(Press-News.org) Medical imaging via X-rays, CT scans, MRIs and ultrasounds provide health-care professionals with unique perspectives and a better understanding of what’s happening inside a patient’s body. Using various forms of waves, these machines can visualize many unseen ailments and diseases.
This imaging is beneficial for health-care professionals to make correct diagnoses, but the added insight of spectroscopy provides even more detail. Spectroscopy offers a means to identify biomolecules within specimens through their characteristic signatures for absorption in the electromagnetic spectrum.
Now, researchers at UBC Okanagan’s School of Engineering want to take that diagnostic imaging a step further.
By recognizing the benefits of imaging and spectroscopy, the researchers in UBCO’s Integrated Optics Laboratory (IOL) are now developing imaging systems that apply terahertz radiation. Terahertz radiation lies in the electromagnetic spectrum, with frequencies between radio and visible waves. This opens the door to fast and accurate terahertz characterizations of biological specimens—and can ultimately help with the creation of effective technologies for cancer detection.
“By working with terahertz radiation, we’re able to glean details on the underlying characteristics of biological specimens,” explains Alexis Guidi, a School of Engineering master's student and lead author of a new study published in Scientific Reports. “This insight comes from the nature of terahertz radiation, which is intricately sensitive to the biomolecular make-up of cells.”
Nonetheless, according to Dr. Jonathan Holzman, IOL Principal Investigator and Electrical Engineering Professor, there are pressing challenges in developing these terahertz systems.
“The characteristics of terahertz radiation that make it an effective probe of biomolecules, in terms of its long wavelengths, also make it challenging to focus and resolve in images. Our recent work solved this by demonstrating terahertz spectroscopy can show a resolution approaching the cellular scale.”
The researchers plan on applying their findings in emerging areas of medical diagnoses, with a particular emphasis on carcinogenesis—the process by which healthy cells become cancerous.
The research is partially funded through support from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, the Canada Foundation for Innovation and Western Economic Diversification Canada.
END
Riding a wave to better medical diagnosis
New UBC Okanagan research takes aim at improving diagnostic imaging
2023-08-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Death tolls from climate disasters will ‘balloon’ without investment in Africa’s weather stations
2023-08-14
The climate crisis is increasing the frequency and intensity of floods, droughts and heatwaves, with Africa expected to be among the global regions hit hardest.
Yet the systems and technologies across the continent that monitor and forecast weather events and changes to water levels are “missing, outmoded or malfunctioning” – leaving African populations even more exposed to climate change.
This is according to a team of risk experts and climatologists from the UK and Africa led by the University of Cambridge, who ...
Transforming flies into degradable plastics
2023-08-14
SAN FRANCISCO, Aug. 14, 2023 — Imagine using insects as a source of chemicals to make plastics that can biodegrade later — with the help of that very same type of bug. That concept is closer to reality than you might expect. Today, researchers will describe their progress to date, including isolation and purification of insect-derived chemicals and their conversion into functional bioplastics.
The researchers will present their results at the fall meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS). ACS Fall 2023 is a hybrid meeting being held virtually and in-person Aug. 13–17, and features about 12,000 presentations on a wide range of science topics.
“For ...
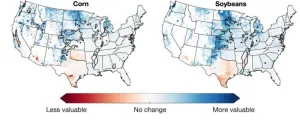
Irrigating more US crops by mid-century will be worth the investment
2023-08-14
With climate change, irrigating more crops in the United States will be critical to sustaining future yields, as drought conditions are likely to increase due to warmer temperatures and shifting precipitation patterns. Yet less than 20% of croplands are equipped for irrigation.
A Dartmouth-led study finds that by the middle of the 21st century under a moderate greenhouse gas emissions scenario, the benefits of expanded irrigation will outweigh the costs of installation and operation over an expanded portion of current U.S. ...
New statement urges engaging patients in their care, collaborating on treatment decisions
2023-08-14
DALLAS, Aug. 14, 2023 - A new American Heart Association scientific statement highlights evidence that supports shared decision-making, a term that describes the process of ensuring patients have the knowledge and tools to make decisions about their health in collaboration with their professional health care team. The statement publishes today in the American Heart Association’s flagship, peer-reviewed journal Circulation.
More than 100 trials have demonstrated that shared decision-making ...
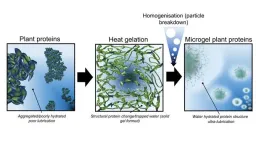
Making plant-based meat alternatives more palatable
2023-08-14
New colloidal technique could give a juicy sensation without adding fat
Switch to plant-based diets needed to hit climate change targets
One of the biggest obstacles to the uptake of plant-based alternatives to meat is their very dry and astringent feel when they are eaten.
Scientists, led by Professor Anwesha Sarkar at the University of Leeds, are revolutionising the sensation of plant proteins, transforming them from a substance that can be experienced as gloopy and dry to one that is juicy and fat like.
And the only substance they are adding to the plant proteins is water.
Plant protein microgels
To ...
3D-printed vegan seafood could someday be what’s for dinner (video)
2023-08-13
SAN FRANCISCO, Aug. 13, 2023 — In the refrigerated grocery store aisle, meat alternatives greatly outnumber plant-based seafoods. But more mock seafood options are needed because of unsustainable fishing and aquaculture practices, which can deplete the supply and harm the environment. Today, researchers present a new approach for creating desirable vegan seafood mimics that taste good, while maintaining the healthful profile of real fish. They 3D-printed an ink made from microalgae protein and mung bean protein, and their proof-of-concept calamari rings can even be air-fried for a quick, tasty snack.
The researchers will present their results at the fall meeting of the American ...
ORNL buildings researchers earn top ASHRAE honors
2023-08-12
Kashif Nawaz and Mahabir Bhandari, building technologies researchers at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, were recognized for research achievements in support of ASHRAE during the 2023 annual conference of the national heating, refrigerating, and air-conditioning engineering society.
Nawaz, a distinguished researcher and head of ORNL’s Buildings Technologies Research Section, received the Crosby Field Award, which honors the highest-rated paper presented before a technical session, a symposium or poster session ...
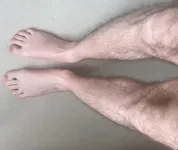
Raising awareness of Long Covid ‘blue legs’ symptom
2023-08-12
An unusual case of a Long Covid patient’s legs turning blue after 10 minutes of standing highlights the need for greater awareness of this symptom among people with the condition, according to new research published in the Lancet.
The paper, authored by Dr Manoj Sivan at the University of Leeds, focuses on the case of one 33-year man who developed with acrocyanosis – venous pooling of blood in the legs.
A minute after standing, the patient’s legs began to redden and became increasingly blue over time, with veins becoming more prominent. After 10 minutes the colour was much more pronounced, with the patient ...
For labrum tears, regrowth rather than repair
2023-08-12
Tears to the glenoid labrum—cartilage tissue that lines the shoulder where the arm joins—can be repaired with arthroscopic surgery, which significantly weakens the joint and involves a lengthy recovery.
Liping Tang, a bioengineering professor at The University of Texas at Arlington, is developing a new method to repair labrum tears that would enable the body to regenerate tissue to completely reattach the sides of the tear. He recently received a five-year, $2.1 million grant from the National Institutes of Health’s National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases for the research, which would improve the current standard of care ...
Call for papers: Special theme issue: Artificial intelligence (AI) and ChatGPT in Asian and Pacific Islander (API) health
2023-08-11
Asian/Pacific Island Nursing Journal (APINJ) Editor-in-Chief: Hyochol (Brian) Ahn, PhD, MSN, MS-ECE, MS-CTS, APRN, ANP-BC, FAAN and guest editor Shu-Fen Wung, Ph.D., RN, ACNP-BC, FAAN welcome submissions to a special theme issue examining "Artificial Intelligence (AI) and ChatGPT in Asian and Pacific Islander (API) Health."
Generative AI, like ChatGPT, can have many applications in health care and medicine, particularly in addressing the unique needs and challenges faced by API communities. Potential topics related to the use of generative AI in health care and nursing care specific to API health that we ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Riding a wave to better medical diagnosisNew UBC Okanagan research takes aim at improving diagnostic imaging