(Press-News.org) In two studies, researchers demonstrate how climate modeling approaches can fill gaps in our understanding of hominin evolution and migration.
Over the last several decades, research efforts into the lives of hominins – humans and their close ancestors – have shifted from identifying fossils and artifacts to understanding the environmental and climate settings in which they lived and how these factors could have influenced hominin evolution and migration. However, like the hominin fossil record, environmental and climate records that accurately capture environmental change and span the period over which hominins evolved and spread across the globe are uncommon and incomplete. Some of these limitations can be addressed through advances in analytical tools, particularly climate and ecosystem models, which can help fill these gaps and provide valuable new insights into hominin migration.
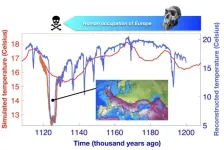
In one study, Vasiliki Margari and colleagues used a deep-sea sediment core, which provided a temperature record for Europe from 800,000 to 1.8 million years ago. Using these data, the authors created a climate envelope model and evaluated the geographic range of hominin species using climate variables such as temperature and precipitation. Margari et al. discovered hominin presence around the Mediterranean before ~1.1 million years ago was characterized by long, stable interglacial conditions with short glacials that would have allowed for hominin establishment and long-term occupation. However, extreme glacial conditions beginning around 1.1 million years ago would likely have made the region too cold for hominins to survive. Margari et al. argue that these extreme conditions likely led to the depopulation of Europe, which could have lasted for several glacial-interglacial cycles.
In another study, Jiaoyang Ruan and colleagues evaluate how climate shifts across central Eurasia during the Pleistocene could have facilitated interbreeding between Denisovans and Neanderthals. Genetic studies have revealed evidence of interbreeding between Neanderthals and Denisovans in Eurasia. However, much about these admixture events remains unknown. Here, Ruan et al. developed a species distribution model combining extensive fossil, archaeological, and genetic data with transient coupled general circulation model simulations of global climate and habitat change for the past 400,000 years, which was used to determine the habitat preferences for both Neanderthals and Denisovans. The authors found that, although both species lived in a variety of environments, Neanderthals preferred temperate forests, whereas Denisovans lived in a much wider range of habitats. However, orbitally driven climate shifts in habitat caused the preferred habitats of Denisovans and Neandertals to overlap, providing opportunities for interbreeding between the two species.
For reporters interested in trends, a similar Earth system model-based approach was used by Zeller et al. in a May 2023 study in Science, which combined climate and fossil datasets to evaluate habitat suitability and preference for several Pleistocene hominin species and how they responded to changing climatic conditions over the last 3 million years.
END
Climate modeling reveals new insights into hominin migration and evolution
2023-08-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New approaches enable chemical upcycling of polyethylene and polypropylene plastics
2023-08-10
In two studies, researchers present new ways to convert common waste plastics, polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP), into high-value chemical products, including alcohols, aldehydes, surfactants, and detergents. The approaches provide a pathway toward creating a circular plastics economy and the ability to produce high-value chemicals more sustainably. Waste plastics are increasingly being considered a potentially abundant source of feedstock to produce valuable chemical compounds. However, some plastics, particularly polyolefin plastics like PE and PP – widely used commodity plastics that account ...
Special Issue: Australia
2023-08-10
In this Special Issue of Science, three Reviews, a Policy Forum, and a Perspective highlight Australia’s exceptional exposure to the risks of climate change and ecosystem degradation. Australia is home to Earth’s most ancient ecosystems and oldest continuous indigenous cultures, which have survived for more than 60,000 years. However, the continent’s unique ecosystems and cultural history have proved vulnerable to waves of European colonization and its associated social and environmental impacts. Ongoing climate change and the ...
Global ecosystem water use efficiency has stalled since 2001
2023-08-10
Increases in global ecosystem water use efficiency – the ratio between carbon assimilation to water evapotranspiration – have stalled since 2001 due to a rising vapor pressure deficit, according to a new study. The findings highlight one way that the adverse effects of our warming climate may undermine human reliance on nature-based climate solutions to achieve carbon neutrality. The rapid rise of atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) has led to substantial changes in global terrestrial carbon and water cycles. One of these impacts has been a generalized increase in ecosystem water use efficiency (WUEeco). On a global scale, WUEeco plays ...
A climate-orchestrated early human love story
2023-08-10
A new study published in the journal Science by an international team finds that past changes in atmospheric CO2 and corresponding shifts in climate and vegetation played a key role in determining when and where early human species interbred.
Modern-day people carry in their cells a small quantity of DNA deriving from other human species, namely the Neanderthals and the elusive Denisovans. Back in 2018, scientists announced to the world the discovery of an individual [Figure 1], later nicknamed Denny, who lived 90,000 years ago and who was identified as a daughter to a Denisovan father and a Neanderthal mother [Slon et al. 2018]. Denny, along with fellow mixed-ancestry ...
How a massive North Atlantic cooling event disrupted early human occupation in Europe
2023-08-10
A new study published in the journal Science finds that around 1.12 million years ago a massive cooling event in the North Atlantic and corresponding shifts in climate, vegetation and food resources disrupted early human occupation of Europe.
The study published by an international group of scientists from the UK, South Korea and Spain presents observational and modelling evidence documenting that unprecedented climate stress changed the course of early human history.
Archaic humans, known as Homo erectus moved from Africa into central Eurasia around 1.8 million years. From there on they spread towards western Europe, reaching the Iberian peninsula around 1.5 million ...
Global consortium creates large-scale, cross-species database and universal ‘clock’ to estimate age in all mammalian tissues
2023-08-10
Scientists at UCLA David Geffen School of Medicine and UCLA Health led an international research team that published two articles detailing changes in DNA – changes that researchers found are shared by humans and other mammals throughout history and are associated with life span and numerous other traits.
“We've discovered that the life spans of mammals are closely associated with chemical modifications of the DNA molecule, specifically known as epigenetics, or more accurately, methylation. In essence, mammals with longer life spans exhibit more pronounced DNA methylation landscapes, whereas those ...
Extreme cooling ended the first human occupation of Europe
2023-08-10
Paleoclimate evidence shows that around 1.1 million years ago, the southern European climate cooled significantly and likely caused an extinction of early humans on the continent, according to a new study led by UCL researchers.
Published in the journal Science, the team of researchers discovered the occurrence of previously unknown extreme glacial conditions around 1.1 million years ago. The glacial cooling pushed the European climate to levels beyond what archaic humans could tolerate, emptying the continent of human populations.
The oldest known human remains in ...
An unexpected way to upcycle: Plastic waste transforms into soap
2023-08-10
A team led by Virginia Tech researchers has developed a new method for upcycling plastics into high-value chemicals known as surfactants, which are used to create soap, detergent, and more.
Plastics and soaps tend to have little in common when it comes to texture, appearance, and, most importantly, how they are used. But there is a surprising connection between the two on a molecular level: The chemical structure of polyethylene — one of the most commonly used plastics in the world today — is strikingly similar ...
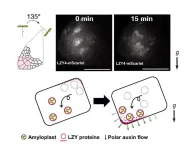
The positional transmitter of statoliths unveiled: It keeps plants from getting lazy
2023-08-10
Plants orient their organs in response to the gravity vector, with roots growing towards gravity and shoots growing in the opposite direction. The movement of statoliths responding to the inclination relative to the gravity vector is employed for gravity sensing in both plants and animals. However, in plants, the statolith takes the form of a high-density organelle, known as an amyloplast, which settles toward gravity within the gravity sensing cell. Despite the significance of this gravity sensing mechanism, the exact process behind it has eluded scientists ...
City of Hope researchers develop a CAR T cell therapy for advanced ovarian cancer
2023-08-10
LOS ANGELES — There are currently few effective treatment options for patients with recurrent ovarian cancer and other solid tumors, but City of Hope researchers are trying to change that.
Researchers with City of Hope, one of the largest cancer research and treatment organizations in the nation, have published preclinical research in Nature Communications demonstrating that a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-engineered T cell therapy worked against ovarian cancer in the laboratory and in preclinical models.
“City of Hope’s ...