(Press-News.org) The longer a person has type 2 diabetes, the more likely they may be to experience changes in brain structure, a Michigan Medicine study finds.
Researchers analyzing data from 51 middle-aged Pima American Indians living with type 2 diabetes used a series of memory and language tests developed by the National Institutes of Health, called the NIH Toolbox Cognitive Battery, as well as MRI, to determine the relationship between diabetes, cognition and makeup of the brain.
Brain imaging suggested that study participants with longer durations of type 2 diabetes had decreased mean cortical thickness and gray matter volumes, and an increased volume of white matter hyperintensities.
The MRI results, researchers say, indicate the negative effects longstanding diabetes may have on brain health outcomes and emphasize the importance of preventing early onset type 2 diabetes.
Cognition in study participants with type 2 diabetes did not differ compared to those without the condition. Results are published in Annals of Clinical and Translational Neurology.
“This is among the first times that alterations of the brain’s structure have been associated with duration of diabetes,” said first author Evan Reynolds, Ph.D., research fellow and lead statistician for the NeuroNetwork for Emerging Therapies at Michigan Medicine
“Although we did not find reduced cognition through the NIH Toolbox, this might not give the entire picture. The fact that we saw negative changes in the brain itself provides evidence for the need for early screening for cognitive disorders in patients with type 2 diabetes to improve patient care and quality of life.”
Investigators also found that diabetes complications, such as chronic kidney disease and damage to the nerves in the heart and blood vessels, are linked to structural changes to the brain. This falls in line with another of the team’s studies, which found that diabetic complications increased the odds of developing a cognitive disorder by 2.45 times in 40 to 60-year-olds.
Researchers were surprised that neuropathy, by which up to 50% of people with diabetes can be affected, was not associated with cognitive function in the study.
“This study is critical to our understanding of how diabetes affects brain health and lays the groundwork for a larger, longitudinal study addressing how persons with diabetes can maintain a healthy brain,” said senior author Eva Feldman, M.D., Ph.D., James W. Albers Distinguished Professor at U-M, the Russell N. DeJong Professor of Neurology at U-M Medical School and director of the NeuroNetwork for Emerging Therapies at Michigan Medicine.
“Regardless of the underlying mechanisms, preventing these conditions in people with type 2 diabetes is critical to maintaining brain health. Educating the public on the risks that diabetes poses to a preserving a healthy brain is part of our mission.”
Additional authors include Kristen Votruba, Ph.D., Rodica Pop-Busui, M.D., Ph.D., and Brian C. Callaghan, M.D., all of Michigan Medicine, Clifford R. Jack, M.D., Gregory M. Preboske, Robert I. Reid, Ph.D., all of Mayo Clinic, Richard Beare, Ph.D., of Monash University, and Camille Waseta, and Robert G. Nelson, M.D., Ph.D., both of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
Dr. Pop-Busui receives research support from Novo Nordisk. Dr. Callaghan consults for DynaMed, receives research support from the American Academy of Neurology and performs medical legal consultations including consultations for the Vaccine Injury Compensation Program.
This research was supported by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases and the National Institute on Aging at the National Institutes of Health (grants (K99DK129785, R01DK107956, U01DK119083, 1U01 DK0945157, R01DK116723, R01DK115687, U24DK115255, R01DK130913 and U01AG057562), the Alexander Family Professorship at Mayo Clinic, the JDRF Center of Excellence at the University of Michigan, the Robert E. Nederlander Sr. Program for Alzheimer’s Research, the Andrea and Lawrence A. Wolfe Brain Health Initiative Fund, the A. Alfred Taubman Medical Research Institute, and the NeuroNetwork for Emerging Therapies.
The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Paper Cited: “Association between brain health outcomes and metabolic risk factors in persons with diabetes,” Annals of Clinical and Translational Neurology. DOI: 10.1002/acn3.51859
END
Diabetes linked to functional and structural brain changes through MRI
Investigators also found that diabetes complications are linked to these changes in the brain
2023-08-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Turning ChatGPT into a ‘chemistry assistant’
2023-08-10
Developing new materials requires significant time and labor, but some chemists are now hopeful that artificial intelligence (AI) could one day shoulder much of this burden. In a new study in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, a team prompted a popular AI model, ChatGPT, to perform one particularly time-consuming task: searching scientific literature. With that data, they built a second tool, a model to predict experimental results.
Reports from previous studies offer a vast trove of information that chemists need, but finding and parsing the most relevant details can be laborious. ...
A therapeutic target for Alzheimer's disease discovered
2023-08-10
Québec City, August 10, 2023 - Scientists at Université Laval and the University of Lethbridge have succeeded in reversing certain cognitive manifestations associated with Alzheimer's disease in an animal model of the disease. Their results have been published in the scientific journal Brain.
"Although this has yet to be demonstrated in humans, we believe that the mechanism we have uncovered constitutes a very interesting therapeutic target, because it not only slows down the progression of the disease but also partially restores certain cognitive functions," ...
Common cold virus linked to potentially fatal blood clotting disorder
2023-08-10
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – Platelets, or thrombocytes, are specialized cellular fragments that form blood clots when we get scrapes and traumatic injuries. Viral infections, autoimmune disease, and other conditions can cause platelet levels to drop throughout the body, termed thrombocytopenia.
After a robust clinical and research collaboration, Stephan Moll, MD, and Jacquelyn Baskin-Miller, MD, both in the UNC School of Medicine, have linked adenovirus infection with a rare blood clotting disorder. This is the first time that the common ...
Education program tackles race-based cancer health disparities
2023-08-10
HOUSTON – (Aug. 10, 2023) Rice University chemist Carolyn Nichol has won a competitive Science Education Partnership Award (SEPA) from the National Institutes of Health to address race-based cancer health disparities by increasing underrepresented minority student populations’ engagement and participation in biosciences education.
The 5-year, $1,038,544 award will support Nichol’s Cancer Health Activism Network for Greater Equity (CHANGE) project in bringing together cutting-edge cancer research with insight on race-based healthcare disparities from the social sciences in a series of transformative high school biology lessons aligned with both ...
Font size can 'nudge' customers toward healthier food choices
2023-08-10
PULLMAN, Wash. -- Restaurants can persuade patrons to choose healthier foods by adjusting the font size of numbers attached to nutritional information on menus, according to a study headed by a Washington State University researcher.
Lead researcher Ruiying Cai, an assistant professor in the WSU School of Hospitality Business Management, said U.S. restaurants with more than 20 locations are already required to show the calorie content of food on their menus. By representing these values incongruously — using physically larger numbers on the page when they’re attached to ...
Researchers unlock mystery of cartilage regeneration in lizards
2023-08-10
A team of researchers from the Keck School of Medicine of USC have published the first detailed description of the interplay between two cell types that allow lizards to regenerate their tails. This research, funded by the National Institutes of Health and published on August 10 in Nature Communications, focused on lizards’ unusual ability to rebuild cartilage, which replaces bone as the main structural tissue in regenerated tails after tail loss.
The discovery could provide insight for researchers studying how to rebuild cartilage damaged by osteoarthritis in humans, a degenerative and debilitating disease that affects about 32.5 million adults ...
Space weather and satellite security: Graz University of Technology and University of Graz supply new forecasting service for the ESA's Space Safety Programme
2023-08-10
After a successful test phase, the Satellite Orbit DecAy (SODA) service, which was jointly developed by TU Graz and the University of Graz, officially became part of the ESA’s Space Safety Programme in mid-July. SODA provides accurate forecasts of the effects of solar storms on low Earth orbiting satellites. This makes TU Graz only the third Austrian institution contributing to this ESA programme. Seibersdorf Laboratories, and the University of Graz, through the Kanzelhöhe Observatory and the Institute of Physics, ...
New high-tech microscope using AI successfully detects malaria in returning travelers
2023-08-10
Each year, more than 200 million people fall sick with malaria and more than half a million of these infections lead to death. The World Health Organization recommends parasite-based diagnosis before starting treatment for the disease caused by Plasmodium parasites. There are various diagnostic methods, including conventional light microscopy, rapid diagnostic tests and PCR.
The standard for malaria diagnosis, however, remains manual light microscopy, during which a specialist examines blood films with a microscope to confirm the presence of malaria parasites. ...
HKUST researchers pioneers technique to self-assemble high-performance biomolecular films
2023-08-10
A research team led by The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) has developed a novel technique to self-assemble a thin layer of amino acids with ordered orientation over a large area that demonstrates high piezoelectric strength, making the manufacturing of biocompatible and biodegradable medical microdevices, such as pacemaker and implantable biosensor, in the near future possible.
The generation of bioelectricity from the piezoelectric effect – reversible conversion between mechanical and electrical energies – has physiological significance in living systems. ...
A platform for integrated spectrometers based on solution-processable semiconductors
2023-08-10
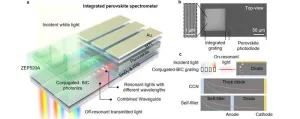
Acquiring real-time spectral information in point-of-care diagnosis, internet-of-thing, and other lab-on-chip applications require spectrometers with hetero-integration capability and miniaturized feature. Compared to conventional semiconductors integrated by heteroepitaxy, solution-processable semiconductors provide a much-flexible integration platform due to their solution-processability, and, therefore, more suitable for the multi-material integrated system. However, solution-processable semiconductors are usually incompatible with the micro-fabrication processes, making them far from practical use in various lab-on-chip applications.
In a new paper published ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How some skills become second nature
SFU study sheds light on clotting risks for female astronauts
UC Irvine chemists shed light on how age-related cataracts may begin
Machine learning reveals Raman signatures of liquid-like ion conduction in solid electrolytes
Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia researchers emphasize benefits and risks of generative AI at different stages of childhood development
Why conversation is more like a dance than an exchange of words
With Evo 2, AI can model and design the genetic code for all domains of life
Discovery of why only some early tumors survive could help catch and treat cancer at very earliest stages
Study reveals how gut bacteria and diet can reprogram fat to burn more energy
Mayo Clinic researchers link Parkinson's-related protein to faster Alzheimer's progression in women
Trends in metabolic and bariatric surgery use during the GLP-1 receptor agonist era
Loneliness, anxiety symptoms, depressive symptoms, and suicidal ideation in the all of us dataset
A decision-support system to personalize antidepressant treatment in major depressive disorder
Thunderstorms don’t just appear out of thin air - scientists' key finding to improve forecasting
Automated CT scan analysis could fast-track clinical assessments
New UNC Charlotte study reveals how just three molecules can launch gene-silencing condensates, organizing the epigenome and controlling stem cell differentiation
Oldest known bony fish fossils uncover early vertebrate evolution
High‑performance all‑solid‑state magnesium-air rechargeable battery enabled by metal-free nanoporous graphene
Improving data science education using interest‑matched examples and hands‑on data exercises
Sparkling water helps keep minds sharp during long esports sessions
Drone LiDAR surveys of abandoned roads reveal long-term debris supply driving debris-flow hazards
UGA Bioinformatics doctoral student selected for AIBS and SURA public policy fellowship
Gut microbiome connected with heart disease precursor
Nitrous oxide, a product of fertilizer use, may harm some soil bacteria
FAU lands $4.5M US Air Force T-1A Jayhawk flight simulator
SimTac: A physics-based simulator for vision-based tactile sensing with biomorphic structures
Preparing students to deal with ‘reality shock’ in the workplace
Researchers develop beating, 3D-printed heart model for surgical practice
Black soldier fly larvae show promise for safe organic waste removal
People with COPD commonly misuse medications
[Press-News.org] Diabetes linked to functional and structural brain changes through MRIInvestigators also found that diabetes complications are linked to these changes in the brain