(Press-News.org) Expensive noble metals often play a vital role in illuminating screens or converting solar energy into fuels. Now, chemists at the University of Basel have succeeded in replacing these rare elements with a significantly cheaper metal. In terms of their properties, the new materials are very similar to those used in the past.
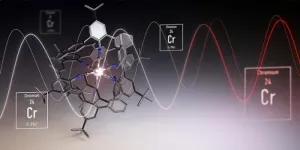
We’re familiar with chromium from everyday applications such as chromium steel in the kitchen or chrome-plated motorcycles. Soon, however, the element may also be found in the screens of ubiquitous mobile phones or used to convert solar energy. Researchers led by Professor Oliver Wenger from the Department of Chemistry at the University of Basel have developed chromium compounds that can replace the noble metals osmium and ruthenium — two elements that are almost as rare as gold or platinum — in luminescent materials and catalysts. Writing in Nature Chemistry, the team reports that the luminescent properties of the new chromium materials are nearly as good as some of the osmium compounds used so far. Relative to osmium, however, chromium is about 20,000 times more abundant in the earth’s crust — and much cheaper.
The new materials are also proving to be efficient catalysts for photochemical reactions, including processes that are triggered by exposure to light, such as photosynthesis. Plants use this process to convert energy from sunlight into energy-rich glucose and other substances that serve as fuel for biological processes.
If the new chromium compounds are irradiated with a red lamp, the energy from the light can be stored in molecules which can then serve as a power source. “Here, there’s also the potential to use our new materials in artificial photosynthesis to produce solar fuels,” explains Wenger.
Tailor-made packaging for chromium
To make the chromium atoms glow and enable them to convert energy, the researchers built them into an organic molecular framework consisting of carbon, nitrogen, and hydrogen. The team designed this organic framework to be particularly stiff, so that the chromium atoms are well packaged. This tailor-made environment helps to minimize energy losses due to undesired molecular vibrations and to optimize the luminescent and catalytic properties. The disadvantage of the new materials is that chromium requires a more complex framework than noble metals — and further research will therefore be needed in the future.
Encased in its rigid organic framework, chromium proves to be much more reactive than noble metals when exposed to light. This paves the way for photochemical reactions that are otherwise difficult to initiate. A potential application could be in the production of active pharmaceutical ingredients.
Competition with other alternatives
For a long time, the search for sustainable and cost-effective materials without noble metals focused primarily on iron and copper. Other research groups have already achieved promising results with both of these elements, and chromium has also been incorporated into luminescent materials in the past.
In many cases, however, the luminescent and catalytic properties of these materials lagged far behind those of materials containing rare and expensive noble metals — therefore failing to represent a real alternative. The new materials made of chromium are different because they contain a form of chromium that is particularly similar to noble metals, thereby achieving luminescent and catalytic efficiencies that come very close to materials containing such metals.
“At the moment, it seems unclear which metal will ultimately win the race when it comes to future applications in luminescent materials and artificial photosynthesis,” says Wenger. “What is certain, however, is that the postdocs Dr. Narayan Sinha and Dr. Christina Wegeberg have made important progress together.”
Next, Wenger and his research group aim to develop their materials on a larger scale to allow broader testing of potential applications. By making additional improvements, they hope to achieve light emission in different spectral colors from blue to green to red. They also want to further optimize the catalytic properties in order to bring us a major step closer to converting sunlight into chemical energy for storage — as in photosynthesis.
END
Chromium replaces rare and expensive noble metals
2023-08-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
No longer ships passing in the night: these electromagnetic waves had head-on collisions
2023-08-14
NEW YORK, August 14, 2023 — A research team at the Advanced Science Research Center at the CUNY Graduate Center (CUNY ASRC) has shown that it is possible to manipulate photons so that they can collide, interacting in new ways as they cross paths. The discovery, detailed in Nature Physics, will allow scientists who develop technologies rooted in electromagnetic wave propagation to make significant advances in telecommunications, optical computing and energy applications.
The breakthrough took place in the lab of Andrea Alù, Distinguished ...
Comparison of particulate air pollution from different emission sources and incident dementia
2023-08-14
About The Study: In this nationally representative study, higher residential levels of fine particulate matter were associated with greater rates of incident dementia, especially for fine particulate matter generated by agriculture and wildfires. These findings also indicate that intervening on key emission sources might have value, although more research is needed to confirm these findings.
Authors: Boya Zhang, Ph.D., of the University of Michigan School of Public Health in Ann Arbor, is the corresponding ...
Socioeconomic adversity and weight gain during the pandemic
2023-08-14
About The Study: In a large, demographically diverse sample of U.S. youth researchers found significantly greater increases in body mass index over time in 10- to 12-year-old youth assessed during the COVID-19 pandemic, compared with pre-pandemic controls. The effects of the pandemic on weight gain were most pronounced in low-income youth, suggesting that the pandemic exacerbated preexisting social inequalities.
Authors: Elizabeth Sowell, Ph.D., of Children’s Hospital Los Angeles, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2023.2823)
Editor’s ...
Lifestyle factors in the association of shift work and depression and anxiety
2023-08-14
About The Study: In this study of 175,000 participants, shift work was significantly associated with a higher risk of depression and anxiety, and lifestyle factors partially mediated the associations. These findings not only support that shift work should be considered an occupational hazard, but also provide evidence for the urgent need for the development of public health interventions that promote healthy lifestyles aimed at improving the mental health of shift workers.
Authors: Yanhong Gong, Ph.D., of the Huazhong University of Science and Technology in Wuhan, ...
Association of intensive lifestyle intervention for type 2 diabetes with labor market outcomes
2023-08-14
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that an intensive lifestyle intervention to prevent the progression and complications of type 2 diabetes was associated with higher levels of employment. Labor market productivity should be considered when evaluating interventions to manage chronic diseases.
Authors: Peter Huckfeldt, Ph.D., of the University of Minnesota School of Public Health in Minneapolis, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2023.3283)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, ...
China’s oldest water pipes were a communal effort
2023-08-14
A system of ancient ceramic water pipes, the oldest ever unearthed in China, shows that neolithic people were capable of complex engineering feats without the need for a centralised state authority, finds a new study by UCL researchers.
In a study published in Nature Water, the archaeological team describe a network of ceramic water pipes and drainage ditches at the Chinese walled site of Pingliangtai dating back 4,000 years to a time known as the Longshan period. The network shows cooperation amongst the community to build and maintain the drainage system, though no evidence of a centralised power or authority.
Dr Yijie Zhuang (UCL Institute of Archaeology), ...
Gene therapy may offer a new treatment strategy for alcohol use disorder
2023-08-14
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Gene therapy might offer a one-time, sustained treatment for patients with serious alcohol addiction, also called alcohol use disorder, according to a new study led by a researcher at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center and College of Medicine.
The animal study, published in the journal Nature Medicine, also involved researchers at the Oregon Health and Science University, the Oregon National Primate Research Center and the University of California San Francisco.
The study used an accepted primate model to show that sustained release of glial-derived ...
Study: Intensive lifestyle counseling and education by health specialists associated with higher employment rate among people with Type 2 diabetes
2023-08-14
USC Schaeffer Center and University of Minnesota researchers found that study participants without a college degree had even larger employment gains from lifestyle changes recommended by specialists.
Study takeaways:
Published in JAMA Internal Medicine, the study reveals that intensive lifestyle intervention to prevent the progression and complications of type 2 diabetes is associated with higher employment.
Lifestyle intervention was associated with a 4% increase in employment overall, and a 7% increase among participants with less than a college degree.
Findings suggest labor market productivity should be considered when evaluating the cost effectiveness ...
New model for the drinking water market in Jordan
2023-08-14
In more than 30 cities around the world, millions of people obtain their drinking water from storage tanks – because tap water is often available for only a few hours at any one time. When the public water supply is insufficient, households and businesses mostly resort to private providers. Trucks bring drinking water – often tapped from groundwater wells – from the countryside to the cities and sell it there. This is partly licensed by the state but largely takes place illegally. “In Jordan, these water deliveries by tanker truck make up for the deficit of the public water supply network”, ...
City of Hope scientists uncover new active regions on cell surface receptor, expanding scope for drug targets to treat heart disease
2023-08-14
FINDINGS
Scientists at City of Hope, one of the largest cancer research and treatment organizations in the United States and a leading research center for diabetes and other life-threatening illnesses, have uncovered new molecular targets on a cell receptor that play a major role in cardiovascular regulation. The findings could lead to improved drugs for heart disease, an unfortunate side effect of some cancer therapies. Science Signaling published the study this week.
The City of Hope researchers led by Nagarajan Vaidehi, Ph.D., professor and chair of the Department of Computational and Quantitative ...