that the Hupehsuchus skulls show the same grooves and notches along the edges of its jaws similar to baleen whales, ...
New research shines light on how COVID-19 vaccination reduces severity and mortality after breakthrough infections
2023-08-08
In one of the largest studies of its kind, researchers provide answers to whether COVID-19 vaccinations reduce sickness and mortality following infection with SARS-CoV-2.
The study published today in The Lancet Microbe found among individuals recently infected with SARS-CoV-2, those who were fully vaccinated had lower concentrations of almost all inflammation markers (cytokines and chemokines) than those who were unvaccinated in the short-term and long-term after symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection.
While vaccinations don’t entirely prevent infection, this study demonstrates that vaccination significantly reduces morbidity and mortality by significantly reducing elevated levels ...
Air pollution linked to higher mental health service use by people with dementia
2023-08-08
Exposure to relatively high levels of air pollution is linked to increased use of community mental health services by people with dementia, finds a large long term study focusing on a large area of London with heavy traffic and published in the open access journal BMJ Mental Health.
Cutting levels of nitrogen dioxide and particulate matter might reduce demand in urban areas and help free up resources in overstretched psychiatric services, suggest the researchers.
An estimated 850,000 people are living with dementia in the UK, with the number projected to increase to 2 million by 2050, in tandem with the ageing of the population. Dementia is already the leading cause of death in the ...
Menstrual discs may be best for heavy monthly blood flow
2023-08-08
Amid widely differing capacities of available menstrual hygiene products, a menstrual disc—similar in shape to a diaphragm—may be best for dealing with heavy monthly blood flow as well as indicating excessive blood loss, suggests research published online in the journal BMJ Sexual & Reproductive Health.
Despite the fact that 800 million women around the globe will be on their period every day, menstruation remains something of a taboo subject—a stance that has hindered research and transformed a normal bodily process into something that is often associated with stigma and normalisation of pain, argue gynaecologists in a linked editorial.
Heavy ...
High level of heart attack protein linked to heightened risk of death from any cause
2023-08-08
A high level of troponin—a protein normally used to exclude the possibility of a heart attack in patients with chest pain—may signal a heightened risk of death from any cause within the next couple of years, even in the absence of known or suspected cardiovascular disease, suggests research published online in the journal Heart.
The finding prompts the researchers to suggest that troponin may therefore have a role as a more general indicator of medium term survival.
High cardiac troponin levels are often seen in hospital patients who don’t have ...
The Lancet Planetary Health: Antibiotic resistance increases may be linked to rising air pollution, first in-depth global analysis suggests
2023-08-08
Peer-reviewed / Observational and modelling study
Curbing levels of harmful air pollution could help reduce antibiotic resistance, according to the first in-depth global analysis of possible links between the two, published in The Lancet Planetary Health journal.
Findings from the study highlight that controlling air pollution could greatly reduce deaths and economic costs stemming from antibiotic-resistant infections.
The analysis indicates that increased air pollution is potentially linked with a higher risk of antibiotic resistance across global regions. It also indicates that the relationship between the two has strengthened over time, ...
Managing domestic and wildcats is likely to remain fraught, new research warns
2023-08-08
Current efforts to protect and restore native biodiversity is being threatened by difficulties in identifying wild and domestic cats, and categorisation is likely to remain fraught for the foreseeable future, experts have warned.
Efforts to restore the native wildcat (Felis sivestris) are ongoing in Britain and conservationists in New Zealand are also trying to protect native species. Domestic cats pose a threat to other species in both countries.
The study shows New Zealanders are much less sentimental about pest management to protect native species. As a result domestic cats are treated very differently in the two countries.
Dr Alexandra Palmer, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
Digital microsteps as scalable adjuncts for adults using GLP-1 receptor agonists
Researchers develop a biomimetic platform to enhance CAR T cell therapy against leukemia
Heart and metabolic risk factors more strongly linked to liver fibrosis in women than men, study finds
Governing with AI: a new AI implementation blueprint for policymakers
Recent pandemic viruses jumped to humans without prior adaptation, UC San Diego study finds
Exercise triggers memory-related brain 'ripples' in humans, researchers report
Increased risk of bullying in open-plan offices
Frequent scrolling affects perceptions of the work environment
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
[Press-News.org] Three-dimensional printing achieves precision light control for structural colorationDr. Jaeyeon Pyo's team at KERI developed a method for printing structural colors through nanoscale 3D printing of diffraction gratings, selected as a cover article for ACS Nano