(Press-News.org) Unexpected new insights into how COVID-19 infects cells may help explain why coronaviruses are so good at jumping from species to species and will help scientists better predict how COVID-19 will evolve.
Throughout the pandemic, there has been much discussion of how COVID-19 infiltrates cells by hijacking a protein called ACE2 found on human cells. But the new research from the School of Medicine reveals that ACE2 isn’t required for infection. Instead, the virus has other means it can use to infect cells.
That versatility suggests that coronaviruses can use multiple “doors” to enter cells, potentially explaining how they are so good at infecting different species.
“The virus that causes COVID-19 uses ACE2 as the front door to infect cells, but we’ve found that if the front door is blocked, it can also use the back door or the windows,” said researcher Peter Kasson, MD, PhD, of UVA’s Departments of Molecular Physiology and Biomedical Engineering. “This means the virus can keep spreading as it infects a new species until it adapts to use a particular species’ front door. So we have to watch out for new viruses doing the same thing to infect us.”
Understanding COVID-19
COVID-19 has killed almost 7 million people around the world. Thankfully, the availability of vaccines and the increase in population immunity means that the virus is no longer the threat it once was to most people (though it remains a concern for groups such as the immunocompromised and elderly). With the expiration of the United States’ official Public Health Emergency in May, most Americans have largely returned to lives similar to the ones they knew before the pandemic emerged in 2019. But COVID-19 continues to evolve and change, and scientists are keeping a close eye on it so that they can take quick action if a more dangerous variant emerges. They also continue to monitor other coronaviruses in case they jump to humans and become the next great public health threat.
As part of this effort, Kasson and his team wanted to better understand how the virus responsible for COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2, can enter human cells. Scientists have known that the virus essentially knocks on the cell’s door by binding to ACE2 proteins. These proteins are bountiful on the surfaces of cells lining the nose and lungs.
SARS-CoV-2 can also bind with other proteins, however. Was it possible, the scientists wondered, that it could use those other proteins to infiltrate cells? The answer was yes. ACE-2 was the most efficient route, but it was not the only route. And that suggests that the virus can bind and infect even cells without any ACE-2 receptors at all.
That unexpected finding may help explain why coronaviruses are so adept at species-hopping, Kasson says. And that makes it even more important that scientists keep a close eye on them, he notes.
“Coronaviruses like SARS-CoV-2 have already caused one pandemic and several near misses that we know of,” he said. “That suggests there are more out there, and we need to learn how they spread and what to watch out for.”
Findings Published
The scientists have published their findings in the scientific journal Chemical Science. The research team consisted of Marcos Cervantes, Tobin Hess, Giorgio G. Morbioli, Anjali Sengar and Kasson. The researchers have no financial interest in the work.
The work was supported by the Commonwealth Health Research Board, grant 207-01-18; UVA’s Global Infectious Diseases Institute; and the Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation, grant KAW2020.0209.
UVA’s Department of Biomedical Engineering is a joint program of its School of Medicine and School of Engineering and Applied Science.
To keep up with the latest medical research news from UVA, subscribe to the Making of Medicine blog.
END
Surprise COVID discovery helps explain how coronaviruses jump species
New insights boost scientists’ efforts to stay ahead of COVID-19, next pandemic
2023-08-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Dry lightning can spark wildfires even under wetter conditions
2023-08-14
VANCOUVER, Wash. – Dry lightning can still be disastrous even when conditions aren’t so dry, a study has found.
These cloud-to-ground strikes during little to no rainfall were previously thought to pose wildfire danger only if occurring with less than 2.5 mm of rain in a day (about 0.10 inches). A Washington State University-led study of lightning-ignited wildfires in the U.S. West found the strikes caused wildfires despite up to 7.7 mm (about 0.3 inches) of precipitation.
While still a low amount of rain, the more accurate estimation could help responders detect fires earlier, especially those known as “holdovers,” which can smolder for many ...
Worcester Polytechnic Institute researcher receives $599,815 grant to develop 3D printable robots for search-and-rescue operations
2023-08-14
Worcester, Mass. – August 10, 2023 – Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) researcher Markus Nemitz is the recipient of a $599,815 CAREER Award from the National Science Foundation to develop an innovative architecture for low-cost custom robots capable of traversing challenging terrains by swimming, crawling, climbing, and diving through hostile and confined spaces as part of search-and-rescue operations.
Nemitz, an assistant professor in WPI’s Department of Robotics Engineering, will focus on developing ...
Riding a wave to better medical diagnosis
2023-08-14
Medical imaging via X-rays, CT scans, MRIs and ultrasounds provide health-care professionals with unique perspectives and a better understanding of what’s happening inside a patient’s body. Using various forms of waves, these machines can visualize many unseen ailments and diseases.
This imaging is beneficial for health-care professionals to make correct diagnoses, but the added insight of spectroscopy provides even more detail. Spectroscopy offers a means to identify biomolecules within specimens through ...
Death tolls from climate disasters will ‘balloon’ without investment in Africa’s weather stations
2023-08-14
The climate crisis is increasing the frequency and intensity of floods, droughts and heatwaves, with Africa expected to be among the global regions hit hardest.
Yet the systems and technologies across the continent that monitor and forecast weather events and changes to water levels are “missing, outmoded or malfunctioning” – leaving African populations even more exposed to climate change.
This is according to a team of risk experts and climatologists from the UK and Africa led by the University of Cambridge, who ...
Transforming flies into degradable plastics
2023-08-14
SAN FRANCISCO, Aug. 14, 2023 — Imagine using insects as a source of chemicals to make plastics that can biodegrade later — with the help of that very same type of bug. That concept is closer to reality than you might expect. Today, researchers will describe their progress to date, including isolation and purification of insect-derived chemicals and their conversion into functional bioplastics.
The researchers will present their results at the fall meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS). ACS Fall 2023 is a hybrid meeting being held virtually and in-person Aug. 13–17, and features about 12,000 presentations on a wide range of science topics.
“For ...
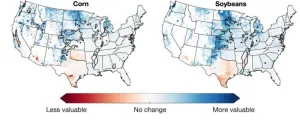
Irrigating more US crops by mid-century will be worth the investment
2023-08-14
With climate change, irrigating more crops in the United States will be critical to sustaining future yields, as drought conditions are likely to increase due to warmer temperatures and shifting precipitation patterns. Yet less than 20% of croplands are equipped for irrigation.
A Dartmouth-led study finds that by the middle of the 21st century under a moderate greenhouse gas emissions scenario, the benefits of expanded irrigation will outweigh the costs of installation and operation over an expanded portion of current U.S. ...
New statement urges engaging patients in their care, collaborating on treatment decisions
2023-08-14
DALLAS, Aug. 14, 2023 - A new American Heart Association scientific statement highlights evidence that supports shared decision-making, a term that describes the process of ensuring patients have the knowledge and tools to make decisions about their health in collaboration with their professional health care team. The statement publishes today in the American Heart Association’s flagship, peer-reviewed journal Circulation.
More than 100 trials have demonstrated that shared decision-making ...
Making plant-based meat alternatives more palatable
2023-08-14
New colloidal technique could give a juicy sensation without adding fat
Switch to plant-based diets needed to hit climate change targets
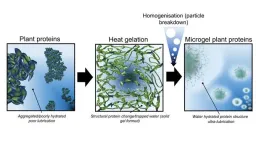
One of the biggest obstacles to the uptake of plant-based alternatives to meat is their very dry and astringent feel when they are eaten.
Scientists, led by Professor Anwesha Sarkar at the University of Leeds, are revolutionising the sensation of plant proteins, transforming them from a substance that can be experienced as gloopy and dry to one that is juicy and fat like.
And the only substance they are adding to the plant proteins is water.
Plant protein microgels
To ...
3D-printed vegan seafood could someday be what’s for dinner (video)
2023-08-13
SAN FRANCISCO, Aug. 13, 2023 — In the refrigerated grocery store aisle, meat alternatives greatly outnumber plant-based seafoods. But more mock seafood options are needed because of unsustainable fishing and aquaculture practices, which can deplete the supply and harm the environment. Today, researchers present a new approach for creating desirable vegan seafood mimics that taste good, while maintaining the healthful profile of real fish. They 3D-printed an ink made from microalgae protein and mung bean protein, and their proof-of-concept calamari rings can even be air-fried for a quick, tasty snack.
The researchers will present their results at the fall meeting of the American ...
ORNL buildings researchers earn top ASHRAE honors
2023-08-12
Kashif Nawaz and Mahabir Bhandari, building technologies researchers at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, were recognized for research achievements in support of ASHRAE during the 2023 annual conference of the national heating, refrigerating, and air-conditioning engineering society.
Nawaz, a distinguished researcher and head of ORNL’s Buildings Technologies Research Section, received the Crosby Field Award, which honors the highest-rated paper presented before a technical session, a symposium or poster session ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
Inside the light: How invisible electric fields drive device luminescence
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
[Press-News.org] Surprise COVID discovery helps explain how coronaviruses jump speciesNew insights boost scientists’ efforts to stay ahead of COVID-19, next pandemic