(Press-News.org) NEW YORK, August 14, 2023 — A research team at the Advanced Science Research Center at the CUNY Graduate Center (CUNY ASRC) has shown that it is possible to manipulate photons so that they can collide, interacting in new ways as they cross paths. The discovery, detailed in Nature Physics, will allow scientists who develop technologies rooted in electromagnetic wave propagation to make significant advances in telecommunications, optical computing and energy applications.
The breakthrough took place in the lab of Andrea Alù, Distinguished Professor and Einstein Professor of Physics at The City University of New York Graduate Center and founding director of the CUNY ASRC Photonics Initiative. It was facilitated by another recent experiment demonstrating time-reflections for electromagnetic waves.
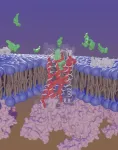
“Our work is building on a series of experiments that show how we can create metamaterials with unique properties that emerge from abrupt time variations of their electromagnetic properties. These variations allow us to manipulate wave propagation in ways not seen in nature,” said Alù. “This newest work shows that we can use abrupt temporal changes in tailored metamaterials – known as time interfaces – to make waves collide as if they were massive objects. We were also able to control whether the waves exchanged, gained or lost energy during these collisions.”
Typically, when two electromagnetic waves cross paths, they move right through each other without interacting. This is very different from what happens when two massive objects, like two balls, bump into each other. In the latter case, the particles collide, and their mechanical features determine whether the energy is conserved, lost or increased in the collision. For example, when two billiard balls collide, the total energy in the system is conserved, while when two rubber balls collide, they typically lose energy in the collision. While photons would be expected to go through each other without any interaction, by triggering a time interface the scientists were able to demonstrate strong photon-photon interactions and control the nature of the collision.
The research team’s work was inspired by speculation about whether it would be possible to erase an unwanted mechanical wave, such as a tsunami or a seismic wave, by throwing another similar wave against it to counter it. “While such an outcome is impossible in conventional wave physics, we knew it was possible in principle with a temporal metamaterial,” said Emanuele Galiffi, a postdoctoral fellow with Alù’s lab and the study’s leading author. “Our experiment allowed us to demonstrate this concept in action for electromagnetic waves.”
The scientists also proposed and demonstrated an application of their concept to shape electromagnetic pulses by colliding them against each other. “This technique allows us to use an additional signal as a mold to sculpt a pulse that we are interested in structuring,” said Gengyu Xu, a postdoctoral fellow with Alù’s lab and co-leading author of the paper. “We have shown this for radio frequencies, and we are now working to realize this sculpting ability at higher frequencies.”
The team’s work developing methods to dictate how propagating electromagnetic waves interact and shape each other could benefit wireless communications, imaging, computing and energy harvesting technologies, among other advances.
DOI # 10.1038/s41567-023-02165-6
Funding sources: Air Force Office of Scientific Research and the Simons Foundation
About the Graduate Center of The City University of New York
The CUNY Graduate Center is a leader in public graduate education devoted to enhancing the public good through pioneering research, serious learning, and reasoned debate. The Graduate Center offers ambitious students nearly 50 doctoral and master’s programs of the highest caliber, taught by top faculty from throughout CUNY — the nation’s largest urban public university. Through its nearly 40 centers, institutes, initiatives, and the Advanced Science Research Center, the Graduate Center influences public policy and discourse and shapes innovation. The Graduate Center’s extensive public programs make it a home for culture and conversation.
About the Advanced Science Research Center at the CUNY Graduate Center
The Advanced Science Research Center at the CUNY Graduate Center (CUNY ASRC) is a world-leading center of scientific excellence that elevates STEM inquiry and education at CUNY and beyond. The CUNY ASRC’s research initiatives span five distinctive, but broadly interconnected disciplines: nanoscience, photonics, neuroscience, structural biology, and environmental sciences. The center promotes a collaborative, interdisciplinary research culture where renowned and emerging scientists advance their discoveries using state-of-the-art equipment and cutting-edge core facilities.
END
No longer ships passing in the night: these electromagnetic waves had head-on collisions
on Collisions ASRC researchers show it’s possible to make photons that cross paths interact, paving the way for technology breakthroughs
2023-08-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Comparison of particulate air pollution from different emission sources and incident dementia
2023-08-14
About The Study: In this nationally representative study, higher residential levels of fine particulate matter were associated with greater rates of incident dementia, especially for fine particulate matter generated by agriculture and wildfires. These findings also indicate that intervening on key emission sources might have value, although more research is needed to confirm these findings.
Authors: Boya Zhang, Ph.D., of the University of Michigan School of Public Health in Ann Arbor, is the corresponding ...
Socioeconomic adversity and weight gain during the pandemic
2023-08-14
About The Study: In a large, demographically diverse sample of U.S. youth researchers found significantly greater increases in body mass index over time in 10- to 12-year-old youth assessed during the COVID-19 pandemic, compared with pre-pandemic controls. The effects of the pandemic on weight gain were most pronounced in low-income youth, suggesting that the pandemic exacerbated preexisting social inequalities.
Authors: Elizabeth Sowell, Ph.D., of Children’s Hospital Los Angeles, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2023.2823)
Editor’s ...
Lifestyle factors in the association of shift work and depression and anxiety
2023-08-14
About The Study: In this study of 175,000 participants, shift work was significantly associated with a higher risk of depression and anxiety, and lifestyle factors partially mediated the associations. These findings not only support that shift work should be considered an occupational hazard, but also provide evidence for the urgent need for the development of public health interventions that promote healthy lifestyles aimed at improving the mental health of shift workers.
Authors: Yanhong Gong, Ph.D., of the Huazhong University of Science and Technology in Wuhan, ...
Association of intensive lifestyle intervention for type 2 diabetes with labor market outcomes
2023-08-14
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that an intensive lifestyle intervention to prevent the progression and complications of type 2 diabetes was associated with higher levels of employment. Labor market productivity should be considered when evaluating interventions to manage chronic diseases.
Authors: Peter Huckfeldt, Ph.D., of the University of Minnesota School of Public Health in Minneapolis, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2023.3283)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, ...
China’s oldest water pipes were a communal effort
2023-08-14
A system of ancient ceramic water pipes, the oldest ever unearthed in China, shows that neolithic people were capable of complex engineering feats without the need for a centralised state authority, finds a new study by UCL researchers.
In a study published in Nature Water, the archaeological team describe a network of ceramic water pipes and drainage ditches at the Chinese walled site of Pingliangtai dating back 4,000 years to a time known as the Longshan period. The network shows cooperation amongst the community to build and maintain the drainage system, though no evidence of a centralised power or authority.
Dr Yijie Zhuang (UCL Institute of Archaeology), ...
Gene therapy may offer a new treatment strategy for alcohol use disorder
2023-08-14
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Gene therapy might offer a one-time, sustained treatment for patients with serious alcohol addiction, also called alcohol use disorder, according to a new study led by a researcher at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center and College of Medicine.
The animal study, published in the journal Nature Medicine, also involved researchers at the Oregon Health and Science University, the Oregon National Primate Research Center and the University of California San Francisco.
The study used an accepted primate model to show that sustained release of glial-derived ...
Study: Intensive lifestyle counseling and education by health specialists associated with higher employment rate among people with Type 2 diabetes
2023-08-14
USC Schaeffer Center and University of Minnesota researchers found that study participants without a college degree had even larger employment gains from lifestyle changes recommended by specialists.
Study takeaways:
Published in JAMA Internal Medicine, the study reveals that intensive lifestyle intervention to prevent the progression and complications of type 2 diabetes is associated with higher employment.
Lifestyle intervention was associated with a 4% increase in employment overall, and a 7% increase among participants with less than a college degree.
Findings suggest labor market productivity should be considered when evaluating the cost effectiveness ...
New model for the drinking water market in Jordan
2023-08-14
In more than 30 cities around the world, millions of people obtain their drinking water from storage tanks – because tap water is often available for only a few hours at any one time. When the public water supply is insufficient, households and businesses mostly resort to private providers. Trucks bring drinking water – often tapped from groundwater wells – from the countryside to the cities and sell it there. This is partly licensed by the state but largely takes place illegally. “In Jordan, these water deliveries by tanker truck make up for the deficit of the public water supply network”, ...
City of Hope scientists uncover new active regions on cell surface receptor, expanding scope for drug targets to treat heart disease
2023-08-14
FINDINGS
Scientists at City of Hope, one of the largest cancer research and treatment organizations in the United States and a leading research center for diabetes and other life-threatening illnesses, have uncovered new molecular targets on a cell receptor that play a major role in cardiovascular regulation. The findings could lead to improved drugs for heart disease, an unfortunate side effect of some cancer therapies. Science Signaling published the study this week.
The City of Hope researchers led by Nagarajan Vaidehi, Ph.D., professor and chair of the Department of Computational and Quantitative ...
What’s your masculine style: Neo-traditional, egalitarian or progressive?
2023-08-14
Men navigate their intimate partner relationships depending on their masculine style, says new research led by UBC men’s health expert John Oliffe.
The study, which drew from in-depth interviews with 92 straight men ages 19 to 43 from diverse cultural backgrounds, found three types of masculinities:
Neo-traditionalists – Some men largely follow traditional gender roles, such as being the provider and protector in the relationship
Egalitarian – Others seek a more equal partnership, with emphasis on mutuality and measurable give and take
Progressive ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI expert and industry leading toxicologist Thomas Hartung hails launch of agentic AI platform a “transformative moment” in chemical safety science
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
[Press-News.org] No longer ships passing in the night: these electromagnetic waves had head-on collisionson Collisions ASRC researchers show it’s possible to make photons that cross paths interact, paving the way for technology breakthroughs