(Press-News.org) Men navigate their intimate partner relationships depending on their masculine style, says new research led by UBC men’s health expert John Oliffe.
The study, which drew from in-depth interviews with 92 straight men ages 19 to 43 from diverse cultural backgrounds, found three types of masculinities:
Neo-traditionalists – Some men largely follow traditional gender roles, such as being the provider and protector in the relationship
Egalitarian – Others seek a more equal partnership, with emphasis on mutuality and measurable give and take
Progressive – Other men work on building gender equity in the partnership through regular, purposeful conversations with their partner to adjust who does what
"We set out to understand how different types of masculinities shape men’s relationships and their mental health. What we found was that these masculine types were associated with different benefits as well as challenges,” noted Dr. Oliffe, the Canada Research Chair in Men’s Health Promotion and a professor of nursing at UBC.
For instance, men who actively promoted gender equity and social justice reported improved mental well-being – but Dr. Oliffe observes that men who challenged these ideals could face isolation or criticism from others, which can impact their mental health. The study also found that some men with an egalitarian style still struggled to grasp the concept of achieving gender equality through splitting domestic tasks strictly 50-50.
“These shifts and stresses have implications for mental health,” says Dr. Oliffe. “To promote meaningful change, we need to address the structures that influence men’s behaviours.”
The study is the latest from UBC’s men’s health research program to explore connections between masculinity and men’s mental health.
“While men are becoming more involved in promoting gender equity, little is known about how younger men work to build partnerships in their private lives,” notes Dr. Oliffe. “With this research, we hope we have helped map that uncharted space and point a way forward for healthier relationships that promote the health of men, their partners and families.”
To share their findings, the team launched an online photo exhibition titled Men Building Intimate Partner Relationships featuring 120 photographs from more than 700 submitted by the study participants.
“There are photos depicting neo-traditional, egalitarian or progressive masculinity, and visitors are invited to take a quiz to decide which images fit with each masculinity. We’re not only highlighting our research outcomes, we’re also inviting input from visitors about how they see themselves—and how they build gender equity in their intimate partner relationships,” says Dr. Nina Gao, research manager for the men’s health research program.
Interview language(s): English (Dr. Oliffe, Dr. Gao)
Multimedia assets:
Link to study
Images (Dropbox)
Selected quotes from study participants END
What’s your masculine style: Neo-traditional, egalitarian or progressive?
2023-08-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Surprise COVID discovery helps explain how coronaviruses jump species
2023-08-14
Unexpected new insights into how COVID-19 infects cells may help explain why coronaviruses are so good at jumping from species to species and will help scientists better predict how COVID-19 will evolve.
Throughout the pandemic, there has been much discussion of how COVID-19 infiltrates cells by hijacking a protein called ACE2 found on human cells. But the new research from the School of Medicine reveals that ACE2 isn’t required for infection. Instead, the virus has other means it can use to infect cells.
That versatility suggests that coronaviruses can use multiple “doors” ...
Dry lightning can spark wildfires even under wetter conditions
2023-08-14
VANCOUVER, Wash. – Dry lightning can still be disastrous even when conditions aren’t so dry, a study has found.
These cloud-to-ground strikes during little to no rainfall were previously thought to pose wildfire danger only if occurring with less than 2.5 mm of rain in a day (about 0.10 inches). A Washington State University-led study of lightning-ignited wildfires in the U.S. West found the strikes caused wildfires despite up to 7.7 mm (about 0.3 inches) of precipitation.
While still a low amount of rain, the more accurate estimation could help responders detect fires earlier, especially those known as “holdovers,” which can smolder for many ...
Worcester Polytechnic Institute researcher receives $599,815 grant to develop 3D printable robots for search-and-rescue operations
2023-08-14
Worcester, Mass. – August 10, 2023 – Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) researcher Markus Nemitz is the recipient of a $599,815 CAREER Award from the National Science Foundation to develop an innovative architecture for low-cost custom robots capable of traversing challenging terrains by swimming, crawling, climbing, and diving through hostile and confined spaces as part of search-and-rescue operations.
Nemitz, an assistant professor in WPI’s Department of Robotics Engineering, will focus on developing ...
Riding a wave to better medical diagnosis
2023-08-14
Medical imaging via X-rays, CT scans, MRIs and ultrasounds provide health-care professionals with unique perspectives and a better understanding of what’s happening inside a patient’s body. Using various forms of waves, these machines can visualize many unseen ailments and diseases.
This imaging is beneficial for health-care professionals to make correct diagnoses, but the added insight of spectroscopy provides even more detail. Spectroscopy offers a means to identify biomolecules within specimens through ...
Death tolls from climate disasters will ‘balloon’ without investment in Africa’s weather stations
2023-08-14
The climate crisis is increasing the frequency and intensity of floods, droughts and heatwaves, with Africa expected to be among the global regions hit hardest.
Yet the systems and technologies across the continent that monitor and forecast weather events and changes to water levels are “missing, outmoded or malfunctioning” – leaving African populations even more exposed to climate change.
This is according to a team of risk experts and climatologists from the UK and Africa led by the University of Cambridge, who ...
Transforming flies into degradable plastics
2023-08-14
SAN FRANCISCO, Aug. 14, 2023 — Imagine using insects as a source of chemicals to make plastics that can biodegrade later — with the help of that very same type of bug. That concept is closer to reality than you might expect. Today, researchers will describe their progress to date, including isolation and purification of insect-derived chemicals and their conversion into functional bioplastics.
The researchers will present their results at the fall meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS). ACS Fall 2023 is a hybrid meeting being held virtually and in-person Aug. 13–17, and features about 12,000 presentations on a wide range of science topics.
“For ...
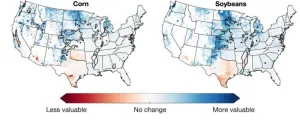
Irrigating more US crops by mid-century will be worth the investment
2023-08-14
With climate change, irrigating more crops in the United States will be critical to sustaining future yields, as drought conditions are likely to increase due to warmer temperatures and shifting precipitation patterns. Yet less than 20% of croplands are equipped for irrigation.
A Dartmouth-led study finds that by the middle of the 21st century under a moderate greenhouse gas emissions scenario, the benefits of expanded irrigation will outweigh the costs of installation and operation over an expanded portion of current U.S. ...
New statement urges engaging patients in their care, collaborating on treatment decisions
2023-08-14
DALLAS, Aug. 14, 2023 - A new American Heart Association scientific statement highlights evidence that supports shared decision-making, a term that describes the process of ensuring patients have the knowledge and tools to make decisions about their health in collaboration with their professional health care team. The statement publishes today in the American Heart Association’s flagship, peer-reviewed journal Circulation.
More than 100 trials have demonstrated that shared decision-making ...
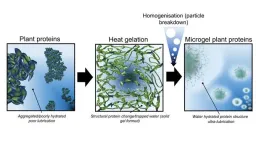
Making plant-based meat alternatives more palatable
2023-08-14
New colloidal technique could give a juicy sensation without adding fat
Switch to plant-based diets needed to hit climate change targets
One of the biggest obstacles to the uptake of plant-based alternatives to meat is their very dry and astringent feel when they are eaten.
Scientists, led by Professor Anwesha Sarkar at the University of Leeds, are revolutionising the sensation of plant proteins, transforming them from a substance that can be experienced as gloopy and dry to one that is juicy and fat like.
And the only substance they are adding to the plant proteins is water.
Plant protein microgels
To ...
3D-printed vegan seafood could someday be what’s for dinner (video)
2023-08-13
SAN FRANCISCO, Aug. 13, 2023 — In the refrigerated grocery store aisle, meat alternatives greatly outnumber plant-based seafoods. But more mock seafood options are needed because of unsustainable fishing and aquaculture practices, which can deplete the supply and harm the environment. Today, researchers present a new approach for creating desirable vegan seafood mimics that taste good, while maintaining the healthful profile of real fish. They 3D-printed an ink made from microalgae protein and mung bean protein, and their proof-of-concept calamari rings can even be air-fried for a quick, tasty snack.
The researchers will present their results at the fall meeting of the American ...