(Press-News.org) SAN FRANCISCO, Aug. 10, 2023 — Period products come in a variety of styles — liners, pads, tampons, cups and underwear — to help people feel comfortable during a menstrual bleed. But their labels don’t usually list the ingredients, so consumers don’t know what’s in their product of choice. Now, researchers have analyzed over 100 period products for fluorinated compounds, an indicator of potentially harmful per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances, or PFAS. Their results show that while PFAS are absent from many products, they might be accidentally or intentionally added to others.
The researchers will present their results Sunday, Aug. 13, on the first day of the fall meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS). ACS Fall 2023 is a hybrid meeting being held virtually and in-person Aug. 13–17, and features about 12,000 presentations on a wide range of science topics.
“Of course, you’re concerned for the wearer, but we’re also concerned about the ecological impact because PFAS are ‘forever chemicals,’” says Graham Peaslee, Ph.D., the principal investigator of the project. “Once these products are thrown away, they go to landfills and decay, releasing PFAS into groundwater. And we, or later generations, could end up inadvertently ingesting them.”
PFAS are a category of over 12,000 compounds that have stick-, stain- and water-resistant properties, which are desirable characteristics for some products. But because these compounds don’t break down easily in the environment or our bodies, they are persistent and bioaccumulative — hence the “forever chemical” moniker. Researchers have also linked exposure to PFAS with an increased risk of negative health outcomes, including some cancers and immune suppression.
Currently, there are few regulatory limits on including PFAS in textiles or period products in the U.S. or Europe. And when it comes to personal products like these, people are concerned about what goes into them, says Peaslee, which is why his research team at the University of Notre Dame started testing them for PFAS.
While it’s not known how much PFAS could pass from different materials through the skin, the team has found these compounds in firefighting gear, school uniforms and period underwear. And other researchers have detected PFAS in additional period products, such as tampons and pads. So, Alyssa Wicks, a graduate student in Peaslee’s lab who is presenting at the meeting, wanted to expand the analyses to a larger variety of period products that haven’t been widely tested, including the packaging for single-use tampons and pads, as well as reusable options, such as menstrual cups.
“Our first step was a screening that’s done quickly and simply,” says Wicks. “We determined if these products had organic fluorine as a surrogate for PFAS.” She cut out a small portion of each item and analyzed it in less than three minutes, using particle-induced gamma-ray emission spectroscopy.
Some pads and period underwear had multiple layers, which were sampled separately. For instance, some of the tested underwear products had as many as 10 layers, though the average was closer to four. Additionally, the researchers measured total fluorine in the single-use product’s wrappers. So far, Wicks has analyzed 123 period products sold in the U.S., 30 of which were different underwear, with this technique. She also plans to analyze similar products sold in Europe.
The results of these analyses suggest that some period products potentially include PFAS, but not all of them. “In general, tampons didn’t seem to contain fluorine,” says Wicks. “Same with menstrual cups and the layers of pads that come in contact with a person’s skin.”
Most surprising to the researchers was the presence of total fluorine in the wrappers for numerous pads and some tampons, as well as the outer layers of some of the period underwear. Some of the highest amounts measured were 1,000 to several thousand parts per million total fluorine. Because of those high concentrations, Wicks hypothesizes that PFAS might be used to keep moisture out of the wrappers so that the items inside remain dry. In addition, she suggests that adding these compounds to the outer layer of the period underwear would keep blood from escaping the inner layers and stop it from spreading onto a person’s clothing.
This initial work has allowed the researchers to home in on which period products likely have PFAS in them. Next, the team will analyze the samples that contained measurable amounts of fluorine specifically for 40 individual PFAS compounds.
In the meantime, the team notes it is interesting that some products tested in the study were actually free of fluorine. “It’s clear that PFAS are not essential,” concludes Peaslee. “Feminine products are essential, but the need for a fluorinated wrapper, or the need for a fluorinated layer, doesn’t seem to be, because plenty of them are made without relying on these compounds.”
The researchers acknowledge support to do independent research of societal impact from the University of Notre Dame.
A recorded media briefing on this topic will be posted today, Aug. 10, at www.acs.org/acsfall2023briefings. Reporters can request access to media briefings during the embargo period by contacting newsroom@acs.org.
For health and safety information for ACS Fall 2023, please visit the FAQ webpage.
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and all its people. The Society is a global leader in promoting excellence in science education and providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a leader in scientific information solutions, its CAS division partners with global innovators to accelerate breakthroughs by curating, connecting and analyzing the world’s scientific knowledge. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive press releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Note to journalists: Please report that this research was presented at a meeting of the American Chemical Society.
Follow us: Twitter | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram
Title
Rapid detection and targeted analysis of fluorinated compounds in feminine hygiene products
Abstract
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are added to consumer goods to provide a range of properties, including stain and oil resistance and water repellency. However, PFAS persist in the environment and are linked to adverse health effects including endocrine disruption and increased risk of cancers. Our research investigates the presence of PFAS in feminine hygiene products, especially menstrual products. While the extent of dermal uptake of PFAS is not well known, many of these products are single use and end up in landfills. As PFAS are readily water soluble they then can leach into water supplies, becoming accessible to humans through other pathways including drinking water and food products. Our group uses the rapid screening method of ex-vacuo particle-induced gamma-ray emission (PIGE) spectroscopy to perform nondestructive isotopic analysis on feminine hygiene products. In three minutes per sample, products were screened for their total fluorine concentrations as a surrogate for PFAS. A subset of samples was then subjected to liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry for targeted PFAS analysis. Products tested include menstrual cups, pads, underwear, and tampons, and incontinence pads and underwear from North American, European and South American manufacturers.
END
Indicator of PFAS found in some — but not all — period products
2023-08-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Exercise training and yoga can help improve lung function in adults with asthma
2023-08-11
Yoga and breathing control practices, in combination with aerobic training, are particularly key exercises for asthmatic people seeking to improve their lung function, a new peer-reviewed study suggests.
The research which is published today in the journal Annals of Medicine highlights the importance of integrating appropriate exercise training into asthma management plans.
The findings demonstrate just how effective specific types of exercise training can be to enhance lung function for those with adults, explains ...
Fat burning during exercise varies widely between individuals
2023-08-11
New York, NY [August 10, 2023]—The best heart rate for burning fat differs for each individual and often does not align with the “fat burning zone” on commercial exercise machines, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai researchers report.
Instead, the researchers said, clinical exercise testing—a diagnostic procedure to measure a person’s physiological response to exercise—may be a more useful tool to help individuals achieve intended fat loss goals. The study, which used a machine learning-based modeling approach, was published online today in Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Disease.
“People with a goal of weight or fat loss may ...
The health impact of climate change is not adequately recorded: study
2023-08-11
A Monash University-led study has proposed a solution for the urgent need to capture real-time data on the impact of climate change-related events on human health, healthcare workforces, and healthcare systems at the point of care.
As the global community faces growing climate challenges, the study calls for action, collaboration, and innovation to safeguard human health and wellbeing in the face of environmental crises.
Published in the Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association, it highlighted key climate ...
New research shows genetic mutation known for Alzheimer’s disease is associated with higher fertility in women
2023-08-10
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — Previous research has revealed that the Apolipoprotein-ε4 (APOE-ε4) allele increases the risk for a variety of diseases in aging populations, specifically Alzheimer’s and cardiovascular disease. And yet, despite the negative effects of this genetic variant, it remains prevalent in approximately 20% of the human population. In a quest to determine how this negative allele is surviving natural selection, a group of researchers have discovered that the APOE-ε4 allele is associated with higher fertility in women.
In a new paper released in Science Advances, researchers including UC Santa ...
Trinity research looks to Latin America for clues on healthy brain ageing
2023-08-10
Researchers at Trinity College Dublin study the factors influencing healthy brain ageing in Latin American and Caribbean (LAC) countries and find the lessons learned there, can also be applied to home.
Ageing is not a uniform process across the globe. Most research into cognitive and functional ageing has been conducted in the US and Europe, in high-income settings. Researchers from the Global Brain Health Institute (GBHI) at Trinity College are filling the knowledge gap that exists for Latin American populations on the factors ...
Transplant recipients experience limited protection with primary COVID-19 vaccination series, but third dose boosts response
2023-08-10
Key Takeaways
Lung and heart transplant recipients experienced diminished and delayed antibody responses to the first two COVID-19 mRNA vaccine doses, but most developed stronger responses following a third dose
A third dose also boosted cross-protection against SARS-CoV-2 viral variants
For lung and heart transplant recipients, vaccine doses beyond the third dose are likely important for maintaining immunity
BOSTON – Transplant recipients must take life-long immunosuppressive medications to prevent rejection, but these drugs ...
Department of Energy announces $11 million for exploratory research in extreme-scale science
2023-08-10
WASHINGTON, D.C. - Today, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) announced $11 million in funding for 15 projects in exploratory research for extreme-scale science that will leverage emerging trends and advances in high-end computing, massive datasets, scientific machine learning, artificial intelligence, and novel computing architectures.
“There is a wide expanse of exciting opportunities as we reach beyond exascale computing,” said Ceren Susut, DOE Acting Associate Director of Science for Advanced Scientific Computing Research. “These ...
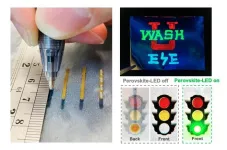
Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs
2023-08-10
Researchers working with Chuan Wang, an associate professor of electrical and systems engineering at the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis, have developed ink pens that allow individuals to handwrite flexible, stretchable optoelectronic devices on everyday materials including paper, textiles, rubber, plastics and 3D objects.
In a paper published Aug. 7 in Nature Photonics, the team reports their simple and versatile fabrication approach to allow anyone to make a custom light-emitting diode (LED) or photodetector ...
Community health program boosts child vaccinations in remote areas of Madagascar
2023-08-10
URBANA, Ill. – Madagascar is one of the poorest countries in the world and access to health care is limited for many people. Childhood vaccinations are a crucial component of preventative care, but vaccination rates remain below the World Health Organization’s goal of reaching 95% of children. A new study from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign examines the effectiveness of a health intervention program that enlists community-based health workers to promote child vaccination uptake.
“Childhood vaccinations are a cost-effective investment that can have large ripple effects. Vaccines can reduce child mortality ...
Athletes have no reason to be concerned by their COVID-19 vaccine this winter but timing matters
2023-08-10
It is now almost a rule of thumb: As soon as an athlete falls to the ground with a sudden cardiac arrest, social media is awash with claims that COVID-19 vaccinations are to blame. This was the case with English footballer Charlie Wyke, cyclist Sonny Colbrelli and, most recently, with college basketballer, and son of LeBron, Bronny James. In the view of Harald Jorstad, Sports Cardiologist at Amsterdam UMC, there is no evidence to support these claims, but timing of the vaccination can be structured to not ...