(Press-News.org)
“We argue that in multicellular organisms, neighbouring cells are in constant competition.”
BUFFALO, NY- August 9, 2023 – A new editorial paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 14, entitled, “A novel theory of ageing independent of damage accumulation.”
The underlying cause or causes of aging are an enduring mystery, but in 1977 Kirkwood postulated that organisms might gain a fitness advantage by reducing investment in somatic maintenance if this allowed them to invest more resources in more crucial processes such as reproduction. The accumulation of somatic damage was therefore inevitable, and his disposable soma theory has dominated gerontology ever since.
However, as our understanding of aging increases, it is becoming increasingly difficult to align all the aspects of aging with accumulating damage. For example, mutations that increase damage accumulation can also increase longevity, while rejuvenation revelations such as parabiosis and Yamanaka factors indicate that youthfulness can be regained without high energetic cost and despite high levels of damage.
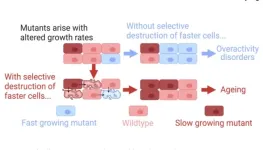
In their new editorial, researchers James Wordsworth and Daryl Shanley from Newcastle University discuss their recently published paper on selective destruction theory (SDT). SDT suggests a mechanism of aging which is both independent of accumulating damage and consistent with epigenetic rejuvenation. The authors used agent-based modeling to describe how aging could undergo positive selection independent of energetic costs.
“The mechanism of selective destruction is currently theoretical. In our most developed model, we demonstrated that if slow cells induced epigenetic changes in faster cells causing their metabolism to slow (rather than killing them) it not only reduced unnecessary cell death, but also further reduced the likelihood of overactivity disorders by preventing the spread of fast cells.”
Continue reading: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.204956
Corresponding Author: James Wordsworth
Corresponding Email: James.Wordsworth2@newcastle.ac.uk
Keywords: ageing, evolution, damage, cell competition, metabolic slowdown
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article: https://aging.altmetric.com/details/email_updates?id=10.18632%2Faging.https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.204956
About Aging:
Launched in 2009, Aging publishes papers of general interest and biological significance in all fields of aging research and age-related diseases, including cancer—and now, with a special focus on COVID-19 vulnerability as an age-dependent syndrome. Topics in Aging go beyond traditional gerontology, including, but not limited to, cellular and molecular biology, human age-related diseases, pathology in model organisms, signal transduction pathways (e.g., p53, sirtuins, and PI-3K/AKT/mTOR, among others), and approaches to modulating these signaling pathways.
Please visit our website at www.Aging-US.com and connect with us:
SoundCloud
Facebook
Twitter
Instagram
YouTube
LabTube
LinkedIn
Reddit
Pinterest
Click here to subscribe to Aging publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com.
Aging (Aging-US) Journal Office
6666 E. Quaker Str., Suite 1B
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957, option 1
###
END
MINNEAPOLIS – People who take acid reflux medications called proton pump inhibitors for four-and-a-half years or more may have a higher risk of dementia compared to people who do not take these medications, according to new research published in the August 9, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. This study does not prove that acid reflux drugs cause dementia; it only shows an association.
Acid reflux is when stomach acid flows into the esophagus, usually after a meal or when lying down. People with acid reflux may experience heartburn and ulcers. People ...
Research from experts at Michigan Medicine, the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and Penn Medicine is breaking ground on new ways of treating blood disorders, such as sickle cell anemia, through gene therapy.
To cure blood disorders, patients must undergo high dose chemotherapy and bone marrow transplantation. This requires a match between the recipient and donor immune system, but ~30% of patients do not have a match. Even when they do the donor immune system can attack the patient, graft versus host disease.
Gene therapy corrects the mutation in a patient’s own cells ...
ITHACA, N.Y. – Despite broad scientific consensus that climate change has more serious consequences for some groups – particularly those already socially or economically disadvantaged – a large swath of people in the U.S. doesn’t see it that way.
A new national survey study found that just over one-third of U.S. adults believe climate change is impacting some groups more than others. Nearly half feel that climate change impacts all groups about equally. And when the question referenced race in climate impacts, even fewer people believed some groups are more adversely affected than others.
“Our earlier research showed that ...
New observations of mud cracks made by the Curiosity Rover show that high-frequency, wet-dry cycling occurred in early Martian surface environments, indicating that the red planet may have once seen seasonal weather patterns or even flash floods. The research was published today in Nature. “These exciting observations of mature mud cracks are allowing us to fill in some of the missing history of water on Mars. How did Mars go from a warm, wet planet to the cold, dry place we know today? These mud cracks show us that transitional time, when liquid water was less abundant but still active on the ...
New research suggests that the US municipal bond market systemically misprices risk, as the pricing of municipal debt does not account for local physical climate risk, but does demand larger credit spreads from communities with a larger proportion of Black residents. Erika Smull of Duke University, US, and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on August 9.
Across the US, local governments issue municipal bonds to help fund various expenses, such as schools and sewer systems. ...
Two-thirds of turtle injuries and strandings recorded in the Maldives across 12 years arose from entanglement with lost and discarded fishing gear
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0289167
Article Title: Evaluation of sea turtle morbidity and mortality within the Indian Ocean from 12 years of data shows high prevalence of ghost net entanglement
Author Countries: Republic of the Maldives
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
At one Antarctic research station, contaminant levels exceeding international guidelines across 18 years have resulted from historic practices that have polluted the local ecosystem
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0288485
Article Title: Contamination of the marine environment by Antarctic research stations: Monitoring marine pollution at Casey station from 1997 to 2015
Author Countries: Australia, Canada
Funding: This research was funded by a Australian Antarctic Science research grants to JSS (AAS 2201, 2948, 4127, 4180, 4633) by the Australian Antarctic Division ...
ChatGPT-authored Japanese writing can be stylistically distinguished with up to 100% accuracy from human-authored text by machine learning algorithms
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0288453
Article Title: Distinguishing ChatGPT(-3.5, -4)-generated and human-written papers through Japanese stylometric analysis
Author Countries: Japan
Funding: This work was partly supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number JP22K12726. The funders did not participate in this study design, data collection, analysis, or decision to publish, except their role in paying the English proofreading and Publication Fee. ...
While engaging in cell division research, Silke Hauf and members of her lab made a surprisingly quiet discovery. When cells express RNA, there is always some fluctuation, or noise, in how much RNA is produced. Hauf’s group found several genes whose noise dips below a previously established threshold, known as the noise floor, during expression.
“We have solid data for this phenomenon,” said Hauf, associate professor in the Department of Biological Sciences at Virginia Tech. “There are some genes that are different and can have super low noise.”
Often upstaged by the more striking, well-publicized high-noise genes, Hauf and her team were intrigued by these ...
Philadelphia, August 9, 2023 – Since the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus, researchers have been trying to determine why this virus creates such negative long-term effects compared with most coronaviruses. Now, a multi-institutional consortium of researchers led by a team at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) and the COVID-19 International Research Team (COV-IRT) has found that the genes of the mitochondria, the energy producers of our cells, can be negatively impacted by the virus, leading to dysfunction ...